It's a sample project that created by the latest Android technologies and frameworks to be a reference/base for everyone want to start his own project/app much faster.
Brief : sample app consist of two screens:-
- Login Screen.
- News screen.
Kotlin is an open source programming language for the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). therefore, be used anywhere Java is used today (which is virtually anywhere). This includes server, client, web, and Android development. It’s a light powerful programming languagne.
https://business.udemy.com/blog/kotlin-vs-java-9-benefits-of-kotlin-for-your-business/
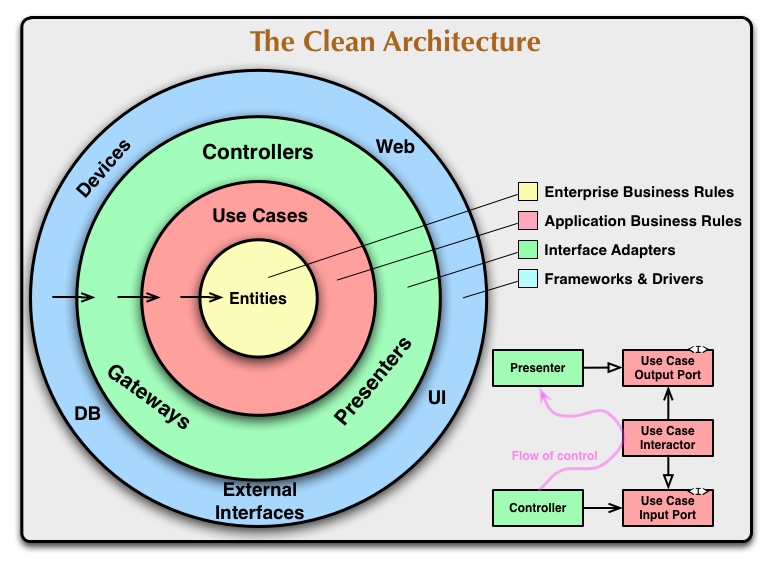
Clean architecture is a software design paradigm that separates the elements of a design into layers. The main rule of clean architecture is that code dependencies can only come from the outer levels inward. Code on the inner layers can have no knowledge of functions on the outer layers. As below we can see the
-
Entities: These are the business objects of the application.
-
Use Cases: These use cases orchestrate the flow of data to and from the entities. Are also called Interactors.
-
Interface Adapters: This set of adapters convert data from the format most convenient for the use cases and entities. - Presenters and Controllers belong here.
-
Frameworks and Drivers: This is where all the details go: UI, tools, frameworks, etc.
Model–view–viewmodel is a software architectural pattern. facilitates a separation of development layers into 3 Layers as following.
-
1- Model Model represents the data and business logic of the app. One of the recommended implementation strategies of this layer, is to expose its data through observables to be decoupled completely from ViewModel or any other observer/consumer.
-
2- Model View ViewModel interacts with model and also prepares observables(Live Data in Android) that can be observed by a View. ViewModel can optionally provide hooks for the view to pass events to the model. One of the important implementation strategies of this layer is to decouple it from the View, i.e, ViewModel should not be aware about the view who is interacting with.
-
3- View (Controllers) the view role in this pattern is to observe (or subscribe to) a ViewModel observable to get data in order to update UI elements accordingly.
Is the powerful lightweight dependency injection framework. Written in pure Kotlin using functional resolution. You create you dependenies graph by yourself . So , you will be aware of all generated code under the hood. You can write more about it here. https://insert-koin.io/
Coroutines is A framework to manage concurrency(threads) in a more performant and simple way with its lightweight thread which is written on top of the actual threading framework to get the most out of it by taking the advantage of cooperative nature of functions.
To read more about Coroutines. I strognally recommend this artical Link
The unit test is one of the fundamental parts of the development life cycle. Writing Unit test lets you found and expect uncovered scenarios which we are not thinking about it during development. therefore, you going to cover it and save your clients from face unexpected behavior.
For Android , There'r two types of Testing :-
-
Local Test: Unit tests that compile and run locally on JVM. So, no need to a real device Also, it's not depend on the Android Framework classes. If your tests depend on objects in the Android framework,you have to use Robolectric.
-
Instrumented tests: Unit tests that run on an Android device or emulator.