Copyright 2021
Revision: V1
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.
Please refer to the article in the journal SoftwareX (Volume 19, July 2022, 101120) using the current repo: irs-partition: An Intrusion Response System utilizing Deep Q-Networks and system partitions.
The repo is forked from 'SecureAI: Deep Reinforcement Learning for Self-Protection in Non-Stationary Cloud Architectures.'
irs-partition software is a Java application that employs RL techniques to build an Intrusion Response System to thwart unseen breaches in a system production environment. The software creates multiple deep neural networks and uses a system model as its input. We utilize a model-free and off-policy Reinforcement Learning (RL) approach in training the deep neural network (DNN) using multiple single RL agents in a non-production environment called training environment. First, the training environment simulates a live non-stationary system by loading the system model through configuration files. Next, we use transfer learning to detach the agents from the training environment and deploy them in a production environment. Finally, we use the agents that leverage the pre-trained DNNs to predict a near-optimal action when the environment detects a threat in the production environment.
Software dependencies of the application include 'Eclipse Deeplearning4J'(dl4j), and 'Reinforcement Learning for Java'(rl4j), both are Java implementations of deep neural network algorithms and the RL framework. In addition, the software extends 'SecureAI: Deep Reinforcement Learning for Self-Protection in Non-Stationary Cloud Architectures'secureai-java that trains a single RL agent for the entire non-stationary system.
Intrusion Response is considered a relatively new field of research. However, the recent research papers use the Reinforcement Learning (RL) technique as a primary strategy for designing a self-protective Intrusion Response System (IRS). Many papers have already demonstrated using model-free, off-policy training, simulated non-production environment, transfer learning, etc., to design an IRS for a non-stationary system. Such IRS attempts to alleviate the continuous management of the rules-based response system, immediate actionable pre-trained agents with the deep neural networks (DNN), and other benefits. However, these IRS uses only one DNN to predict the following optimal action. The paper introduces system partitions to create multiple DNNs for each partition, focusing on the local optima.
- dl4j
- rl4j
Reference: The Online Boutique (OB) application from here.
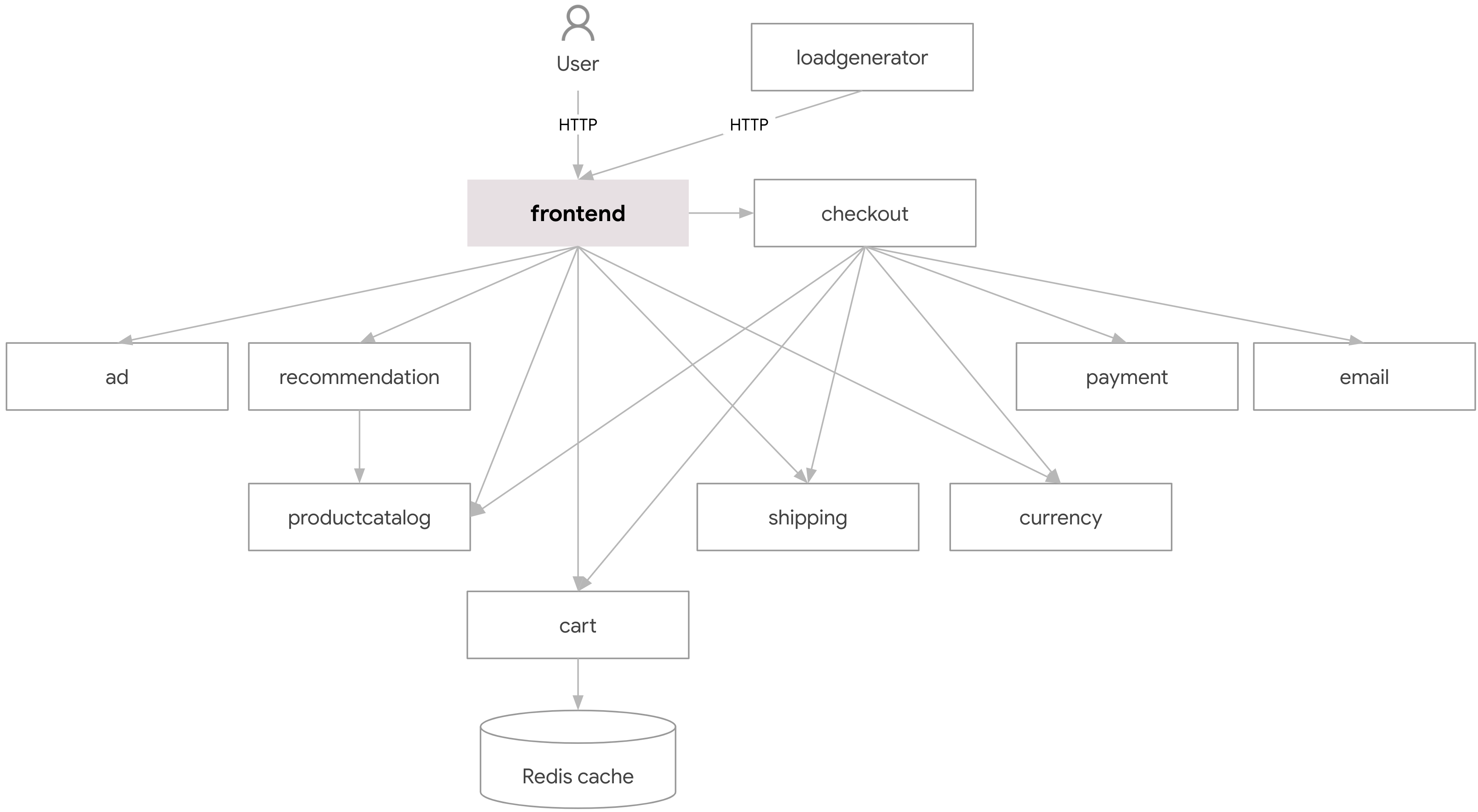
Find below are the critical part of the diagrams. They show how the software is creating system partitions.The design uses the creational, structural, and behaviorial design patterns to do so.
The system model consists of information on all the microservices used in the system. A service provides the software implementation in a container image. We define a component as an executable unit of a service, that holds the image, and a partition as a running unit of all the containers of a particular component image. Each partition contains at least one container of the respective component in a \textit{secure} state of the system. Every service has a corresponding component with its separate partition, as shown in the diagram below:
The below diagram shows how the monolothic System's state variables are broken down into multiple set of variables one for each partitions.
The below diagram shows how the monolothic System's action set is broken down into multiple action set one for each partitions.
- Clone the repo
- Build, package, and run using Maven
- pom.xml executes com.secureai.partition.main.PartitionDQNMain.main()
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| c240g2 | 4 nodes (Haswell, 20 core, 8 disks) |
| CPU | Two Intel E5-2660 v3 10-core CPUs at 2. |
| 60 GHz (Haswell EP) | |
| RAM | 160GB ECC Memory (10x 16 GB DDR4 2133 |
| MHz dual rank RDIMMs) | |
| Disk | Two Intel DC S3500 480 GB 6G SATA SSDs |
| Disk | Two 1TB HDDs |
| Disk | Four 3TB HDDs |
| NIC | Dual-port Intel X520 10Gb NIC (PCIe v3. |
| 0, 8 lanes | |
| NIC | Onboard Intel i350 1Gb |
We used the following JVM parameters: -Xms102400 m -Xmx102400 m -XX:MaxMetaspaceSize=40960m.
We initialize the system state to simulate an exploit based on the common vulnerability CVE-2019-5736, based on the lack of authentication of Redis server. We measure the effectiveness of the proposed IRS prototype in terms of cumulative reward and convergence time, as typical in IRSs based on Reinforcement Learning. We carried out experiments to gather the cumulative rewards in training the DQNs for both, the entire system and the front-end partition only. As depicted in Fig. 6, the training time to converge to a near-optimal cumulative reward of the front-end partition, 173 sec, is smaller than the convergence time for the case in which the entire system is considered, 220 sec. We calculated the optimal cumulative reward using our implementation of the Value Iteration algorithm (classes VIMain and PartitionVIMain). Fig. 6(a) and 6(b) respectively show the cumulative reward obtained according to the time spent on training for both, the single front-end partition and the system. We do not provide a detailed analysis of the time overhead introduced by the IRS, because it is negligible with respect to the execution time of the response actions. Indeed, once the model has been trained, the IRS overhead consists in a single forward pass on the neural network, which can be accomplished in the order of milliseconds, while the execution time of the response actions is in the order of seconds or minutes.