| title | description | position | category |
|---|---|---|---|
Proxied commands |
Proxied commands |
3 |
Call&Debugging |
The proxied commands are used to implement cloud-terminal joint debugging in Function Compute.
- Principles - Enable device-cloud joint debugging - Close the device-cloud joint debugging
- Command description
- proxied setup command
- proxied invoke command
- proxied cleanup command
- Best practices
- Permissions and policies
- Examples of actual combat scenarios
In the serverless mode, your business may be associated with cloud services over virtual private clouds (VPCs). However, the tools that you use to debug code in the development environment cannot connect the on- and off-premises environments. Function Compute supports cloud-terminal joint debugging that allows you to map cloud resources to on-premises environments by using the proxy mode. This way, you can debug on-premises code of the services that are deployed over VPCs.
The following figure shows how Function Compute implements cloud-terminal joint debugging.
The architecture diagram of the device-cloud joint debugging is shown in the figure above, and the deep integration between the S tool and the channel service is carried out.
As long as the user executes s proxied setup in the s.yaml directory, the command does the following:
-
Create an auxiliary Service/Function based on your s.yaml vpc configuration and other information, and reserve 1 instance for the auxiliary function. The role of this helper function is to act as a proxy service through which all incoming and outgoing traffic of the local instance will pass.
-
Start the proxy container instance of the local environment, and establish a two-way communication TCP tunnel with the FC network proxy container instance in 1 through the channel service.
-
Start the local function container instance. For example, if you are a Custom Runtime and run the SpringBoot application directly, start the SpringBoot local function container instance and the proxy container instance in 2 to share the network. The springboot application can already access online VPC resources on the intranet.
-
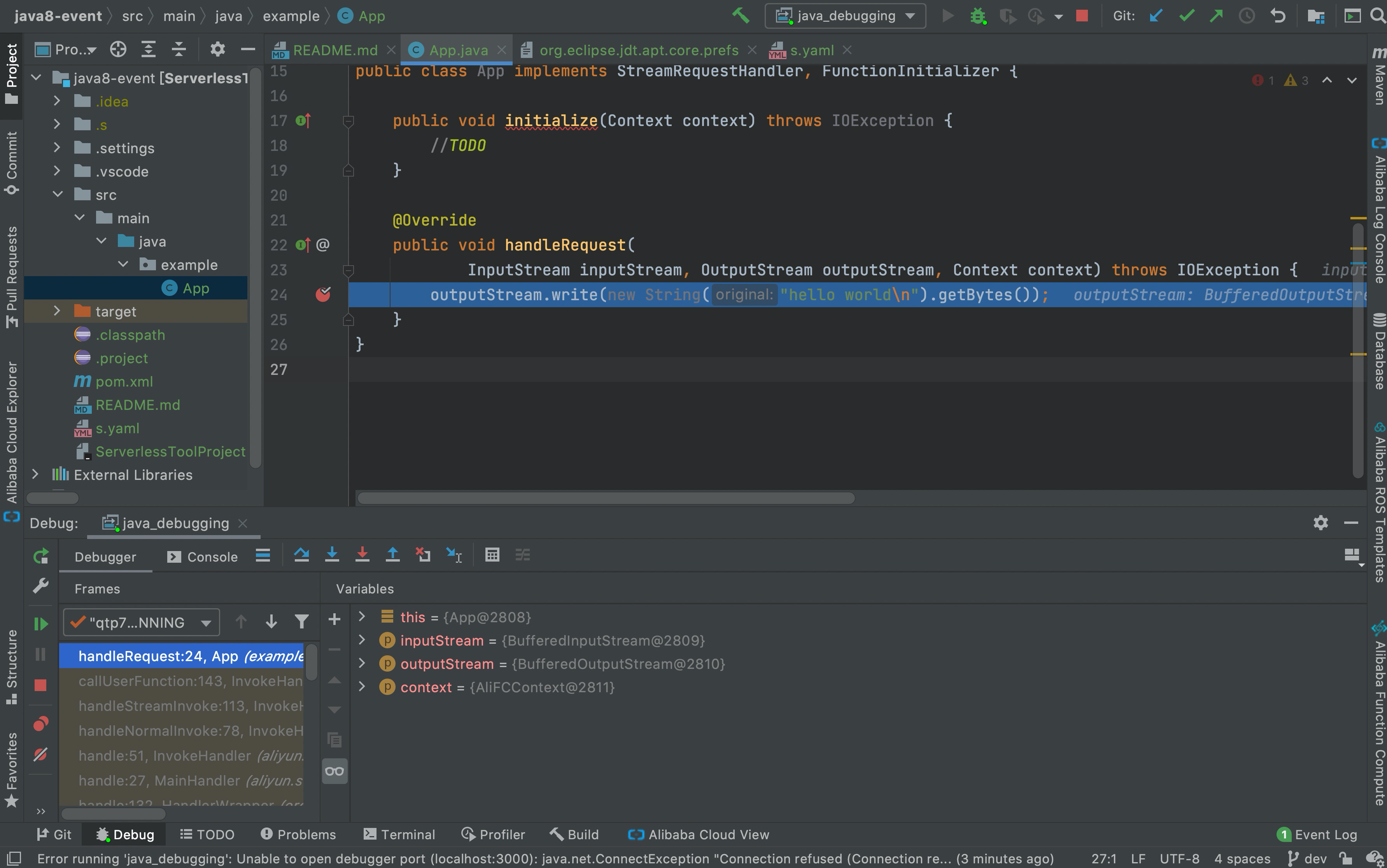
After the local function container instance is successfully started, debugging can be started, directly use
s proxied invokeorcurlcustom domain name to call the auxiliary Service/Function, the traffic will be sent back to the local function container instance through the proxy service, and the local function will be turned on. The IDE performs breakpoint debugging on the application within the instance.
Because there will be a helper function to reserve 1 instance, after debugging, you can manually clean up resources to avoid unnecessary charges
-
In the terminal where the end-cloud joint debugging is enabled, directly press
CTRL + Cto interrupt -
Or in another terminal, execute
s proxied cleanupin the same directory
You can use one of the methods 1 or 2 above. If you are worried, you can execute s proxied cleanup multiple times
Even if you forget to clean up, if the local developer shuts down or disconnects from the network, the channel session will be automatically closed and the reserved resources will be automatically cleaned up.
You can run the proxied -h or proxied --help command to obtain the help information.
The sample code contains the following subcommands:
- setup: Initialize or configure cloud-terminal joint debugging.
- invoke: Invoke or call on-premises functions.
- cleanup: Clean helper resources or environments.
The proxied setup command is used to initialize or configure cloud-terminal joint debugging.
You can run the proxied setup -h or proxied setup --help command to obtain the following help information.
| Parameter | Abbreviation | Required in YAML mode | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| config | c | No | The IDEs that you want to use for breakpoint debugging. Valid values: vscode and intellij. |
| debug-args | - | No | The parameters that you want to configure during breakpoint debugging. |
| debug-port | d | No | The port number of the breakpoint debugger. |
| debugger-path | - | No | The path of the breakpoint debugger. |
| tmp-dir | - | No | The on-premises path to mount the tmp directory of the custom function environment. Default value: ./.s/tmp/invoke/serviceName/functionName/. |
The current command also supports some global parameters (such as
-a/--access,--debug, etc.). For details, please refer to Serverless Devs global parameters document
If the YAML description file of a resource exists, you can run the s proxied setup command to initialize cloud-terminal joint debugging. The following sample code shows the command output:
✔ Make service SESSION-S-d1564 success.
✔ Make function SESSION-S-d1564/python-event success.
Proxied resource setup succeeded.
> Next step tips: s proxied invoke
After the cloud-terminal joint debugging is initialized, you can run commands such as the s proxied invoke command to call functions. After you perform related operations, you can run the s proxied cleanup command to clean helper resources.
The proxied invoke command is used to call or invoke a function when you implement cloud-terminal joint debugging.
You can run the proxied invoke -h or proxied invoke --help command to obtain the help information.
| Parameter | Abbreviation | Required in YAML mode | Required in CLI mode | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| event | e | No | No | The event function. You can invoke an event function to query event data. You can run the s cli fc-event command to query the event. For more information, see Here ;The HTTP function. You can invoke an HTTP function to query the request parameters. For more information about the format of the request parameters, see Here |
| event-file | f | No | No | You must specify the value of the event parameter by using files. |
| event-stdin | s | No | No | You must specify the value of the event parameter by using standard input streams. |
The current command also supports some global parameters (such as
-a/--access,--debug, etc.). For details, please refer to Serverless Devs global parameters document
If the YAML description file of a resource exists, you can run the s proxied invoke command to call the function for which cloud-terminal joint debugging is implemented. In this example, the s proxied invoke -e '{}' command is used.
[2021-07-13T08:55:05.260] [INFO ] [S-CLI] - Start ...
========= FC invoke Logs begin =========
Not all function logs are available, please retry
FC Invoke End RequestId: bb720e13-e57a-4040-a920-82621e275ff1
Duration: 42.66 ms, Billed Duration: 43 ms, Memory Size: 512 MB, Max Memory Used: 40.85 MB
========= FC invoke Logs end =========
FC Invoke Result:
hello world
For event functions, you need to specify an event type such as the OSS or Alibaba Cloud CDN (CDN) event, create a temporary trigger, and then change the function and the service in Function Compute to the helper service and the helper function, which is
SESSION-S-d1564/python-eventin the command output of the proxied setup command. Then, you can use the trigger to call the function to implement cloud-terminal joint debugging. For example, when you upload an OSS object, the cloud trigger can invoke an on-premises function to implement cloud-terminal joint debugging for the function. After the test is completed, you need to restore the trigger that temporarily points to the helper resources to the resources of the original service and function.
The proxied cleanup command is used to clean helper resources that are used during cloud-terminal joint debugging.
You can run the proxied cleanup -h or proxied cleanup --help command to obtain the help information.
The current command also supports some global parameters (such as
-a/--access,--debug, etc.). For details, please refer to Serverless Devs global parameters document
If the YAML description file of a resource exists, you can run the s proxied cleanup command to clean helper resources that are used during cloud-terminal joint debugging. The following sample code shows the command output:
Resource cleanup succeeded.
To implement cloud-terminal joint debugging, perform the following steps:
- Step 1: Run the
s proxied setupcommand to enable cloud-terminal joint debugging in a project. Create helper resources that are required for cloud-terminal joint debugging. - Step 2: After you enable cloud-terminal joint debugging, open a new terminal, and run the
s proxied invokecommand or use a cloud event to call and debug the function. - Step 3: After you complete cloud-terminal joint debugging, run the
s proxied cleanupcommand to clean the helper resources that are used during the cloud-terminal joint debugging.
You can implement breakpoint debugging during cloud-terminal joint debugging in common integrated development environments (IDEs).
-
Step 1: Run the
$ s proxied setup --config vscode --debug-port 3000command to initialize cloud-terminal joint debugging in a project. After you run the command, the on-premises environment in which functions are invoked is blocked and pending to be invoked. The execution environment is similar to an HTTP server.Serverless Devs generates the
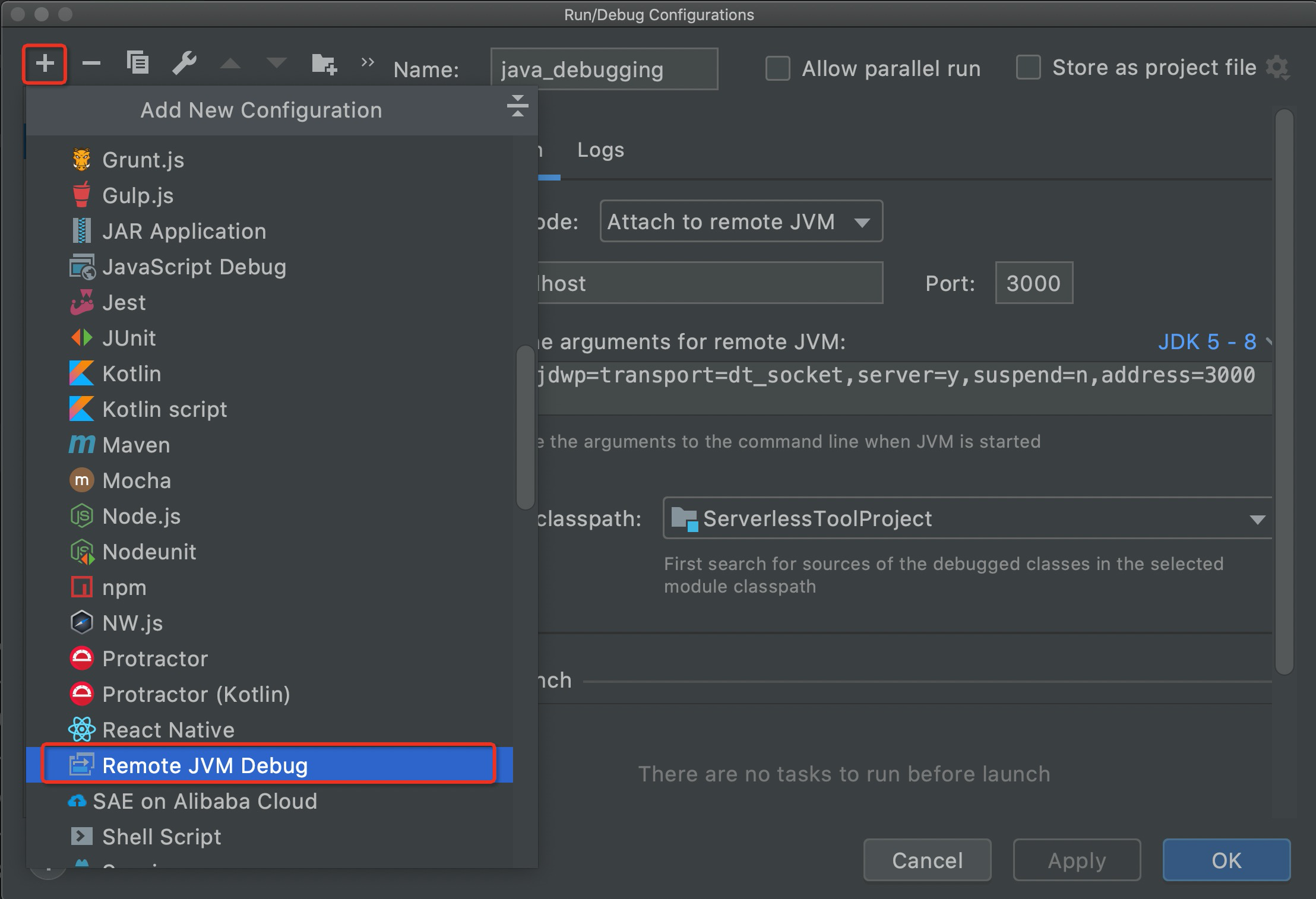
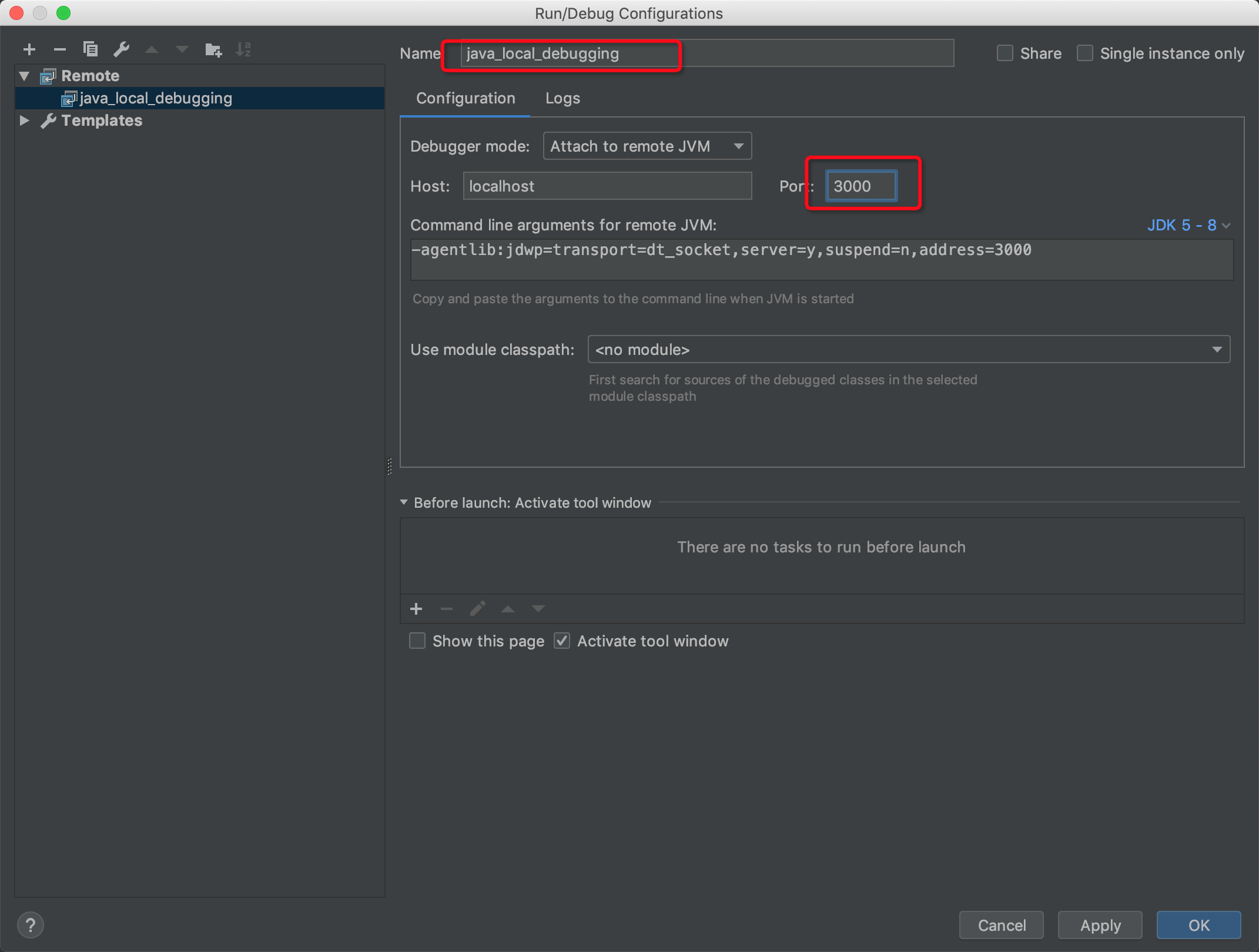
.vscode/launch.jsonfile in the project directory. If you want to perform breakpoint debugging, you need to perform operations that are described in the following figure in VScode. -
Step 2: Open a terminal and run the
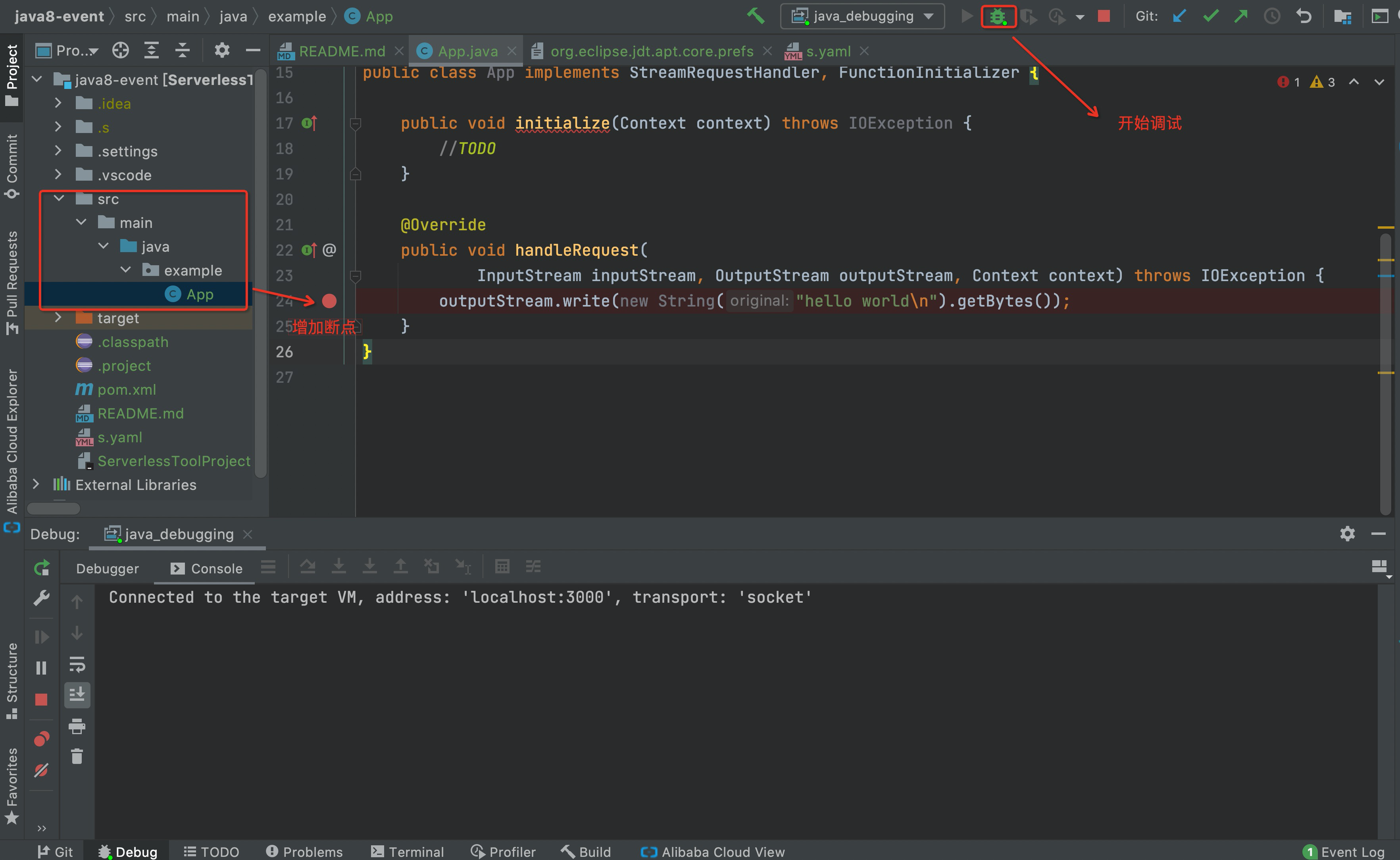
proxied invokecommand such as thes proxied invoke command to call the function. If the function is an event function, you can use a cloud trigger to call the function. The trigger must temporarily point to the helper function. For more information, see proxied invoke command. Go back to the VSCode interface. Then, you can perform the breakpoint debugging.The command output is returned after the cloud-terminal joint debugging is completed.
If you need to use a custom event parameter when you invoke the function, run the
--eventcommand. For example, you can use the event command in thes proxied invoke -hcommand. -
Step 3: After you complete cloud-terminal joint debugging, run the
s proxied cleanupcommand to clean the helper resources that are used during the cloud-terminal joint debugging.
-
Step 1: Run the
$ s proxied setup --config intellij --debug-port 3000command to enable cloud-terminal joint debugging in a project. After you run the command, the on-premises environment in which functions are invoked is blocked and pending to be invoked. The on-premises environment is similar to an HTTP server.If you need to implement breakpoint debugging, perform the following operations in Intellij IDEA:
-
Step 2: Open a terminal and run the
proxied invokecommand such as thes proxied invokecommand to call the function. If the function is an event function, you can use a cloud trigger to call the function. The trigger must temporarily point to the helper function. For more information, see proxied invoke command. Go back to the Intellij IDEA interface. Then, you can perform breakpoint debugging.The command output is returned after the cloud-terminal joint debugging is completed.
If you need to use a custom event parameter when you invoke the function, run the
--eventcommand. For example, you can use the event command in thes proxied invoke -hcommand.
-Step 3: After you complete cloud-terminal joint debugging, run the s proxied cleanup command to clean helper resources that are used during the cloud-terminal joint debugging.
-
If you need to run the
proxied setupcommand, obtain the permissions on the command. The permissions are related to the parameters that are configured in the YAML file of the function for which you want to implement cloud-terminal joint debugging. For more information about how to configure the parameters and the relevant permissions, see Yaml syntax. -
You also need to run the following command to configure the policy that is required by the
proxiedcommand.{ "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": "tns:*", "Resource": "*" } ], "Version": "1" } -
If you need to run the
proxied invokecommand, obtain the permissions on theinvokecommand based on your business requirements.-
To obtain the highest level of permissions, attach the
AliyunFCInvocationAccessorAliyunFCFullAccesspolicy. -
To obtain the lowest level of permissions, run the following command:
{ "Version": "1", "Statement": [ { "Action": "fc:InvokeFunction", "Effect": "Allow", "Resource": "acs:fc:<region>:<account-id>:services/<serviceName>.<qualifier>/functions/<functionName>" } ] }
-
-
If you need to clean helper resources of the function, obtain the permissions that allow you to
deleteresources based on your business requirements.-
To obtain the highest level of permissions, attach the
AliyunFCInvocationAccessorAliyunFCFullAccesspolicy. -
To obtain the lowest level of permissions, run the following command:
{ "Statement": [ { "Action": [ "fc:ListOnDemandConfigs", "fc:DeleteFunctionOnDemandConfig", "fc:ListProvisionConfigs", "fc:PutProvisionConfig", "fc:ListAliases", "fc:DeleteAlias", "fc:ListServiceVersions", "fc:DeleteServiceVersion", "fc:ListTriggers", "fc:DeleteTrigger", "fc:ListFunctions", "fc:DeleteFunction", "fc:DeleteService" ], "Effect": "Allow", "Resource": "*" } ], "Version": "1" }
-
Take a real enterprise customer of Alibaba Cloud Function Computing as an example: Xiao Wang is a developer of a business-driven company. In order to improve the efficiency of business iteration, the company has evolved its technical architecture towards a comprehensive cloud-native approach, reducing the management and operation and maintenance of basic facilities. The structure is roughly as follows:
Xiao Wang migrates the most frequently iterated external front-end and back-end projects to the Custom Runtime of Function Compute with one click, in which SpringBoot projects need to be able to use various VPC intranet addresses to access downstream services (such as registry or other microservice interfaces) ), at this time, the device-cloud joint debugging provided by Serverless Devs can come in handy. You only need to execute it in the directory where s.yaml (the VPC configuration with functions defined in s.yaml) is located:
$s proxied setup
This command will establish a secure network channel with the cloud VPC environment and start the application instance locally. At this time, the local instance can seamlessly access the resources in the cloud VPC environment, such as using the intranet address to access the registry, RDS, Kafka, etc. This means that your application configuration does not require any changes to interact with resources in the on-premises and cloud environments.
At the same time, directly using the custom domain name on the Function Compute FC corresponding to this SpringBoot backend project, the traffic will be routed to the local application instance. For example, the function name of your front-end project deployed to FC is frontend, and the corresponding custom domain name is frontend.abc.com. The function name of the backend service that the frontend depends on deployed on the FC is backend, and the corresponding custom domain name is backend.abc.com. At this time, you open fronted.abc.com directly in the browser and perform operations with back-end requests. The traffic is automatically routed from the online to the local SpringBoot instance, and the SpringBoot logs are displayed in real time on the terminal. Point to debug traffic from online.
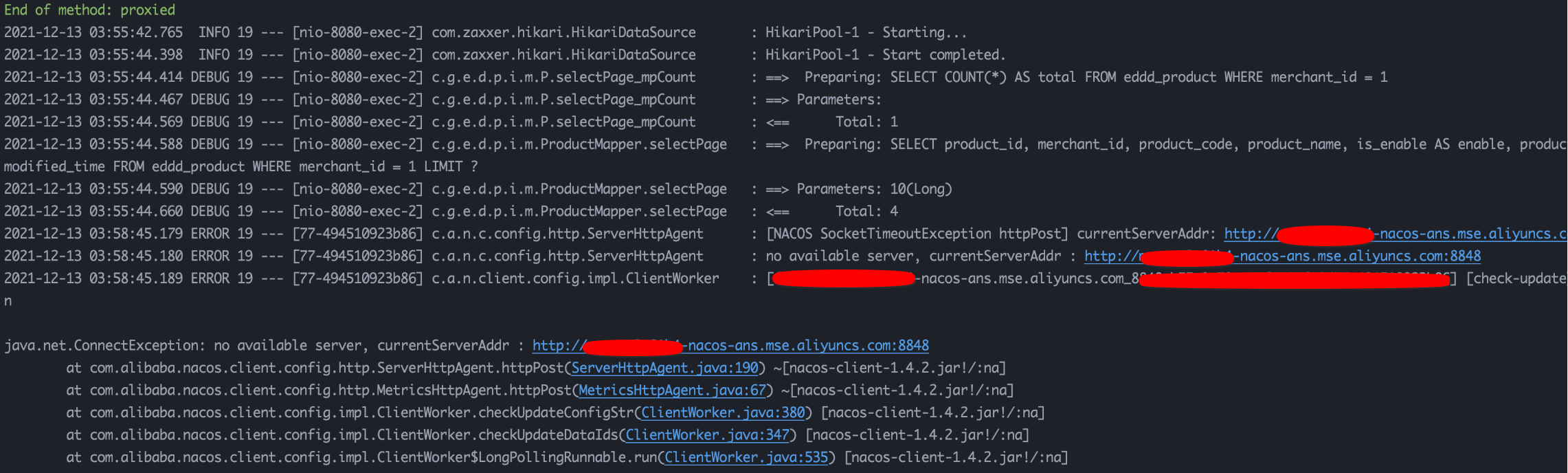
Assuming that the instance of the SpringBoot backend project fails to be started locally, the possible reasons include the wrong VPC configuration of Function Compute, the whitelist restriction of the corresponding downstream service, and so on. At this point, you can reproduce the same startup process as the cloud environment instance locally, which is extremely helpful for troubleshooting instance startup issues. As shown below:
We can clearly locate the reason from the startup process information of the local instance that Nacos cannot access. We need to check whether the function is correctly configured with the VPC information where Nacos is located, or whether Nacos has whitelist restrictions, etc.