The field of human genetics is being revolutionized by exome and genome sequencing. A massive amount of data is being produced at ever-increasing rates. Targeted exome sequencing can be completed in a few days using NGS, allowing for new variant discovery in a matter of weeks. The technology generates considerable numbers of false positives, and the differentiation of sequencing errors from true mutations is not a straightforward task. Moreover, the identification of changes-of-interest from amongst tens of thousands of variants requires annotation drawn from various sources, as well as advanced filtering capabilities.
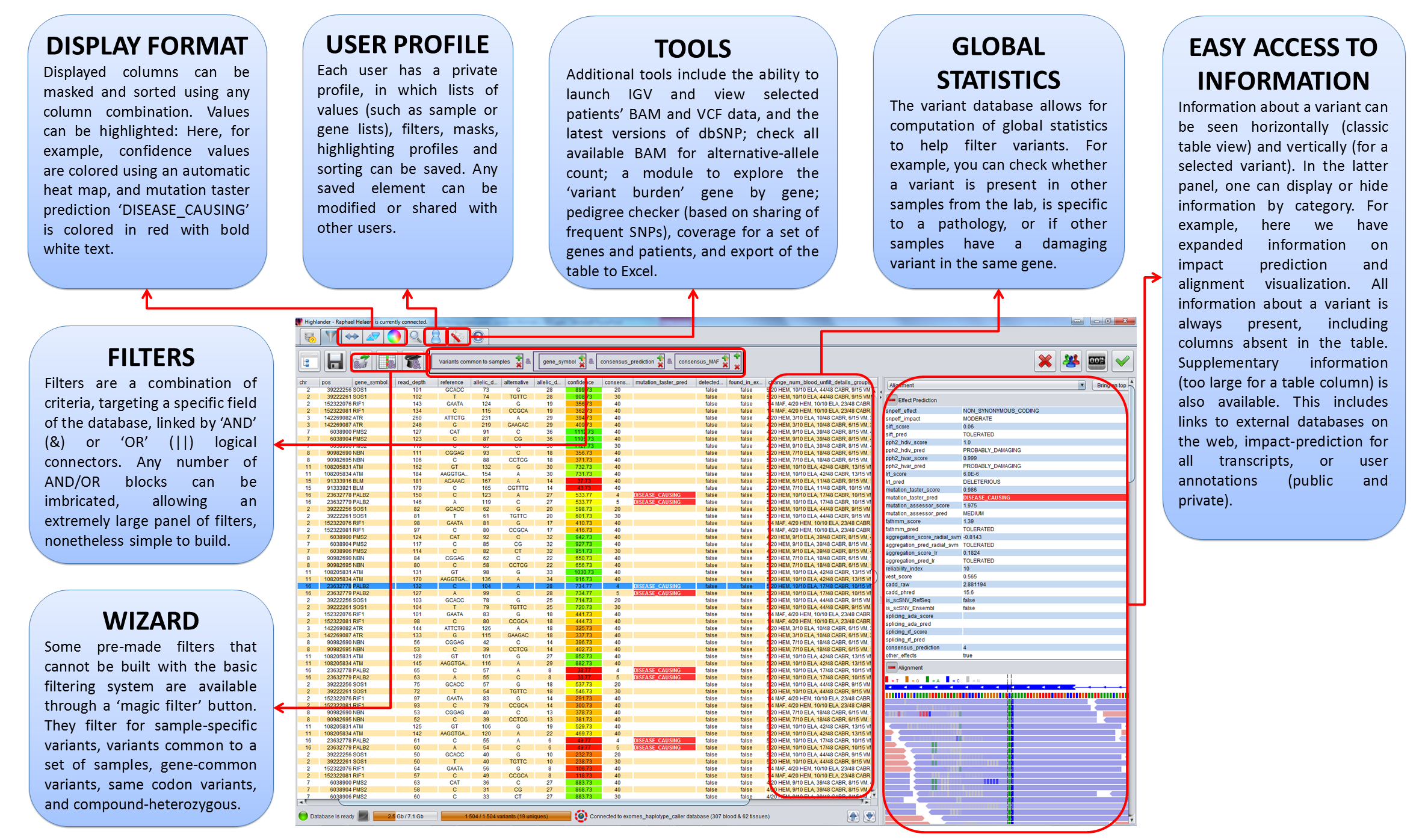
We have developed Highlander, a Java software coupled to a local database, in order to centralize all variant data and annotations from the lab, and to provide powerful filtering tools that are easily accessible to the biologist. Data can be generated by any NGS machine, (such as those of Illumina) and most variant callers (such as Broad Institute's GATK) for SNVs, small INDELs, CNVs (using e.g. ExomeDepth) and other SVs such as gene fusions (using e.g. GRIDSS). Somatic calls are also supported (using e.g. Mutect2). Variant calls are annotated using DBNSFP (providing predictions from 20 different programs, splicing predictions, prioritization scores from CADD or VEST, amongst others), SnpEff (providing topological and functional annotation) and gnomad (providing minor allele frequencies), subsequently imported into the database. The database is used to compute local minor allele frequencies (possibly compartmentalized per pathology), allowing for the discrimination of variants based on their representation in the database. The Highlander GUI easily allows for complex queries to this database, using shortcuts for certain standard criteria, such as "sample-specific variants", "variants common to specific samples" or "combined-heterozygous genes". Users can browse through query results using sorting, masking and highlighting of information. Quality control can be performed with a variety of tools such as FastQC reports, pedigree and sex checker, coverage visualization and histograms displaying various metrics. Highlander also gives access to useful additional tools, including visualization of the alignment, an algorithm that checks all available alignments for allele-calls at specific positions, or access to external tools such as Exomiser or Kraken.
Installers of the client and administration tools can be downloaded from the official webpage
To use those, you need a working local Highlander database (and associated NGS pipeline) which is not provided. Please contact Miikka Vikkula if you are interested.