This study presents an implementation of the Q Learning algorithm, a form of reinforcement learning, to autonomously navigate an agent through a maze. The agent's objective is to traverse from a defined start position to a designated end position by identifying the most effective path, while circumventing obstacles. The efficacy of the agent is determined by its ability to find the shortest possible route to the goal without hitting any barriers. Through iterative training, the agent learns to make strategic decisions to achieve its target with increasing efficiency.
- Python
- Reinforcement Learning
- Q Learning
- Maze Solving
- Agent Navigation
- Q Table
- R Table
- PySimpleGUI
- PyGame
- Numpy
- Jupyter Notebook
- Matplotlib
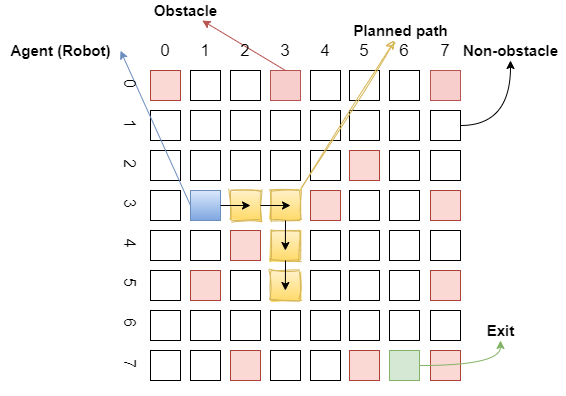
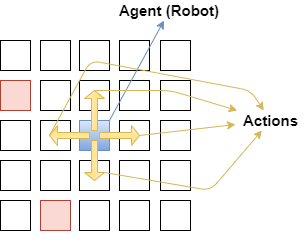
The research focuses on applying the Q Learning algorithm to empower a virtual agent, akin to a robotic entity, to solve a maze challenge. The problem space is a grid-like maze where the agent must maneuver from an initial blue square to a terminal green square. The agent can move in four cardinal directions—north, south, east, and west—on the white squares that constitute the traversable path. Successful navigation relies on the agent's ability to minimize the path length while avoiding collisions with red squares, which represent obstacles. The learning process is driven by rewards and penalties, with each action impacting the agent's performance from inception to completion.
Developed in Python 3 and leveraging the interactive capabilities of Jupyter Notebook, the project integrates various libraries to support development and visualization. PyGame is utilized for dynamic rendering of the maze-solving process, Numpy for numerical computations essential to the Q Learning algorithm, PySimpleGUI for crafting a user-friendly interface, and Matplotlib for visual representation of the agent's learning progress and strategies.
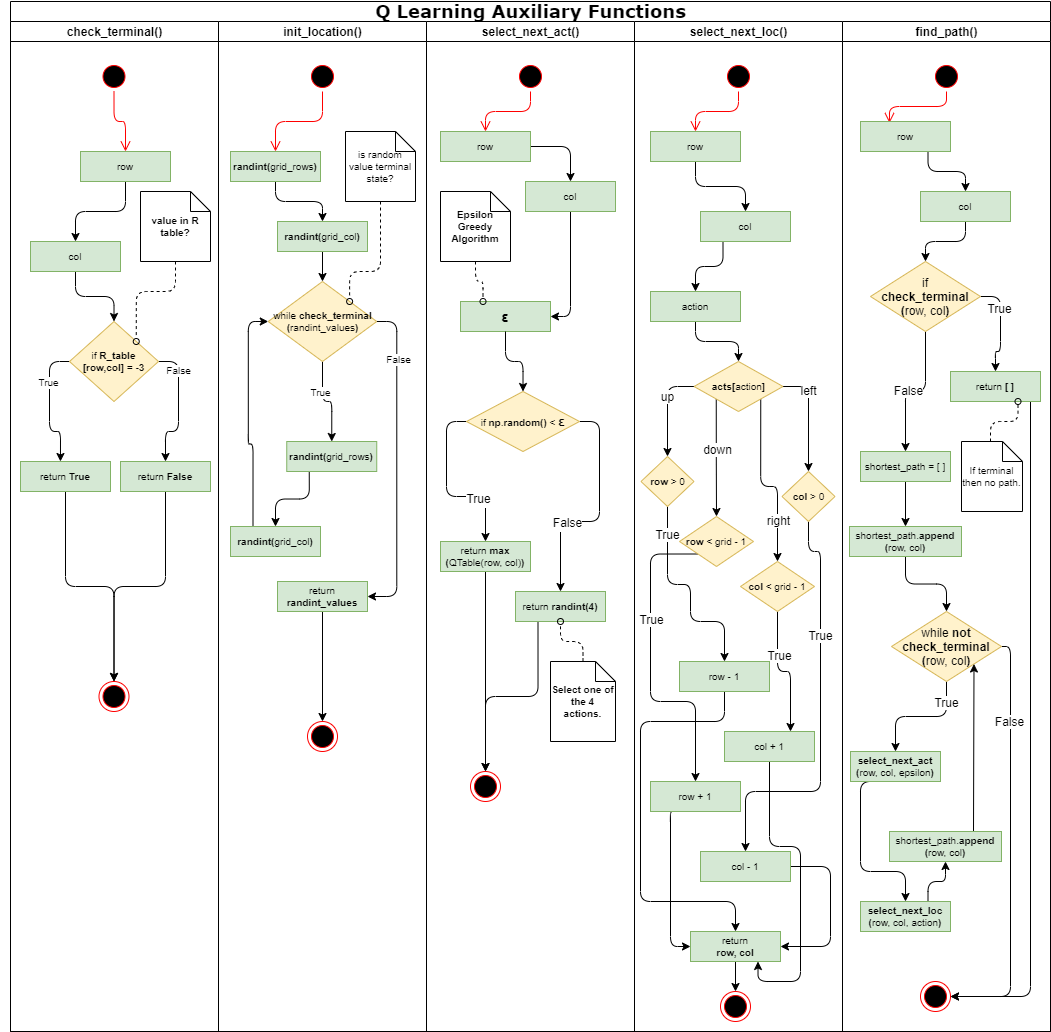
Q Learning, a model-free reinforcement learning algorithm, is central to this study. It functions by evaluating potential actions in given states and computing the rewards associated with those actions. These values are stored in a reward matrix (R Table), which informs the agent's decision-making process. Additionally, the Q Table maintains a record of experiences, which are iteratively updated as the agent accrues knowledge of the environment.
The Q Learning framework is built upon states, actions, and rewards:
- States: Each grid cell is a discrete state, with specific coordinates in the maze. Certain states are designated as terminal (red and green squares).
- Actions: The agent can move in four directions, learning to avoid obstacles (red squares) and aim for the goal (green square).
- Rewards: Each state is assigned a reward value, with the agent's goal being the maximization of its cumulative reward.
The agent's training consists of episodes in which it explores the grid. The Q Table is updated according to the Bellman equation:
TD = r_t + (γ * Q_max(x,y)) - Q_old
With sufficient training, the agent is expected to gain proficiency in solving the maze efficiently.
Upon conclusion of the training sessions, the agent demonstrated the capability to effectively navigate from the starting point at (0,0) to the goal at (49,49). The successful implementation of the Q Learning algorithm illustrates its potential for solving complex pathfinding problems and paves the way for its application in various domains requiring autonomous navigation and decision-making.