Reading texts of MSc and MPhil courses, Department of Sociology, Oxford University, 2019/2020.
The article is posted on my website (in Chinese) and includes introductions of each course and a summary at the end which omitted here.
- Elster, J. (2015) Explaining Social Behavior: More Nuts and Bolts for the Social Sciences, 2nd ed., Cambridge University Press.
- Collins, R. (1994) Four Sociological Traditions, Oxford University Press.
- Arskey, H & P. Knight (1996) Interviewing for Social Scientists, Sage.
- Burgess, R. (1984) In the Field, Routledge.
- King, G., R.O. Keohane and S. Verba (1994) Designing Social Inquiry: scientific inference in qualitative research. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Krippendorff, K. (2004) Content Analysis, second ed. Sage.
- Whyte, W. F. ([1943]1993) Street corner society: the social structure of an Italian slum. 4th Edition Chicago; London: University of Chicago Press.
- Agresti, A. and B. Finlay (1997/2009/2017) Statistical Methods for the Social Sciences, Pearson (3rd, 4th, or 5th edition; any will do).
- Hamilton, L.C. (2013) Statistics with Stata, Version 12, 8th Edition. Cengage
- King, G., R. Keohane and S. Verba (1994) Designing Social Inquiry, Princeton University Press.
- Rick H. Hoyle, Charles M. Judd, Monica J Harris. 2001. Research Methods in Social Relations, (International Edition), Fort Worth, Holt, Rinehart and Winston. 7th edition. 🈚️
- Elster, J. 1989. Nuts and Bolts for the Social Sciences. Cambridge University Press.
- Livi Bacci, M. (2012) A Concise History of World Population, Wiley-Blackwell.
- Wachter, K.W. (2014) Essential Demographic Methods, Harvard University Press.
- Preston, S.H, P. Heuveline and M. Guillot (2001) Demography: Measuring and Modeling Population Processes, Blackwell Publishers
- A series of articles detailed in the syllabus.
- Mayer, K. (2009). New directions in life course research. Annual Reviews in Sociology. 35: 413-433.
- Crosnoe, R. & G.H. Elder Jr. (2015). Life Course: Sociological Aspects, J. Wright (Ed.) International Encyclopedia of the Social and Behavioral Sciences, 2nd edition. London: Elsevier. 🈚️
- Billari, F.C. (2001) The Analysis of Early Life Courses: Complex Descriptions of the Transition to Adulthood, Journal of Population Research, 18(2): 119-142.
- Blossfeld, H-P, and S Drobnic. (2001). "Theoretical perspectives on couples’ careers." pp. 16-50 in Careers of couples in contemporary societies: from male breadwinner to dual-earner families, edited by H-P Blossfeld and S Drobnic. Oxford: Oxford University Press. 🈚️
- Garret Christensen, Jeremy Freese, Edward Miguel (2019), Transparent and Reproducible Social Science Research, 1st Edition, University of California Press, ISBN: 9780520296954. 🈚️(only chap 1)
- Gerber and Malhotra (2008), Publication Bias in Empirical Sociological Research: Do Arbitrary Significance Levels Distort Published Results? Sociological Methods and Research, 37, 1, 3-30.
- John Ionnidis (2005), Why Most Published Research Findings are False, Plos Medicine, 2, 8.
- Gary King (2006), Publication, Publication, PS: Political Science and Politics, 39, 1, 119-125.
- Edward Leamer (1983), Let's Take the Con Out of Econometrics, The American Economic Review, 73, 1, 31- 43.
- Freese and Peterson (2017), Replication in Social Science, Annual Review of Sociology, 43, 1, 147-165.
- Joshua D. Angrist and Jorn-Steffen Pischke, Mostly Harmless Econometrics. Princeton University Press, 2009 [e-book, available from Bodleian through SOLO].
- Carina Mood. (2010) ‘Logistic Regression: Why We Cannot Do What We Think We Can Do, and What We Can Do About It’, European Sociological Review 26 : 67–82.
- Paul D. Allison, Fixed Effect Regression Models. Sage, 2009 [e-book, available from Bodleian through SOLO].
- Charles N. Halaby, ‘Panel models in sociological research: theory into practice’, Annual Review of Sociology, 30:507-544, 2009.
- Long, J. Scott, & Freese, Jeremy. (2014). Regression Models for Categorical Dependent Variables Using Stata (3rd ed.). College Station, TX: Stata Press.
- Rabe-Hesketh, Sophia, & Skrondal, Anders. (2012). Multilevel and Longitudinal Modeling Using Stata. Volume I: Continuous Responses (3rd ed.). College Station, TX: Stata Press.
- Rabe-Hesketh, Sophia, & Skrondal, Anders. (2012). Multilevel and Longitudinal Modeling Using Stata. Volume II: Categorical Responses, Counts, and Survival (3rd ed.). College Station, TX: Stata Press. 🈚️
- Paul D. Allison (2004). ‘Using panel data to estimate the effects of events’, Sociological Methods and Research, 23(2):174-199.
- Douglas C. Montgomery, Elizabeth A. Peck and G Geoffrey Vining. (2012). Introduction to Linear Regression Analysis. John Wiley & Sons [e-book, available from Bodleian through SOLO].
- Richard Breen et. al. (2014). ‘Correlations and Nonlinear Probability Models’, Sociological Methods & Research 43: 571- 605.
- Mark L. Bryan and Stephen P. Jenkins. (2016). ‘Multilevel Modelling of Country Effects: A Cautionary Tale’. European Sociological Review, 32(1): 3–22.
Week 1: Review of Probability
Week 2: Review of Least Squares regression and properties of estimators
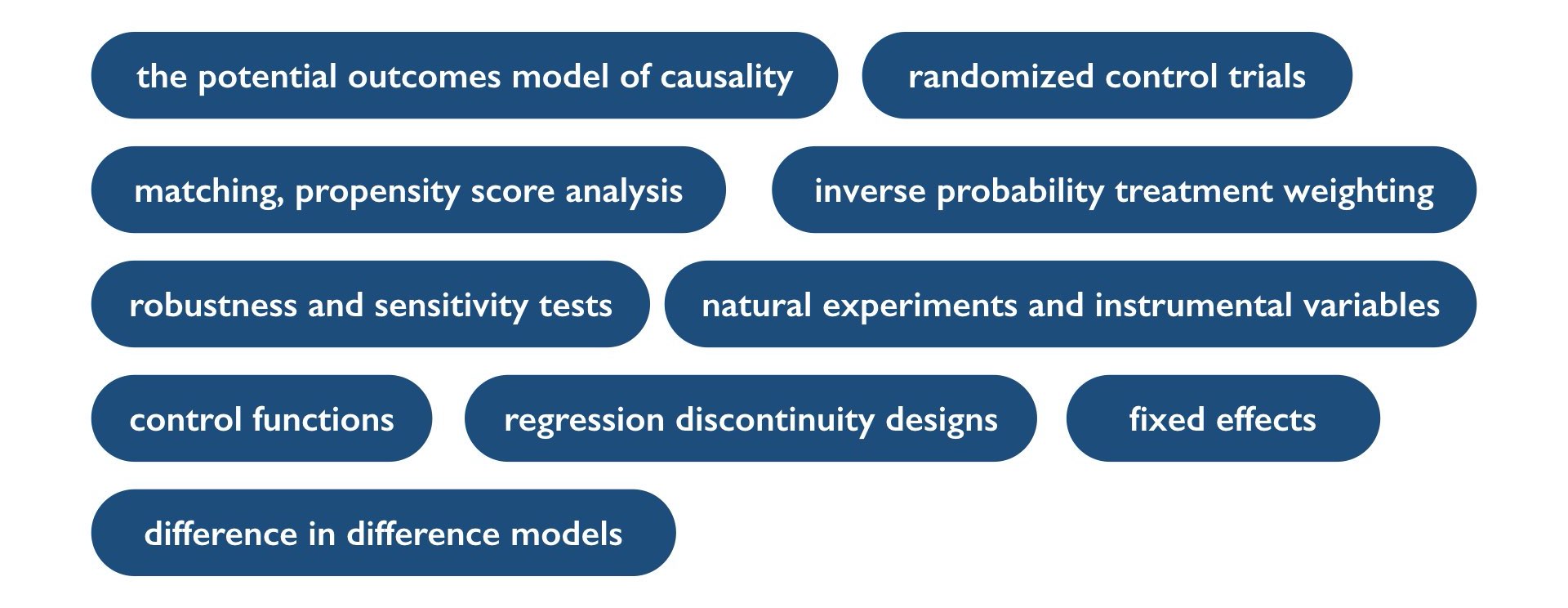
Week 3: The counterfactual model of causality, the fundamental problem of causality, randomized control trials.
Week 4: Matching estimators; regression and propensity scores
Week 5: Inverse probability of treatment weighting; robustness analysis
Week 6: Instrumental variables; natural experiments
Week 7: Control functions
Week 8: Regression discontinuity; fixed effects; difference in difference models
- Fox, John. 2008. A Mathematical Primer for Social Statistics. QASS 159, Sage.
- Morgan, Stephen L. and Christopher Winship. 2014. Counterfactuals and Causal Inference: Methods and Principles for Social Research (2nd edition), Cambridge University Press.
- Angrist, Joshua and Jörn-Steffen Pischke. 2009. Mostly Harmless Econometrics. Princeton University Press.
E (Essential)
- Fielding, N. G., Lee, R. M., & Blank, G. (Eds.). (2008). The SAGE handbook of online research methods. Sage.
- Online Social Networks: Concepts for Data Collection. pp. 241-258.
- Harrington, H. A., Beguerisse-Díaz, M., Rombach, M. P., Keating, L. M., & Porter, M. A. (2013). Commentary: Teach network science to teenagers. Network science, 1(2), 226-247.
- Borgatti, S. P., Everett, M. G., & Johnson, J. C. (2018). Analyzing social networks. Sage.
- Chapters 1-2.
R (Recommended)
- Granovetter, M. S. (1977). The strength of weak ties. In Social networks (pp. 347-367). Academic Press.
- Wellman, B., & Berkowitz, S. D. (Eds.). (1988). Social structures: A network approach (Vol. 2). CUP Archive.
- Structural Analysis: From Method and Metaphor to Theory and Substance. pp. 19-61.
- Hidalgo, C. A. (2016). Disconnected, fragmented, or united? a trans-disciplinary review of network science. Applied Network Science, 1(1), 6.
- Butts, C. T. (2008). Social network analysis: A methodological introduction. Asian Journal of Social Psychology, 11(1), 13-41.
- Hennig, M., Brandes, U., Pfeffer, J., & Mergel, I. (2012). Studying social networks: A guide to empirical research. Campus Verlag.
- Chapter 1. Pp 13-26. 🈚️
E
- Crossley, N., Bellotti, E., Edwards, G., Everett, M. G., Koskinen, J., & Tranmer, M. (2015). Social network analysis for ego-nets: Social network analysis for actor-centred networks. Sage. 🈚️
- Chapter 3. Pp 44-75.
- Hogan, B., Melville, J. R., Phillips II, G. L., Janulis, P., Contractor, N., Mustanski, B. S., & Birkett, M. (2016, May). Evaluating the paper-to-screen translation of participant-aided sociograms with high-risk participants. In Proceedings of the 2016 CHI conference on human factors in computing systems (pp. 5360-5371). ACM.
- Dunbar, R. I. (2016). Do online social media cut through the constraints that limit the size of offline social networks?. Royal Society Open Science, 3(1), 150292.
R
- Reyes, C. (2016). Eliciting data on social relationships: The use of hand-drawn network maps in tracing the perception of digitally mediated social ties. International Review of Social Research, 6(4), 256-268.
- Hogan, B. (2016). Social media giveth, social media taketh away: Facebook, friendships, and APIs. International Journal of Communication, Forthcoming.
- Van Duijn, M. A., Van Busschbach, J. T., & Snijders, T. A. (1999). Multilevel analysis of personal networks as dependent variables. Social networks, 21(2), 187-210.
- Giannella, E., & Fischer, C. S. (2016). An inductive typology of egocentric networks. Social Networks, 47, 15-23.
E
- Borgatti, S. P., Everett, M. G., & Johnson, J. C. (2018). Analyzing social networks. Sage.
- Chapters 3-4.
- Ugander, J., Karrer, B., Backstrom, L., & Marlow, C. (2011). The anatomy of the facebook social graph. arXiv preprint arXiv:1111.4503.
- 1-17
- Hodas, N. O., Kooti, F., & Lerman, K. (2013, June). Friendship paradox redux: Your friends are more interesting than you. In Seventh International AAAI Conference on Weblogs and Social Media.
R
- Feld, S. L. (1991). Why your friends have more friends than you do. American Journal of Sociology, 96(6), 1464-1477.
- Travers, J., & Milgram, S. (1977). An experimental study of the small world problem. In Social Networks (pp. 179-197). Academic Press.
- de Sola Pool, I., & Kochen, M. (1978). Contacts and influence. I, 1(1), 5-51.
E
- Rivera, M. T., Soderstrom, S. B., & Uzzi, B. (2010). Dynamics of dyads in social networks: Assortative, relational, and proximity mechanisms. Annual Review of Sociology, 36, 91-115.
- Bakshy, E., Messing, S., & Adamic, L. A. (2015). Exposure to ideologically diverse news and opinion on Facebook. Science, 348(6239), 1130-1132.
- McPherson, M., Smith-Lovin, L., & Cook, J. M. (2001). Birds of a feather: Homophily in social networks. Annual review of sociology, 27(1), 415-444.
- Crossley, N., Bellotti, E., Edwards, G., Everett, M. G., Koskinen, J., & Tranmer, M. (2015). Social network analysis for ego-nets: Social network analysis for actor-centred networks. Sage. 🈚️
- Chapter 4. Pp. 76-104.
R
- Gould, R. V., & Fernandez, R. M. (1989). Structures of mediation: A formal approach to brokerage in transaction networks. Sociological methodology, 89-126.
- Mizruchi, M. S., & Marquis, C. (2006). Egocentric, sociocentric, or dyadic?: Identifying the appropriate level of analysis in the study of organizational networks. Social Networks, 28(3), 187-208.
- Van Alstyne, M., & Brynjolfsson, E. (2005). Global village or cyber-balkans? Modeling and measuring the integration of electronic communities. Management Science, 51(6), 851-868.
- Aral, S., & Van Alstyne, M. (2011). The diversity-bandwidth trade-off. American Journal of Sociology, 117(1), 90-171.
- Feld, S. L. (1982). Social structural determinants of similarity among associates. American sociological review, 797-801.
E
- Smith, M. A., Rainie, L., Shneiderman, B., & Himelboim, I. (2014). Mapping Twitter topic networks: From polarized crowds to community clusters. Pew Research Center, 20, 1-56.
- Porter, M. A., Onnela, J. P., & Mucha, P. J. (2009). Communities in networks. Notices of the AMS, 56(9), 1082-1097.
- Hric, D., Darst, R. K., & Fortunato, S. (2014). Community detection in networks: Structural communities versus ground truth. Physical Review E, 90(6), 062805.
R
- Newman, M. E. (2006). Modularity and community structure in networks. Proceedings of the national academy of sciences, 103(23), 8577-8582.
- Gest, S. D., Moody, J., Rulison, K. L., Gest, S. D., Moody, J., & Rulison, K. L. (2007). Density or distinction? The roles of data structure and group detection methods in describing adolescent peer groups. Journal of Social Structure, 8, 1-27.
- Brooks, B., Hogan, B., Ellison, N., Lampe, C., & Vitak, J. (2014). Assessing structural correlates to social capital in Facebook ego networks. Social Networks, 38, 1-15.
- Kossinets, G., & Watts, D. J. (2006). Empirical analysis of an evolving social network. science, 311(5757), 88-90.
- Yang, J., & Leskovec, J. (2015). Defining and evaluating network communities based on ground-truth. Knowledge and Information Systems, 42(1), 181-213.
- Fortunato, S. (2010). Community detection in graphs. Physics reports, 486(3-5), 75-174.
E
- Lusher, D., Koskinen, J., & Robins, G. (Eds.). (2013). Exponential random graph models for social networks: Theory, methods, and applications. Cambridge University Press.
- Chapters 2-5. Pp 9-36.
- Wimmer, A., & Lewis, K. (2010). Beyond and below racial homophily: ERG models of a friendship network documented on Facebook. American Journal of Sociology, 116(2), 583-642.
R
- Snijders, T. A., Van de Bunt, G. G., & Steglich, C. E. (2010). Introduction to stochastic actor-based models for network dynamics. Social networks, 32(1), 44-60.
- Sloan, Luke, and Anabel Quan-Haase, eds. The SAGE handbook of social media research methods. Sage, 2017.
- Chapter 15: Scale, Time, and Activity Patterns: Advanced Methods for the Analysis of Online Networks. Pp. 259–276.
- Lewis, K., Gonzalez, M., & Kaufman, J. (2012). Social selection and peer influence in an online social network. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 109(1), 68-72.
E
- Freeman, L. C. (2000). Visualizing social networks. Journal of social structure, 1(1), 4.
- Lee, A., & Archambault, D. (2016, May). Communities Found by Users--not Algorithms: Comparing Human and Algorithmically Generated Communities. In Proceedings of the 2016 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (pp. 2396-2400). ACM.
- Brashears, M. E. (2013). Humans use compression heuristics to improve the recall of social networks. Scientific reports, 3, 1513.
- Welser, H. T., Gleave, E., Fisher, D., & Smith, M. (2007). Visualizing the signatures of social roles in online discussion groups. Journal of social structure, 8(2), 1-32.
R
- Fruchterman, T. M., & Reingold, E. M. (1991). Graph drawing by force‐directed placement. Software: Practice and experience, 21(11), 1129-1164.
- Purchase, H. C., Pilcher, C., & Plimmer, B. (2010). Graph drawing aesthetics—created by users, not algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 18(1), 81-92.
- Borgatti, S. P., Everett, M. G., & Johnson, J. C. (2018). Analyzing social networks. Sage.
- Chapter 7.
- McGrath, C., Blythe, J., & Krackhardt, D. (1997). The effect of spatial arrangement on judgments and errors in interpreting graphs. Social networks, 19(3), 223-242.
- Noack, A. (2009). Modularity clustering is force-directed layout. Physical Review E, 79(2), 026102.
- Kieffer, S., Dwyer, T., Marriott, K., & Wybrow, M. (2015). Hola: Human-like orthogonal network layout. IEEE transactions on visualization and computer graphics, 22(1), 349-358.
E
- Emirbayer, M. (1997). Manifesto for a relational sociology. American journal of sociology, 103(2), 281-317.
- Healy, K. (2015). The performativity of networks. European Journal of Sociology/Archives Européennes de Sociologie, 56(2), 175-205.
- Graham, M., & Dutton, W. H. (Eds.). (2019). Society and the internet: How networks of information and communication are changing our lives. Oxford University Press.
- The relational self-portrait: Selfies meet social networks. Pp 53-66.
R
- Abbott, A. (1988). Transcending general linear reality. Sociological theory, 169-186.
- Latour, B., Jensen, P., Venturini, T., Grauwin, S., & Boullier, D. (2012). ‘The whole is always smaller than its parts’. A digital test of Gabriel Tarde’s monads. The British journal of sociology, 63(4), 590-615.
- Martin, J. L. (2010). Life's a beach but you’re an ant, and other unwelcome news for the sociology of culture. Poetics, 38(2), 229-244.
- Pachucki, M. A., & Breiger, R. L. (2010). Cultural holes: Beyond relationality in social networks and culture. Annual review of sociology, 36, 205-224.
- Kalyvas, Stathis (2006) The Logic of Violence in Civil War. Cambridge University Press
- Kapuscinski, R. (2007). Another day of life. Vintage.
- Petersen, Roger D. (2002) Understanding Ethnic Violence: Fear, Hatred, and Resentment in Twentieth Century Eastern Europe. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
- Tilly, Charles (2003) The Politics of Collective Violence. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Weinstein Jeremy (2006). Inside Rebellion: The Politics of Insurgent Violence. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Clemens, Elizabeth S. (2016) What is Political Sociology? Cambridge: Polity Press. 🈚️
- Crouch, Colin (1999) Social Change in Western Europe. Oxford: Oxford University Press. 🈚️
- Dalton, Russell (2014). Citizen Politics: Public Opinion and Political Parties in Advanced Industrial Democracies (6th edition). Washington, DC: Congressional Quarterly Press. 🈚️
- Dalton, Russell Leighley (2007) The Oxford Handbook of Political Behavior. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Tilly, C and S Tarrow. (2015) Contentious Politics, 2nd ed., Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Crossley, N. (2002) Making Sense of Social Movements, Buckingham: Open University Press.
- Opp, K-D. (2009) Theories of Political Protest and Social Movements: A Multidisciplinary Introduction, Critique, and Synthesis, Abingdon: Routledge.
- Staggenborg, S. (2012) Social Movements, 2nd. ed., Oxford: Oxford University Press. 🈚️
- Arrow, K., S. Bowles and S. Darlauf, eds. (2000) Meritocracy and Economic Inequality, Princeton University Press. 🈚️
- Bowles, S., H. Ginits and M. Osborne Groves, eds. (2005) Unequal Chances: Family Background and Economic Success, Princeton University Press.
- Wright, E.O. ed. (2005) Approaches to Class Analysis, Cambridge University Press.
- Devlin, B. et al. eds. (1997) Intelligence, Genes and Success, Copernicus.
- Grusky, D.B. ed. (2008) Social Stratification, 3nd ed, Westview Press.
- Goldthorpe, J.H. (1987) Social Mobility and Class Structure in Modern Britain, 2nd ed, Clarendon Press.
- Goldthorpe's lecture Video
- Marshall, G., A. Swift and S. Roberts (1997) Against the Odds? Oxford University Press.
- Firebaugh, G. (2003) The New Geography of Global Income Inequality, Harvard University Press. 🈚️
- Goodman, D (2014) Class in Contemporary China, Polity Press.
- Jacka, T, A. Kipnis and S. Sargeson (2013) Contemporary China: Society and Social Change, Cambridge University Press. 🈚️
- Gries, P.H and S. Rosen, eds. (2004) State and Society in 21st Century China: Crisis, Contention and Legitimation. London: Routledge.
- Chan, A, R Madsen, and J Unger. (2009). Chen village: Revolution to globalization. Berkeley: Univ. of California Press 🈚️
- Perry, E.J. and M. Selden, eds. (2003) Chinese Society: Change, Conflict and Resistance, London: Routledge.
- Gold, T, D Guthrie, and D Wank, eds. (2002). Social connections in China: Institutions, culture, and the changing nature of guanxi. New York: Cambridge Univ. Press
- Walder, A G. (1986). Communist neo-traditionalism: Work and authority in Chinese industry. Berkeley: Univ. of California Press
- M Frezzo, The Sociology of Human Rights 🈚️
- D Levy, Sovereignty Transformed: The Sociology of Human Rights
- G Sjoberg et al “A Sociology of Human Rights” in Social Problems
- M Delflen & S Chicoine, “The Sociological Discourse on Human Rights: Lessons from the Sociology of Law” in Development and Society
- T Vaugn & G Sjoberg, “Human Rights Theory and the Classical Sociological Tradition” in Sociological Theory in Transformation 🈚️
- TR Young, The Sociology of Human Rights, Humanity, and Society
- Woodiweiss, “Taking the Sociology of Human Rights Seriously” in Interpreting Human Rights
- B Turner, “Outline of a Theory of Human Rights Sociology” in Sociology
- B Turner, “Sociology of Human Rights” in Oxford Handbook of International Human Rights Law
- M Somers & C Roberts, “Toward a New Sociology of Rights,” in Annual Review of Law and Social Sciences
- M Buraway, “Introduction: A Public Sociology for Human Rights,” in Public Sociology Reader
- RW Connel “Sociology and Human Rights” Australian and New Zealand Journal of Sociology 🈚️
- J Hagan & R Levi, “Justiciability as Field Effect: When Sociology Meets Human Rights” in Sociological Forum
- L Morris “Sociology and Rights: An Emergent Field” in Rights
- R Fine, Towards a Sociology of Human Rights 🈚️
- P Hynes et al, “Sociology and Human Rights” in International Journal of Human Rights
- K Nash, The Political Sociology of Human Rights
[none]
- Sugimoto, Y. An introduction to Japanese society, Cambridge, Cambridge University Press, 2003.
- Kariya, T. Education Reform and Social Class in Japan, Routledge, 2013. 🈚️
- Brinton, C. M., Lost in Transition, Cambridge University Press, 2010. 🈚️
- Mouer, R. and Kawanishi, H. A Sociology of Work in Japan, 2005.
- Schoppa, L. J. Race for the exits: the unraveling of Japan's system of social protection, Ithaca, N.Y. ; London, Cornell University Press, 2006. 🈚️
- Ishida H. and Slater D eds. Social Class in Contemporary Japan, Routledge, 2010.
- Yoichi F. and Kushner B. eds. Examining Japan’s lost decades, Routledge, 2015.*
Previews
- Pistone, J.D. and R. Woodley. Donnie Brasco: My Undercover Life in the Mafia, 1988.
- Arlacchi, P. Men of Dishonor. 1992.
- Maas, P. Underboss: Sammy the Bull Gravano’s Story of Life in the Mafia, 1997.
- Escobar, R. Escobar. 2009. 🈚️
- Leeson, The Invisible Hook. 2009.
- Poulsen, K. Kingpin. 2011.
- Glenny, M. Nemesis. 2015.
Pre-course Viewings
Mean Steets; The Godfathers: Parts One and Two; Goodfellas; Casino; Donnie Brasco; Narcos TV Series; Cartel Land (documentary).
Key texts
- Gambetta, D. 1993. The Sicilian Mafia. Harvard University Press.
- Varese, F. 2017. Mafia Life. Profile and OUP.
- Some key papers are collected in: Varese, F. (ed.) 2010. Organized Crime. Critical Concepts in Criminology, Routledge, 2010. 🈚️
- Bergstrom, T.C. (1997) A survey of theories of the family. In: Rosenzweig, M.R. & O. Stark (Eds). Handbook of Population and Family Economics. Elsevier Science.
- Cherlin, A. (2009) The marriage-go-round. Alfred Knopf.
- Esping-Andersen, G. (2009) The Incomplete revolution: Adapting welfare states to women's new roles. 🈚️
- McLanahan, S. (2004). Diverging destinies: How children are faring under the second demographic transition. Demography 41: 607–27.
- Raymo, J. M., Park, H., Xie, Y., & Yeung, W. J. J. (2015) Marriage and family in East Asia: Continuity and change. Annual Review of Sociology 41: 471-492.
- Thomson, E. (2014) Family complexity in Europe. The Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science 654:245-58.
- Zaidi, B. & Morgan, S.P. (2017) The Second Demographic Transition Theory: A Review and Appraisal. Annual Review of Sociology 43: 473-492.
- Cohen, P. N. (2019). The Coming Divorce Decline. Socius 5:1-6.
- Belsky, D. W., & Israel, S. (2014). Integrating genetics and social science: genetic risk scores. Biodemography and Social Biology, 60(2), 137–55.
- Belsky, Daniel W., et al. (2016): The genetics of success: How single- nucleotide polymorphisms associated with educational attainment relate to life-course development. Psychological Science 27.7: 957-972.
- Cesarini, D., & Visscher, P. M. (2017). Genetics and educational attainment. Npj Science of Learning, 2(1), 4.
- Courtiol, A., Tropf, F. C., & Mills, M. C. (2016). When genes and environment disagree: Making sense of trends in recent human evolution. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 113(28), 7693–7695.
- Conley, D. (2009). The promise and challenges of incorporating genetic data into longitudinal social science surveys and research. Biodemography and Social Biology, 55(2), 238–251.
- Conley, D., et al. (2015). Is the Effect of Parental Education on Offspring Biased or Moderated by Genotype? Sociological Science, 2, 82–105.
- Conley, D., & Fletcher, J. (2017). Genome Factor. What the Social Genomics Revolution Reveals about Ourselves, Our History and the Future. Princeton University Press.
- Domingue, B. W., Fletcher, J., Conley, D., & Boardman, J. D. (2014). Genetic and educational assortative mating among US adults. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 111(22), 7996–8000.
- Euesden, Jack, Cathryn M. Lewis, and Paul F. O’Reilly (2014). PRSice: polygenic risk score software. Bioinformatics 31.9: 1466-1468.
- Harmon, A. (2018). Why White Supremacists are Chugging Milk (and Why Geneticists are Alarmed). The New York Times, Oct. 17, 2018. https://www.nytimes.com/2018/10/17/us/ white-supremacists-science-dna.html
- Khan, R. & D. Mittelman. (2018). Consumer genomics will change your life, whether you get tested or not, Genome Biology, 19: 120.
- Mehta, D., Tropf, F. C., et al. (2016). Evidence for Genetic Overlap Between Schizophrenia and Age at First Birth in Women. JAMA Psychiatry, 73(5), 497–505.
- Mills, M. C., & Tropf, F. C. (2016). The Biodemography of Fertility: A Review and Future Research Frontiers. Kölner Zeitschrift Für Soziologie Und Sozialpsychologie, 55, 397–424.
- Mills, M.C. (2019). How do genes affect same- sex behaviour? Science, 365: 869-870.
- Mills, M.C. & F.C. Tropf (2020). Sociology, Genetics and the Coming of Age of Sociogenomics. Annual Review of Sociology (forthcoming, available upon request). 🈚️
- Mills, M.C. et al. (2020). “Ethical Issues in Genomics Research,” pp. 359-376, An Introduction to Applied Statistical Genetic Analysis. Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press. 🈚️
- Mills, M.C. & C. Rahal (2019). A scientometric review of genome-wide association studies, Communications Biology, 2: 10.1038/s42003- 018-0261-x.
- Neale, M. C., & Cardon, L. R. (1992). Methodology for genetic studies of twins and families. Dordrecht, the Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
- Okbay, A., et al. (2016). Genome-wide association study identifies 74 loci associated with educational attainment. Nature, 533(7604), 539– 542.
- Plomin, R. & S. von Stumm. (2018). The new genetics of intelligence, Nature Review Genetics, 19, 148-159.
- Rietveld, C. A., et al. (2013). Molecular genetics and subjective well-being. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 110(24), 9692–9697.
- Torkamani, N.E et al. (2018). The personal and clinical use of polygenic risk scores. Nature Review Genetics, 19, 582-590.
- Tropf, F. C., Stulp, G., Barban, N., Visscher, P., Yang, J., Snieder, H., & Mills, M. C. (2015). Human fertility, molecular genetics, and natural selection in modern societies. PloS One, 10(6), e0126821.
- Tropf, F. C., Barban, N., Mills, M. C., Snieder, H., & Mandemakers, J. J. (2015). Genetic influence on age at first birth of female twins born in the UK, 1919-68. Population Studies, 69(2), 129–145.
- Tropf, F. C., & Mandemakers, J. J. (2017). Is the Association Between Education and Fertility Postponement Causal? The Role of Family Background Factors. Demography, 54(1), 71–91.
- Tropf, Felix C., et al (2017). Hidden heritability due to heterogeneity across seven populations. Nature human behaviour 1.10: 757.
- Zimmer, C. (2018). Genetic intelligence tests are next to worthless. The Atlantic.