Rapid In Silico SeroTyping for three common swine bacterial pathogens
This is a tool for rapid serotype predict for three swine bacterial pathogens, Streptococcus suis, Glaesserella parasuis, and Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae. Serotyping is very important for diagnostics, epidemiology surveillance or microbiology research. Traditionally, serotyping was based on serological tests, subsequently, serotype determine locus was identified in bacteria genome, majorly polysaccharides such as lipopolysaccharide and capsular polysaccharide, for three swine bacterial pathogens focused by this tool, all of their serotype determine locus are capsular polysaccharide. Multiplex PCR replaced serological tests in many lab, and now, it time to let in silico methods to replace multiplex PCR.
In this tool, we have collected all known serotype determine locus of these pathogens and made reference databases for them to let the user could high-throughput and rapidly predict the serotype of these three pathogens. It will output the serotype of your genome, the coverage and similarity, and genes homologous with reference in the cps locus of your sequence, and genes homologous with other reference in the cps locus of your sequence, and the whole length of cps of your genome, After I update the RISST to v2.1, now it could generate a gene map of cps of your inputfile. The speed of this tool is very fast, almost 1 second for 1 genome, we can see it below. To aviod the uncorrected prediction, we displayed the coverage and identity of predicted serotype, if it lower than the threshold (we set as 95% prelimitarily), a "?" will be added to the end of output string of predicted serotype.
At the beginning, I just give three reference databases of these pathogens, It could be recongnized by Kaptive(https://github.com/katholt/Kaptive/), it just like a DLC for Kaptive. However, with my study of python more deeper, I have a strong motivation to write a new tool which can also do this job my own, also, for trainning my python skill (Annother reason I want to update this tool from DLC to a independent tool because I think I gave it a very good name). It gives me a strong sense of accomplishment when I realized one of my idea.
The write of this tool is inspired by Kaptive and Hicap, but not duplicate of them, the calculation logics of output was thought by my own, you can find out from my redundant code, the major aim to write this tool is trainning my python skill, so if anyone used this tool and give me some advices I will be very grateful!
BLAST+
Prodigal (https://github.com/hyattpd/Prodigal)
DNA features Viewer (https://github.com/Edinburgh-Genome-Foundry/DnaFeaturesViewer)
The using of this tool is very easy, put the script, a trainning file "risst.tr" and the reference file you want to use to the filefolder of your sequence.
For example, if the species of your genome dataset are Sreptococcus suis, you just need to put Streptococcus_suis_cps_locus_reference.gbk and risst.tr in the folder contain your genome sequence files, open a terminal and into the folder, get in the evironment if you create one by conda, and run like this:
python RISST.py -i *.fasta -r Streptococcus_suis_cps_locus_reference.gbkThen wait to it finish.
- We default to think the genome sequence file have a ".fasta" suffix, if your file is not, please change the ".fasta" within above command to the suffix of your file.
The usage details are listed below:
RISST [-i] [-r] [-o] [-t] [--minimun_piece] [--min_gene_cov] [--min_gene_id ] [--no_cps_sequence] [-f] [-v]
Input and Output:
-i, --input Input FASTA file
-r, --reference Reference cps locus file
-o, --output Output file
Parameters:
-t, --threads Threads to use for BLAST searches
--minimum_piece Minimum cps match in input sequence, fragments lower than this threshold will be ignore
--min_gene_cov Minimum percentage coverage to consider a single gene complete. [default: 80.0%]
--min_gene_id Minimum percentage identity to consider a single gene complete. [default: 70.0%]
--no_cps_sequence Suppress output of cps sequence file
-f, --figure Export the gene structure map of cps locus in inputfile
-v, --version Show version number and exit
A simlified result will generated in terminal, inputfile : serotype
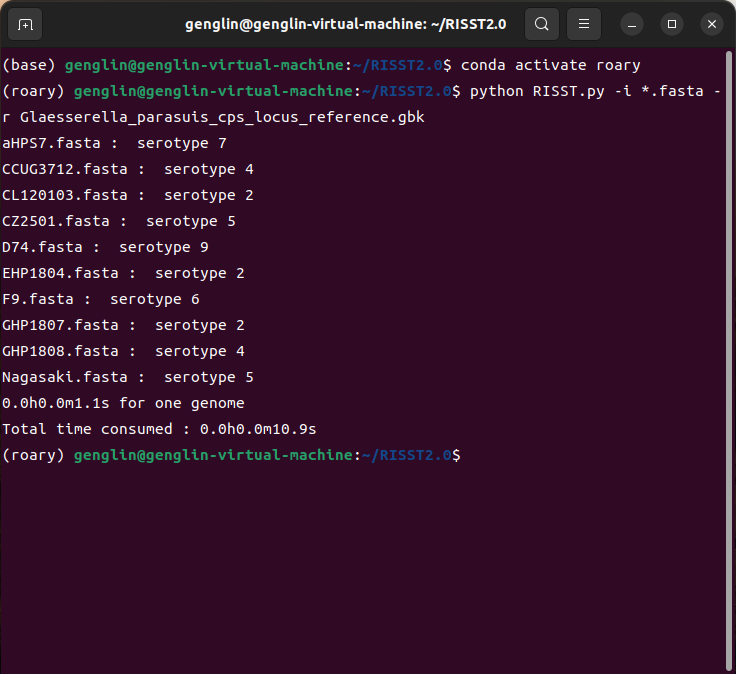
A detailed table generated in work folder
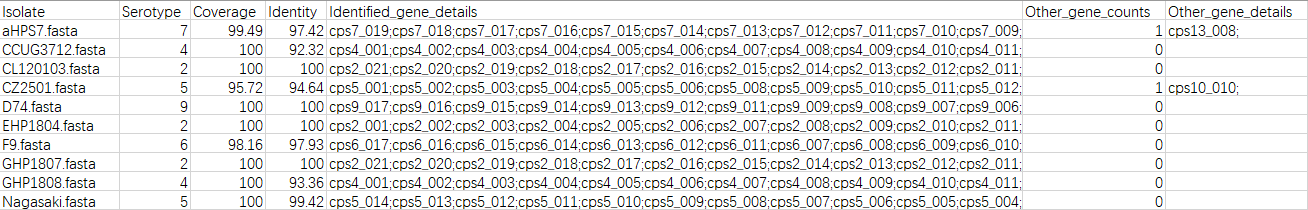
And extract the cps locus of your inputfile in filefolder "result_cps_dict"
After we updated the script to v2.1, now a gene map will be export if you add a "-f" or "--figure" in the command in filefoler "gene_structure_map"
The genes homologous with the reference cps of predicted serotype are marked by soft color, homologous with other reference cps are marked by intense color
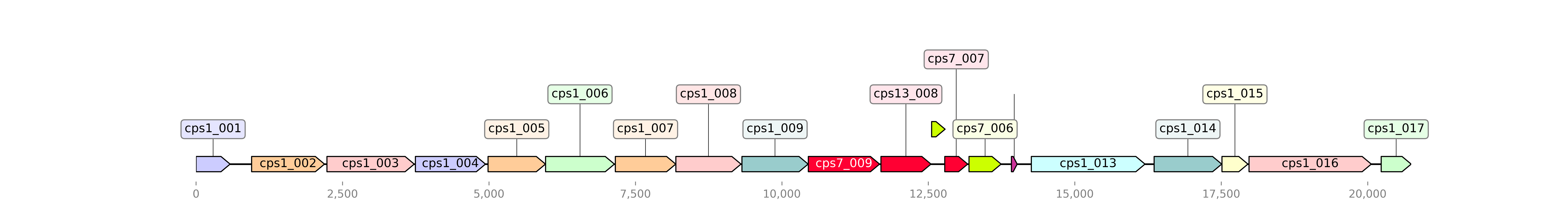
You can also create a reference sequence files for the bacteria you want to predict the serotypes, or other gene clusters which have different types. Just according to our template and notice that your multi-record reference sequence file should include nucleotide sequences for each whole locus and protein sequences for their genes, if you download it from NCBI, choose Genbank(full) format to download.