FaSTPACE (Fast and Scalable Tool for Peptide Alignment and Consensus Extraction) is a Python package implemented in C++ programming language.
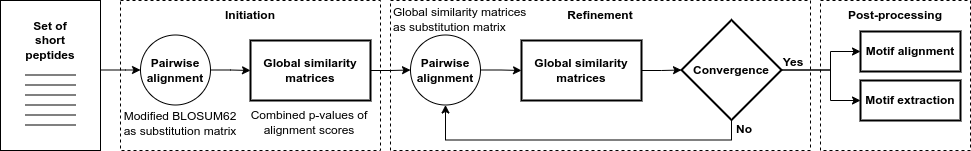
The core of the algorithm produces a refined global similarity matrix from which these outputs are produced. A global similarity matrix is a probabilistic representation of the similarity of the peptide to all other peptides in the dataset. The method consists of three steps: initiation, refinement and post-processing of the global similarity matrix.
pip install fastpace
from fastpace import run_motif_discovery, rerun_motif_discovery
Calculate per residue similarity scores, align peptides, and extract putative motifs.
Parameters:
peptides(list): List of strings of standard sequence letters representing peptides in the dataset. It should contain 2 or more peptides. No sequence with less than 2 letters or longer than 32 characters is allowed.weights(list, optional, default=None): List of positive numbers representing weights. The number of weights must be equal to the number of peptides. If not provided, each peptide is assigned a weight of 1.refine(int, optional, default=1): Flag with 0 or 1. (0 means return the results after the initiation step, 1 means doing the refinement step)normalization_factor(float, optional, default=-1): The dataset size is corrected to be equal to this number in order to compare different datasets with different sizes. It must be equal to or greater than 1. By default, -1 means to use the dataset size with no normalization.
Returns:
- Dictionary: The dictionary object returned contains information about the discovered motif, alignment results, and similarity scores for each peptide. Below is a breakdown of the key elements in the output:
.
├── Refinement Information:
│ └── refinement_iterations: The number of refinement iterations performed.
├── Consensus Motif Information:
│ ├── best_motif: The best consensus motif represented as a regular expression.
│ ├── best_motif_p_val: P-value associated with the best consensus motif.
│ ├── best_motif_significance: Significance level of the best consensus motif.
│ ├── best_motif_num_matches: Number of matches found for the best consensus motif.
│ └── best_motif_coverage: Coverage percentage of the best consensus motif.
├── Alignment Information:
│ ├── template: The template sequence used for alignment.
│ └── aligned_sequences: A dictionary mapping each input sequence to its aligned counterpart.
└── Peptide-specific Information:
For each peptide in the dataset, the following information is provided:
├── similarity_matrix: A matrix of peptide's global similarity scores.
├── similarity_motif: The motif represented as a regular expression extracted from the peptide's global similarity matrix.
├── similarity_p_val: P-value associated with the similarity motif.
├── similarity_significance: Significance level of the similarity motif.
├── similarity_num_matches: Number of matches found for the similarity motif.
├── similarity_coverage: Coverage percentage of the similarity motif.
├── similarity_score: Cumulative similarity score for the peptide.
├── matched_motif: The motif with the best p-value that matches the peptide.
├── matched_p_val: P-value associated with the matched motif.
├── matched_significance: Significance level of the matched motif.
├── matched_num_matches: Number of matches found for the matched motif.
├── matched_coverage: Coverage percentage of the matched motif.
└── alignment_score: Alignment score for the peptide on the template sequence.
Example:
peptides = ['TSPDGGTTFEHLWSSL', 'SPEVFQHIWDFLEQPI', 'CPVDPFEAQWAALENK', 'EPPLSQETFSDLWKLL', 'APELDPFEAQWAALEG']
run_motif_discovery(peptides, refine=0)Output:
{
"refinement_iterations": 0,
"consensus": {
"best_motif": ".*F...W..L.*",
"best_motif_p_val": 4.030701364259203e-12,
"best_motif_significance": 6.449063505442609e-09,
"best_motif_num_matches": 5,
"best_motif_coverage": 1.0
},
"alignment": {
"template": "TSPDGGTTFEHLWSSL",
"aligned_sequences": {
"TSPDGGTTFEHLWSSL": "TSPDGGTTFEHLWSSL----",
"SPEVFQHIWDFLEQPI": "----SPEVFQHIWDFLEQPI",
"CPVDPFEAQWAALENK": "---CPVDPFEAQWAALENK-",
"EPPLSQETFSDLWKLL": "EPPLSQETFSDLWKLL----",
"APELDPFEAQWAALEG": "--APELDPFEAQWAALEG--"
}
},
"peptides": {
"TSPDGGTTFEHLWSSL": {
"similarity_matrix": {
// ...
},
// ...
},
"SPEVFQHIWDFLEQPI": {
// ...
},
// ...
}
}
Example with weighting:
peptides = ['TSPDGGTTFEHLWSSL', 'SPEVFQHIWDFLEQPI', 'CPVDPFEAQWAALENK', 'EPPLSQETFSDLWKLL', 'APELDPFEAQWAALEG']
weights = [1, 2, 4, 1.5, 0.1]
run_motif_discovery(peptides, weights)Output:
{
"refinement_iterations":30,
"consensus":{
"best_motif":".*F...W..L.*",
"best_motif_p_val":4.030701364259203e-12,
"best_motif_significance":2.8327562517915794e-09,
"best_motif_num_matches":5,
"best_motif_coverage":1.0
},
"alignment":{
"template":"APELDPFEAQWAALEG",
"aligned_sequences":{
"TSPDGGTTFEHLWSSL":"TSPDGGTTFEHLWSSL----",
"SPEVFQHIWDFLEQPI":"----SPEVFQHIWDFLEQPI",
"CPVDPFEAQWAALENK":"---CPVDPFEAQWAALENK-",
"EPPLSQETFSDLWKLL":"EPPLSQETFSDLWKLL----",
"APELDPFEAQWAALEG":"--APELDPFEAQWAALEG--"
}
},
"peptides": {
"TSPDGGTTFEHLWSSL": {
"similarity_matrix": {
// ...
},
// ...
},
"SPEVFQHIWDFLEQPI": {
// ...
},
// ...
}
}
Calculate per residue similarity scores and extract putative motifs after masking previously extracted motifs.
Parameters:
original_peptides(list): List of the original peptides before masking.masked_peptides(list): List of the masked peptides. The masked positions should be substituted with the characterX. The number of masked peptides must be equal to the number of original peptides.weights(list, optional, default=None): List of positive weights.
Returns:
- Dictionary: The dictionary object returned contains information about the discovered motif, alignment results, and similarity scores for each peptide. The output has the same format as the previous function.
Example:
peptides = ['TSPDGGTTFEHLWSSL', 'SPEVFQHIWDFLEQPI', 'CPVDPFEAQWAALENK', 'EPPLSQETFSDLWKLL', 'APELDPFEAQWAALEG']
masked_peptides = ['TSPDGGTTXXXXXSSL', 'SPEVXXXXXDFLEQPI', 'CPVDPXXXXXAALENK', 'EPPLSQETXXXXXKLL', 'APELDPXXXXXAALEG']
rerun_motif_discovery(peptides, masked_peptides)Output:
{
"refinement_iterations": 23,
"consensus": {
"best_motif": ".*D........LE.*",
"best_motif_p_val": 0.00033767412104890706,
"best_motif_significance": 0.41746722746831066,
"best_motif_num_matches": 2,
"best_motif_coverage": 0.4
},
"alignment": {
"template": "CPVDPXXXXXAALENK",
"aligned_sequences": {
"TSPDGGTTXXXXXSSL": "TSPDGGTTXXXXXSSL----",
"SPEVXXXXXDFLEQPI": "----SPEVXXXXXDFLEQPI",
"CPVDPXXXXXAALENK": "---CPVDPXXXXXAALENK-",
"EPPLSQETXXXXXKLL": "EPPLSQETXXXXXKLL----",
"APELDPXXXXXAALEG": "--APELDPXXXXXAALEG--"
}
},
"peptides": {
"TSPDGGTTXXXXXSSL": {
"similarity_matrix": {
// ...
},
// ...
},
"SPEVXXXXXDFLEQPI": {
// ...
},
"CPVDPXXXXXAALENK": {
// ...
},
"EPPLSQETXXXXXKLL": {
// ...
},
"APELDPXXXXXAALEG": {
// ...
}
}
}
A script is designed to process fasta files, align peptides, perform motif discovery, and generate sequence logos. It utilizes the fastpace module for motif discovery and the logomaker library for creating sequence logos.
- Before using this script, ensure that you have the required Python libraries installed. You can install them using the following command:
pip install fastpace pandas matplotlib seaborn logomaker- Clone the repository (to download the script):
git clone https://github.com/hkotb/fastpace.git
cd fastpace/test/
python fastpace_cmd.py --input_file input.fasta --output_file output.fasta [--draw_logo] [--sequence SEQUENCE] [--num_reruns NUM_RERUNS] [--refine REFINE]
--input_file: The path to the input fasta file. (Required)--output_file: The path to the output fasta file. (Required)--draw_logo: Draw sequence logo of the best peptide or the peptide passed by --sequence. (Optional)--sequence: Draw sequence logo of this peptide. (Optional)--num_reruns: Number of times to rerun the algorithm before returning the results. This is useful for identifying multiple motifs. For instance, to discover a second motif after masking the first one found, set 'num_reruns' to 2. (Default: 1)--refine: Flag to run the refinement. (Default: 1)
Basic Usage
python fastpace_cmd.py --input_file input.fasta --output_file output.fasta
Drawing Sequence Logo
python fastpace_cmd.py --input_file input.fasta --output_file output.fasta --draw_logo
Drawing Sequence Logo for a Specific Peptide
python fastpace_cmd.py --input_file input.fasta --output_file output.fasta --draw_logo --sequence GATCGATCG
Running Multiple Reruns
python fastpace_cmd.py --input_file input.fasta --output_file output.fasta --num_reruns 3
Running without Refinement
python fastpace_cmd.py --input_file input.fasta --output_file output.fasta --refine 0
The script generates an output fasta file of the aligned peptides, a JSON file containing the motif discovery results, and a PNG file containing the sequence logo (if --draw_logo is specified).
- Output Fasta File:
output.fasta - JSON Result File:
output.json - Sequence Logo File:
output.png
We recommend that you clone the repository and install it as a development package with:
python setup.py develop
To generate a distribution archive from your machine:
python -m build
To distribute binary Python extensions as wheels on Linux:
docker pull quay.io/pypa/manylinux2014_x86_64
docker run --rm -e PLAT=manylinux2014_x86_64 -v `pwd`:/io quay.io/pypa/manylinux2014_x86_64 /io/build-wheels.sh
This source code is licensed under the MIT license found in the LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree.
If you find the pipeline useful in your research, we ask that you cite our paper:
Coming soon.