This is a project for the course of Neural Networks for Data Science Applications. It is based on this paper by Niklaus, Mai and Liu. The purpose of this project is to reproduce the video frame interpolation via adaptive convolution as presented in the paper, with Tensorflow via Google Colab.
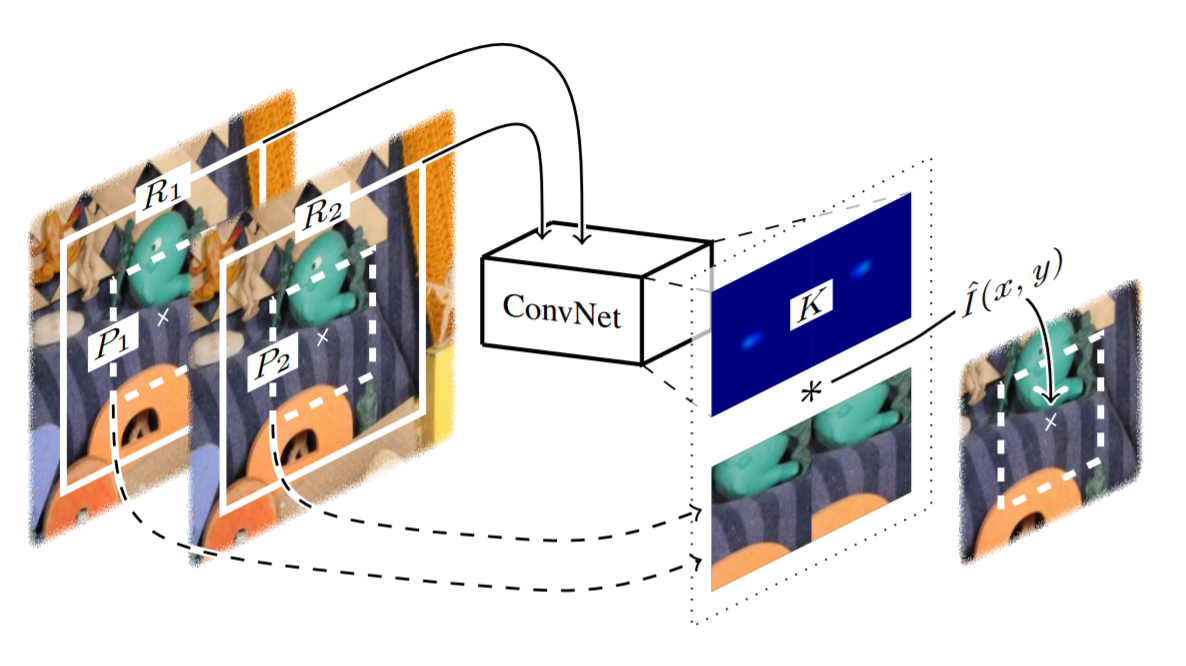
This paper presents a video frame interpolation method that combines in a single fully convolutional neural network model the two basic steps of frame interpolation: model motion estimation and pixel synthesis.The neural network model considers pixel synthesis for the interpolated frame as local convolution over two input frames. The convolution kernel captures both the local motion between the input frames and the coefficients for pixel synthesis. The formulation of video interpolation as a single convolution process allows the handle of challenges like occlusion, blur, and abrupt brightness change and enables high-quality video frame interpolation. Specifically, for a pixel (x, y) in the interpolated frame, this deep neural network takes two receptive field patches R1 and R2 centered at that pixel as input and estimates a convolution kernel K. This convolution kernel is used to convolve with the input patches P1 and P2 to synthesize the output pixel, as illustrated in Figure 1.
Compared to other techniques of frame interpolation, this methos to have some advantages:- It is able to make proper trade-offs among competing constraints and can provide a robust interpolation approach.
- Can be directly trained end to end using widely available video data, without any difficult-to-obtain ground truth data like optical flow.
- This method is able to generate high-quality frame interpolation results for challenging videos such as those with occlusion, blurring artifacts, and abrupt brightness change, as demonstrated in the paper and reproduced in this project.
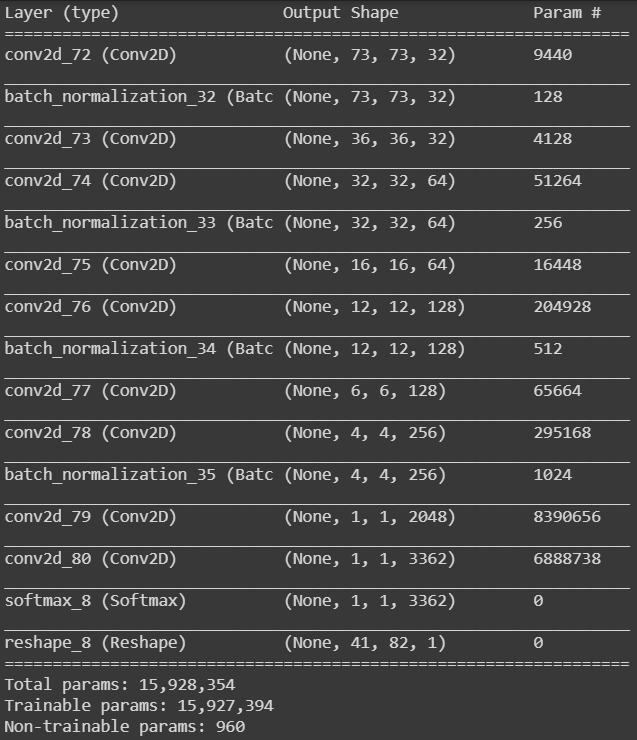
The neural network model presented in the paper and reproduced in this project consists of several convolutional layers as well as down-convolutions as alternatives to max-pooling layers. The architecture of the network is the following:
The model takes in input two images (each with the three channels), making the input tensor of shape (79, 79, 3). The output of the model is a kernel of shape (82,41) which needs to be convolved with a patch (crop) of the input images concatenated in order to produce the output color. The patch shape is (82,41,3) and convolved with the kernel will return respectively the value in each channel. A larger receptive field than the patch is used in order to better handle the aperture problem in motion estimation. Rectified Linear Units is used as activation functions, meanwhile and Batch Normalization is used for regularization. A critical constraint is that the coefficients of the output convolution kernel should be non-negative and sum up to one. Therefore, we connect the final convolutional layer to a spatial softmax layer to output the convolution kernel.Paper link: http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_cvpr_2017/papers/Niklaus_Video_Frame_Interpolation_CVPR_2017_paper.pdf