.
Cryptogrphy Algorithms implemented using Python 3.6.0.
I have implemented the following Algorithms :
- MD5 (Message Digest Algorithm)
- RSA (Ronald Rivest, Adi Shamir, Leonard Adleman based Public Key Cryptography)
- PGP (Pretty Good Privacy. An Email Encryption Algorithm although I have not added the Symmetric key Encrytpion)
The MD5 algorithm is a widely used hash function producing a 128-bit hash value. Creating a HASH out of the Message is an irreversible process. This means that once a HASH is created for a Message, it is not possible to produce the message from the HASH value. We tell that a pair of Message is Authentic if their hash values are same. But many message might end up with the same hash value.
So, Do we mean that the two different messages are same ?. Unfortunately and luckily YES. However, it is worth noting that the probability of 2 different messages arriving at the same hash value is almost 0.
def md5(message):
message = bytearray(message) #copy our input into a mutable buffer
orig_len_in_bits = (8 * len(message)) & 0xffffffffffffffff
message.append(0x80)
while len(message)%64 != 56:
message.append(0)
message += orig_len_in_bits.to_bytes(8, byteorder='little')
hash_pieces = init_values[:]
for chunk_ofst in range(0, len(message), 64):
a, b, c, d = hash_pieces
chunk = message[chunk_ofst:chunk_ofst+64]
for i in range(64):
f = functions[i](b, c, d)
g = index_functions[i](i)
to_rotate = a + f + constants[i] + int.from_bytes(chunk[4*g:4*g+4], byteorder='little')
new_b = (b + left_rotate(to_rotate, rotate_amounts[i])) & 0xFFFFFFFF
a, b, c, d = d, new_b, b, c
for i, val in enumerate([a, b, c, d]):
hash_pieces[i] += val
hash_pieces[i] &= 0xFFFFFFFF
return sum(x<<(32*i) for i, x in enumerate(hash_pieces)ac4a2ff915edefbc151938a70f4a6db3 <= "He is a good person"RSA is an algorithm used by modern computers to encrypt and decrypt messages. It is based on the Asymmetric Encryption or Public Key Cryptography. In asymmetric encryption, there are 2 keys i.e. a private key(KR) and a public key(KU). If any of these keys are used for encryption, the other key is used for decryption. This can only mean that there exist a mathematical relationship between both the keys.
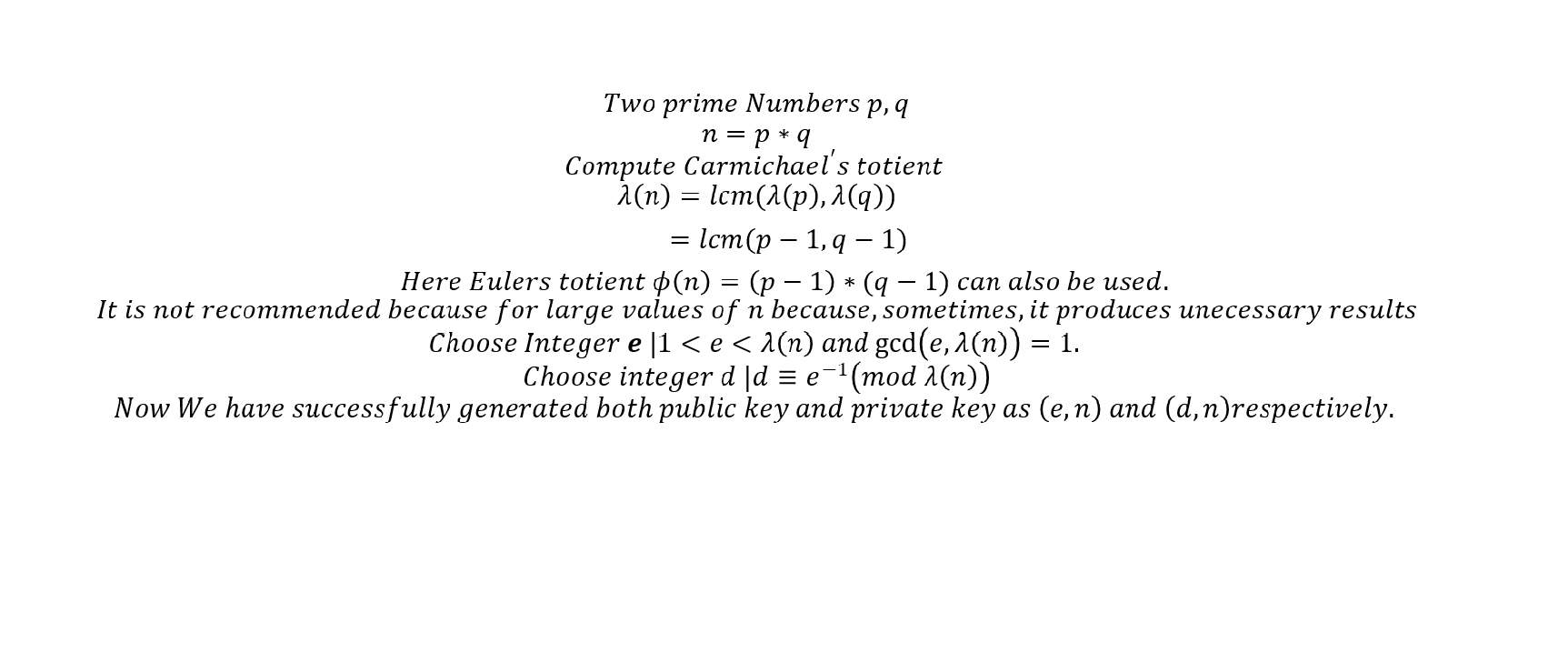
There are 4 major steps in RSA crytpography:
- Key Generation (Generate Public Key and Private Key)
- Key Distribution
- Encryption
- Decryption
Suppose 2 persons say Alice and Bob wants to securely communicate with each other with Alice as the sender, Alice encrypts the message using Bob's public key and send the Message. Bob uses his private key and successfully decrypt the message.
Encrytpion is done Using Bob's public key in the following manner:
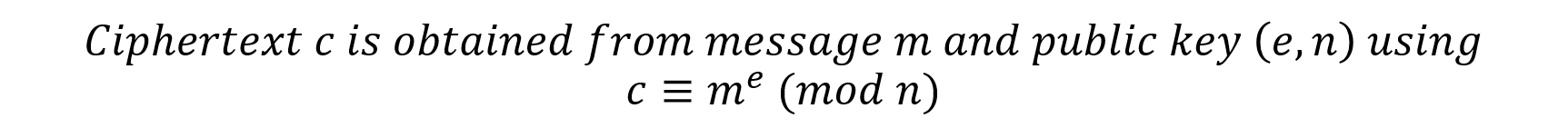
Decryption is done using Bob's private key in the following manner:
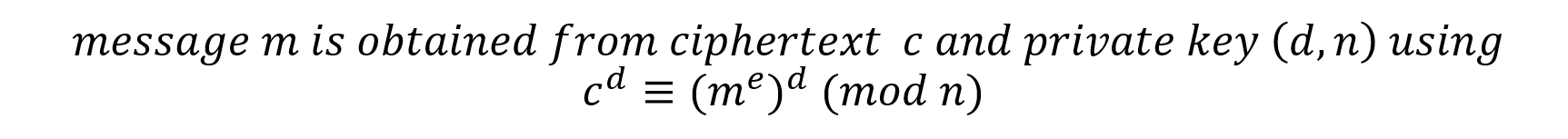
def keyGen():
''' Generate Keypair '''
i_p=randint(0,20)
i_q=randint(0,20)
# Instead of Asking the user for the prime Number which in case is not feasible,
# generate two numbers which is much highly secure as it chooses higher primes
while i_p==i_q:
continue
primes=PrimeGen(100)
p=primes[i_p]
q=primes[i_q]
#computing n=p*q as a part of the RSA Algorithm
n=p*q
#Computing lamda(n), the Carmichael's totient Function.
# In this case, the totient function is the LCM(lamda(p),lamda(q))=lamda(p-1,q-1)
# On the Contrary We can also apply the Euler's totient's Function phi(n)
# which sometimes may result larger than expected
lamda_n=int(lcm(p-1,q-1))
e=randint(1,lamda_n)
#checking the Following : whether e and lamda(n) are co-prime
while math.gcd(e,lamda_n)!=1:
e=randint(1,lamda_n)
#Determine the modular Multiplicative Inverse
d=modinv(e,lamda_n)
#return the Key Pairs
# Public Key pair : (e,n), private key pair:(d,n)
return ((e,n),(d,n))
def encrypt(pk,message):
""" Perform RSA Encryption Algorithm"""
key, n = pk
#Convert each letter in the plaintext to numbers based on the character using a^b mod m
cipher = [(ord(char) ** key) % n for char in message]
#Return the array of bytes
return cipher
def decrypt(pk,cipher):
'''Perform RSA Decryption Algorithm '''
key, n = pk
#Generate the plaintext based on the ciphertext and key using a^b mod m
message = [chr((int(char) ** key) % n) for char in cipher]
#Return the array of bytes as a string
return ''.join(message)Performing the RSA Cryptography on the Encrypted Hash to get the following Ciphertext
[114, 75, 108, 41, 118, 18, 114, 75, 54, 68, 45, 108, 13, 113, 68, 75, 108, 113, 114, 13, 41, 57, 57, 114, 45, 13, 38, 45, 39, 82, 45, 113]
Applying the RSA Cryptography to Decrypt the above Ciphertext
b10a8db164e0754105b7a99be72e3fe5It is a file/email based encryption covering three major aspects:
- Data Communication (Achieved via HASH function. I have used MD5. however, SHA-1 or SHA-2 can also be used)
- Data Privacy (Achieved through Symmetric Encryption. I have currently excluded this part)
- Authentication. (Achieved using the RSA Cryptography)
PGP follows the following steps for Encryption according to OpenPGP Standard RFC 4880
- Create Secure Hash function for the message
- Perform RSA crytpography on the Hashed Message
- Concatenate the Original message along with the ciphertext obtained at the previous step
- Perform ZIP compression algorithm on the concatenation and send the final ZIP
def encrypt(message,public):
'''
FUNCTION
----------
PGP follows the Following steps for Encryption according to OpenPGP Standard RFC 4880
1. Create Secure Hash function for the message
2. Perform RSA crytpography on the Hashed Message
3. Concatenate the Original message along with the ciphertext obtained at the previous step
4. Perform ZIP compression algorithm on the concatenation and send the final ZIP
PARAMETERS
----------
1. Message : Type <str>. Plaintext which is to be encrypted
2. Public Key : Type <tuple> containing the pairs (e,n).
RETURN
-------
pgpCipher : Zipped Ciphertext of type <Bytes>
For More information, please read RFC 4880, RFC 3447, RFC 1321
'''
message=message.encode('ascii')
# Step 1.
print("1. Applying the HASH Function on the Message")
md5hashed=md5.md5_to_hex(md5.md5(message))
print(md5.md5_to_hex(md5.md5(message)),' <= "',message.decode('ascii'),'"', sep='')
# Step 2.
print("Performing the RSA Cryptography on the Encrypted Hash")
ciphertext=rsa.encrypt(public,md5hashed)
# Step 3.
ctext=''
for i in ciphertext:
ctext=ctext+str(i)+' '
ciphertext=ctext
print("Concatenating RSA Ciphertext with the Original Message")
concat_text=ciphertext+'!!!'+message.decode('ascii')
byte_text=concat_text.encode('ascii')
# Step 4.
print("Applying ZIP compression Algorithm on the Concatenation Text")
pgpCipher=zip.compress(byte_text)
print("Successfully Performed PGP encryption !")
return pgpCipher1. Applying the HASH Function on the Message
b10a8db164e0754105b7a99be72e3fe5 <= "Hello World"
Performing the RSA Cryptography on the Encrypted Hash
[114, 75, 108, 41, 118, 18, 114, 75, 54, 68, 45, 108, 13, 113, 68, 75, 108, 113, 114, 13, 41, 57, 57, 114, 45, 13, 38, 45, 39, 82, 45, 113]
Concatenating RSA Ciphertext with the Original Message
Applying ZIP compression Algorithm on the Concatenation Text
Successfully Performed PGP encryption !
CipherText=b"x\x9c-\xcb\xc1\r\x800\x0c\x03\xc0U\xdc\r0Ii\xd8\x80\rX\x80\xfe*Ub\xff\x07I\x8a\xe4O\xce\x0e\xa9h\x15\xdc\x0cJ\x90\x86\xc8\xc2\xaa8\x9cWKq\x96\x80\x7f\xce\x14\x8d\xc2?k\x8b\xc4\x1d{\x81\xe4\xa3\x9c\xb0=\xc5\xa9\x94r\xf51&\xee\xf9\x8e\xe7\x036\xb1\x17\xa1"PGP follows the Following steps for Decryption according to OpenPGP Standard RFC 4880.
- Apply the ZIP Decompression Algorithm on the PGP Cipher Text to get the concatenated text.
- De-concatenate the Concatenated text to split into ciphertext and plain text.
- Apply RSA cryptography to decrypt the ciphertext into the HASHED message.
- Apply the HASH function on the separated plain text.
- Compare the two hash functions. If the two hashes are same, the PGP decryption is successful.
#def decrypt(pgpCipher,private):
'''
FUNCTION
----------
PGP follows the Following steps for Decryption according to OpenPGP Standard RFC 4880.
1. Apply the ZIP Decompression Algorithm on the PGP Cipher Text to get the concatenated text.
2. De-concatenate the Concatenated text to split into ciphertext and plain text.
3. Apply RSA cryptography to decrypt the ciphertext into the HASHED message.
4. Apply the HASH function on the separated plain text.
5. Compare the two hash functions. If the two hashes are same, the PGP decryption is successful.
PARAMETERS
----------
1. PGPCiphertext : Type <Bytes>. Ciphertext which is to be decrypted
2. Private Key : Type <tuple> containing the pairs (d,n).
RETURN
-------
Message : Original type <str>
For More information, please read RFC 4880, RFC 3447, RFC 1321
'''
print("Applying the PGP decryption Algorithm")
print("1. Applying the ZIP Decompression Algorithm on the PGP Cipher Text")
concat_text=(zip.decompress(pgpCipher)).decode('ascii')
print("2. De-concatenating the Concatenated text")
separate=concat_text.split('!!!')
cipher=[int(i) for i in separate[0].split()]
print("3. Applying the RSA Cryptography to Decrypt the Ciphertext")
md5hashed=rsa.decrypt(private,cipher)
print("4. Applying the HASH function for the De-concatenated plaintext")
print(md5.md5_to_hex(md5.md5(separate[1].encode('ascii'))),' <= "',separate[1],'"', sep='')
print("5. Comparing the HASH of Decrypted Ciphertext and HASHED Plaintext")
md5hashed1=md5.md5_to_hex(md5.md5(separate[1].encode('ascii')))
if md5hashed==md5hashed1:
print ("Successfully Decrypted the Message")
return (separate[1])
else:
print ("Invalid Private Key Provided")
return 0Applying the PGP decryption Algorithm
1. Applying the ZIP Decompression Algorithm on the PGP Cipher Text
2. De-concatenating the Concatenated text
3. Applying the RSA Cryptography to Decrypt the Ciphertext
b10a8db164e0754105b7a99be72e3fe5
4. Applying the HASH function for the De-concatenated plaintext
b10a8db164e0754105b7a99be72e3fe5 <= "Hello World"
5. Comparing the HASH of Decrypted Ciphertext and HASHED Plaintext
Successfully Decrypted the Message