[toc]
https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cuda-c-programming-guide/
-
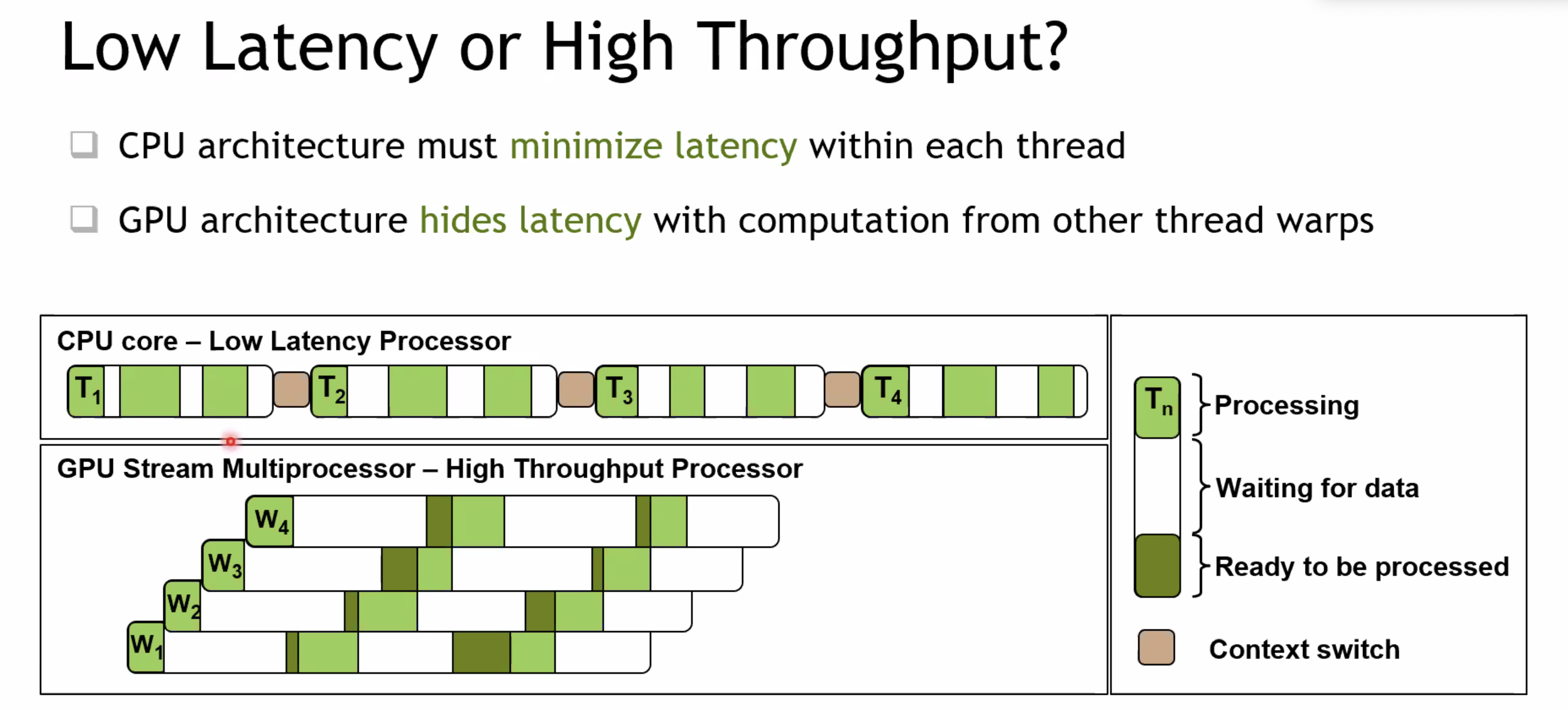
CPU: latency-optimized low latency processor
- 前端消耗大
-
GPU: throughput-optimized high throughput processor
-
隔离方式:时间片 vs 空间
-
隔离级别:不隔离 vs 强隔离 vs 弹性
-
几种隔离技术对比:
- vGPU(Grid)(Nvidia):虚拟化;容器化支持不好,license
- vCuda(腾讯):cuda hook;性能损耗严重
- cGPU(Alibaba):ioctl;损耗小,硬隔离,侵入内核(机器容易坏)
- MPS(Nvidia):thread;显存隔离,故障隔离不好
- 进程级别,进程数量会受限于显存
- MIG(~A100):sm/global memory;硬件层面隔离
-
3 ways to accelerate applications:
- Libraries
- OpenACC (add directive, for applications like HPC)
- Programming Languages
https://developer.nvidia.com/dcgm
- Note:
- 监控 PCIE-RX ---> H2D 带宽
- Health Check
nvidia-smi
nvidia-smi --query-gpu=name --format=csv,noheader- OAM是一种异构计算设备的接口协议,对标nvlink. nvlink是封闭的协议,OAM是若干大厂共建的一个开放协议。
- 目的:避免每一种卡都有自己的卡间通信标准,尽量做到 (除了NV的卡之外)任何厂家的计算卡都兼容
- 技术层面, OAM 和 NVSWITCH (对应A100 这代) 基本是对等的
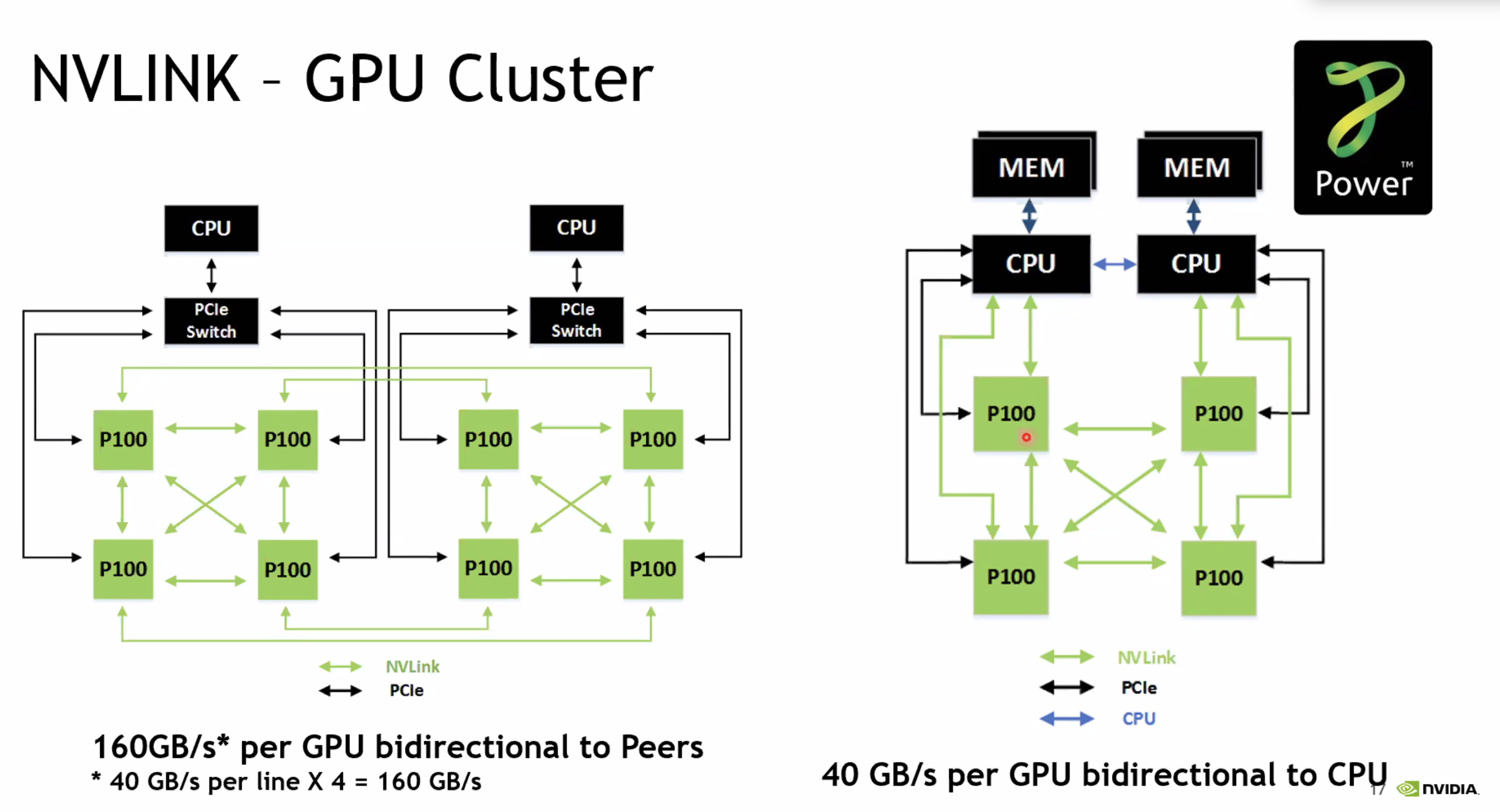
- OAM:是 full connect 模式, 各卡独享约 ~80GB/s 带宽
- full connect 的结构更为简单,有一些散热和能耗的优势
- NV switch: 整个switch提供 600GB/s 带宽
- 单机八卡时,OAM 和 NV switch 差不多;卡数少时 nvsiwtch 效率高
- OAM:是 full connect 模式, 各卡独享约 ~80GB/s 带宽
-
CUDA accelerates applications drastically with little effort, has an ecosystem of highly optimized libraries for DNN, BLAS, graph analytics, FFT, and more, and also ships with powerful command line and visual profilers.
-
CUDA supports many, if not most, of the world's most performant applications in, Computational Fluid Dynamics, Molecular Dynamics, Quantum Chemistry, Physics and HPC.
nvidia-smi
cudaMallocManaged()
cudaDeviceSynchronize()
nvcc -arch=sm_70 -o hello-gpu 01-hello/01-hello-gpu.cu -run- code executed on the CPU is referred to as host code, and code running on the GPU is referred to as device code
- cudaDeviceSynchronize只需要在使用cudaStream时使用,平时“Although CUDA kernel launches are asynchronous, all GPU-related tasks placed in one stream (which is the default behavior) are executed sequentially.”
void CPUFunction()
{
printf("This function is defined to run on the CPU.\n");
}
__global__ void GPUFunction()
{
printf("This function is defined to run on the GPU.\n");
}
// __global__表示CPU/GPU均可执行,必须返回void
int main()
{
CPUFunction();
// launch a kernel, provide an execution configuration
GPUFunction<<<1, 1>>>();
cudaDeviceSynchronize();
// CPU等待GPU
}At a high level, execution configuration allows programmers to specify the thread hierarchy for a kernel launch, which defines the number of thread groupings (called blocks), as well as how many threads to execute in each block.
NVIDIA CUDA Compiler, documentation
arch flag, virtual architecture features
-
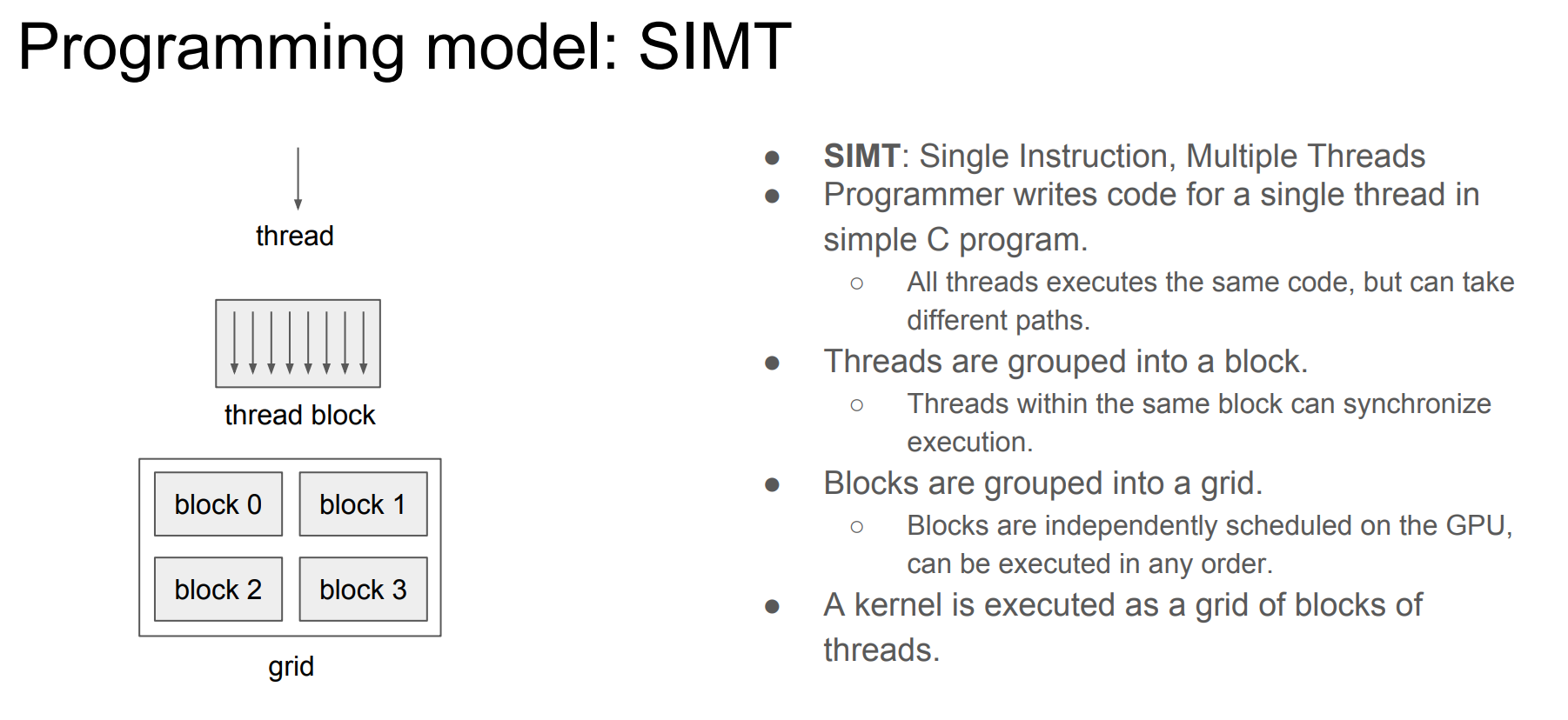
Programming model: SIMT
- 三层抽象:grid, block, thread
-
Kernel Execution
-
configuration ~ grid
-
Each block is executed by one SM and does not migrate.
-
Several concurrent blocks can reside on one SM depending on block’s memory requirement and the SM’s memory resources.
-
-
CUDA-Provided Thread Hierarchy Variables,可以在
__global__函数里直接用,作为标识来实现并行 -
并行是无序的
-
threadIdx.x + blockIdx.x * blockDim.x
gridDim.x: num of blocks
blockDim.x: num of threads in a block
blockIdx.x: block index
threadIdx.x: thread index// e.g.
__global__ void vecAddKernel(const float* A, const float* B, float* C, int n) {
int i = blockDim.x * blockIdx.x + threadIdx.x;
if (i < n) {
C[i] = A[i] + B[i];
}
}
#define THREADS_PER_BLOCK 512
void vecAdd(const float* A, const float* B, float* C, int n) {
float *d_A, *d_B, *d_C;
int size = n * sizeof(float);
cudaMalloc((void **) &d_A, size);
cudaMemcpy(d_A, A, size, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
cudaMalloc((void **) &d_B, size);
cudaMemcpy(d_B, B, size, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
cudaMalloc((void **) &d_C, size);
int nblocks = (n + THREADS_PER_BLOCK - 1) / THREADS_PER_BLOCK;
vecAddKernel<<<nblocks, THREADS_PER_BLOCK>>>(d_A, d_B, d_C, n);
cudaMemcpy(C, d_C, size, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
cudaFree(d_A); cudaFree(d_B); cudaFree(d_C);
}- 如果不同的线程在不同的Warp里,他们的执行顺序会有所不同(但如果执行的操作非常简单,那么它们执行的先后时间也相差非常小),因为硬件(SM)是以Warp为单位调度线程运行的,每个Warp有32个线程
// CPU-only
int N = 2<<20;
size_t size = N * sizeof(int);
int *a;
a = (int *)malloc(size);
// Use `a` in CPU-only program.
free(a);
// Accelerated
int N = 2<<20;
size_t size = N * sizeof(int);
int *a;
// Note the address of `a` is passed as first argument.
cudaMallocManaged(&a, size);
// Use `a` on the CPU and/or on any GPU in the accelerated system.
cudaFree(a);- 这个地址在统一的内存空间里,GPU和CPU都可以使用,但物理上数据可以不在它被访问的设备里,这时会产生page fault(缺页错误),对这个错误的处理就是把数据拷贝到需要访问它的设备或主机内存里,这个操作是透明的(自动执行)。
https://on-demand.gputechconf.com/gtc/2018/presentation/s8430-everything-you-need-to-know-about-unified-memory.pdf https://developer.nvidia.com/blog/unified-memory-cuda-beginners/
- 精讲UnifiedMemory的博客 https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41172895/article/details/115403922
- 使用了虚拟内存(cudaMallocManaged),降低代码复杂度,系统会将大于gpu内存的空间自动放到cpu上,内存申请cudaMemPrefetchAsync
- cudaMemAdvise
- cudaMemAdviseSetReadMostly 及 cudaMemAdviseUnSetReadMostly 这两个是cudaMemAdvise的Flag,用来为某个device设定/解除内存空间ReadMostly的特性,device所指的设备可以有一个只读副本而不发生数据迁移,当两端没有写入时,两个副本的数据是一致的。
- cudaMemAdvise(cudaMemAdviseSetAccessedBy), gpu上有的直接使用,cpu上就直接pci访问,什么时候搬运到gpu可以自行指定
#define GPU_DEVICE 0
{
char * array = nullptr;
cudaMallocManaged(&array, N) //分配内存
fill_data(array);
cudaMemAdvise(array, N, cudaMemAdviseSetReadMostly, GPU_DEVICE); //提示GPU端几乎仅用于读取这片数据
cudaMemPrefetchAsync(array, N, GPU_DEVICE, NULL); // GPU prefetch
qsort<<<...>>>(array); //GPU 无缺页中断,产生read-only副本
//cudaDeviceSynchronize();
use_data(array); //CPU process 没有page-fault.
cudaFree(array);
}-
Amount Mismatch
-
size_t number_of_blocks = (N + threads_per_block - 1) / threads_per_block; -
threads_per_block最大为1024
-
-
- By using a loop with stride equal to the grid size, we ensure that all addressing within warps is unit-stride, so we get maximum memory coalescing, just as in the monolithic version.
- 所有warp同步寻址都是在一个grid里,这是最大显存聚合
__global__ void kernel(int *a, int N)
{
int indexWithinTheGrid = threadIdx.x + blockIdx.x * blockDim.x;
int gridStride = gridDim.x * blockDim.x;
for (int i = indexWithinTheGrid; i < N; i += gridStride)
{
// do work on a[i];
}
}cudaError_t err;
err = cudaMallocManaged(&a, N) // Assume the existence of `a` and `N`.
if (err != cudaSuccess) // `cudaSuccess` is provided by CUDA.
{
printf("Error: %s\n", cudaGetErrorString(err)); // `cudaGetErrorString` is provided by CUDA.
}
someKernel<<<1, -1>>>(); // -1 is not a valid number of threads.
cudaError_t err;
err = cudaGetLastError(); // `cudaGetLastError` will return the error from above.
if (err != cudaSuccess)
{
printf("Error: %s\n", cudaGetErrorString(err));
}#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
inline cudaError_t checkCuda(cudaError_t result)
{
if (result != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "CUDA Runtime Error: %s\n", cudaGetErrorString(result));
assert(result == cudaSuccess);
}
return result;
}
int main()
{
/*
* The macro can be wrapped around any function returning
* a value of type `cudaError_t`.
*/
checkCuda(cudaDeviceSynchronize())
}利用dim3完成2d、3d任务
dim3 threads_per_block(16, 16, 1);
dim3 number_of_blocks(16, 16, 1);
someKernel<<<number_of_blocks, threads_per_block>>>()https://github.com/NVIDIA/nvidia-docker
Peruse GPU-Accelerated Libraries for Computing to learn where you can use highly optimized CUDA libraries for tasks like basic linear algebra solvers (BLAS), graph analytics, fast fourier transforms (FFT), random number generation (RNG), and image and signal processing, to name a few.
Assess, Parallelize, Optimize, Deploy(APOD) design cycle
Profile configuration details, Report file(s) generation details, CUDA API Statistics, CUDA Kernel Statistics, CUDA Memory Operation Statistics (time and size), OS Runtime API Statistics
nvcc -o single-thread-vector-add 01-vector-add/01-vector-add.cu -run
nsys profile --stats=true -o output-report ./single-thread-vector-addGPU and Programming Model
-
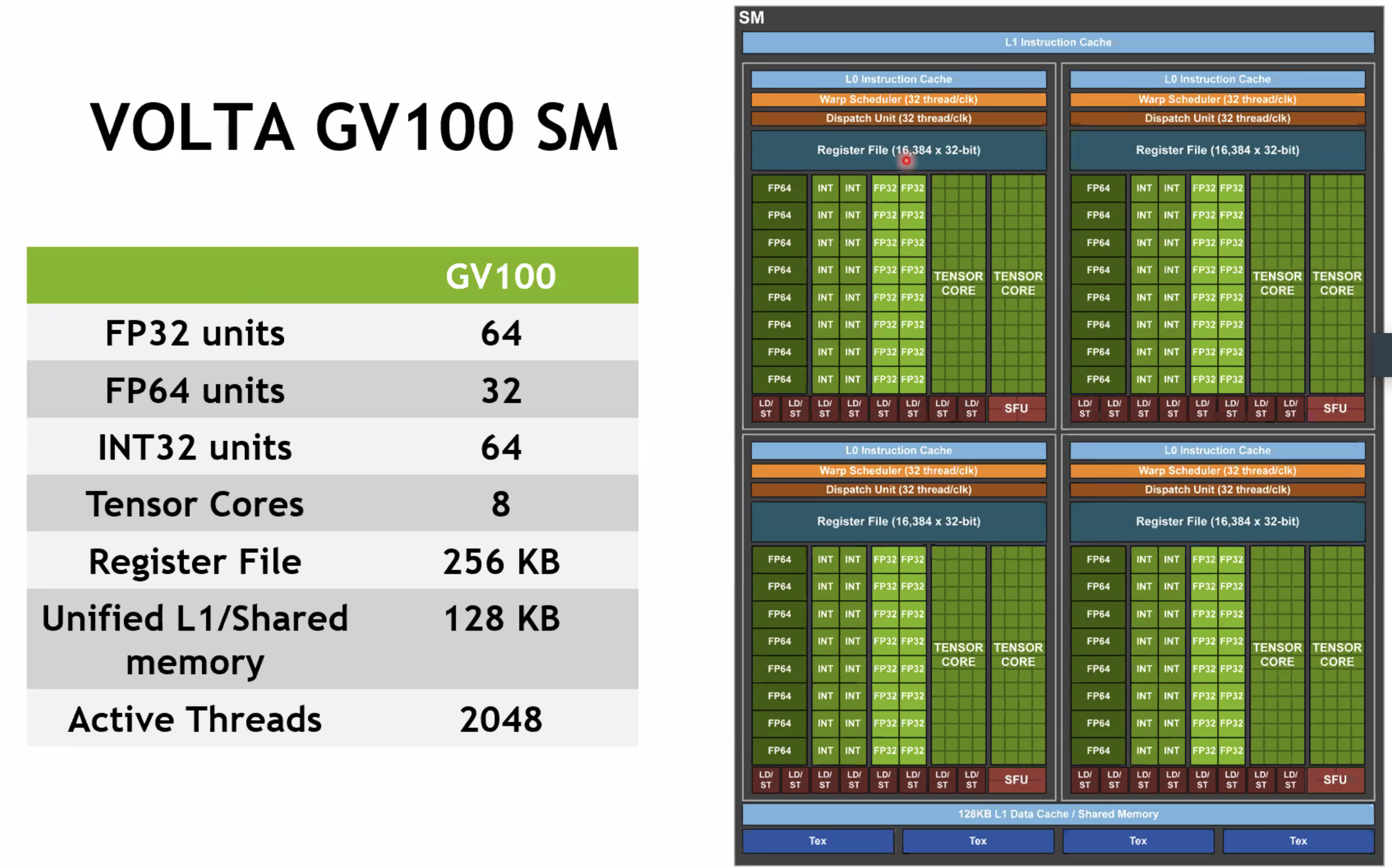
GPU内部很多functional units: SMs(Streaming Multiprocessors),一个SM可以schedule多个block,但同一时间只能执行一个
-
A set of CUDA cores
-
Tensor core相比CUDA core,实现了MMA operations,支持2:4 sparsity,支持in8和int4,更高效
-
CUDA Core<->Thread --> registers&local memory
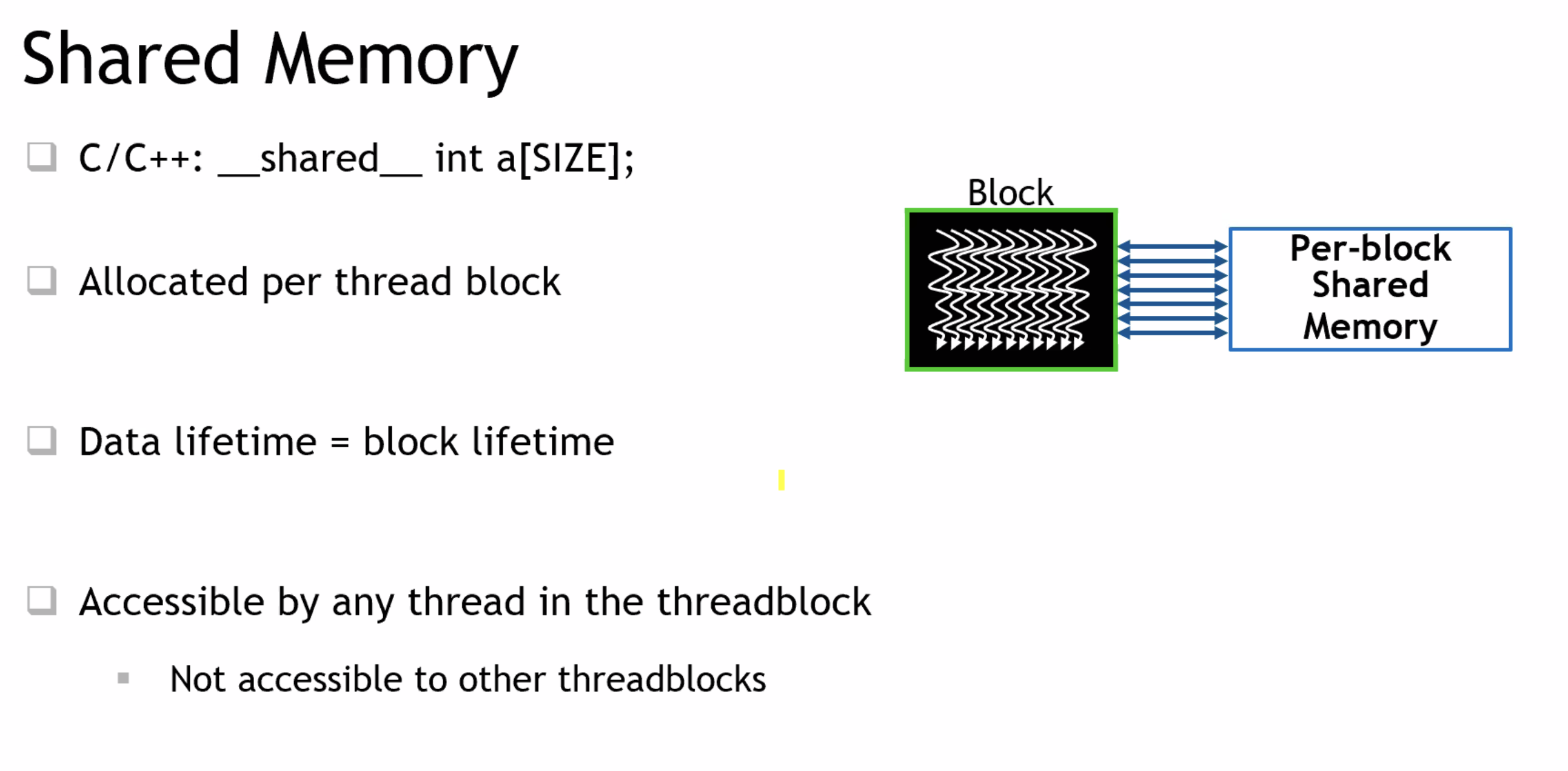
-
SM <-> Thread Block pool ---> shared memory
-
Device <-> Grid ---> global memory
-
白框:subpartition
-
-
A warp is the basic schedule unit in kernel execution
-
一个warp是successive 32 threads in a block
- thread如果不能被32整除,余数占据one more warp
-
一个SM有一个thread block pool,一个thread block有多个warp,一个warp scheduler 16个warp
- How to choose how many threads/blocks to have?
- The only thing that really matters for occupancy and if performance depends on occupancy is warps. You want to have as close to 64 active warps as possible, all other factors being equal.
- very small block sizes (e.g. 32 threads per block) may limit performance due to occupancy. Very large block sizes for example 1024 threads per block, may also limit performance, if there are resource limits (e.g. registers per thread usage, or shared memory usage) which prevent 2 threadblocks (in this example of 1024 threads per block) from being resident on a SM
- 推荐值:one thread block, 128~512 threads
-
Instructions are SIMD synchronous within a warp
- 一个warp中的线程执行同一指令(Volta架构之后,可以执行不同指令,但不同时)
- e.g. 【code/reduce.cu】
reduce3()- 各种优化技巧,包括unrolling、algorithm cascading
- each thread should sum O(log n) elements
- e.g. 【code/reduce.cu】
- 对于control flow,可能是周期T一半的线程执行if语句,周期T+1另一半的线程执行else语句
- 一个warp中的线程执行同一指令(Volta架构之后,可以执行不同指令,但不同时)
-
Instructions will be issued to execution units by warp.
- warp scheduler: Decode and schedule the next instructions
-
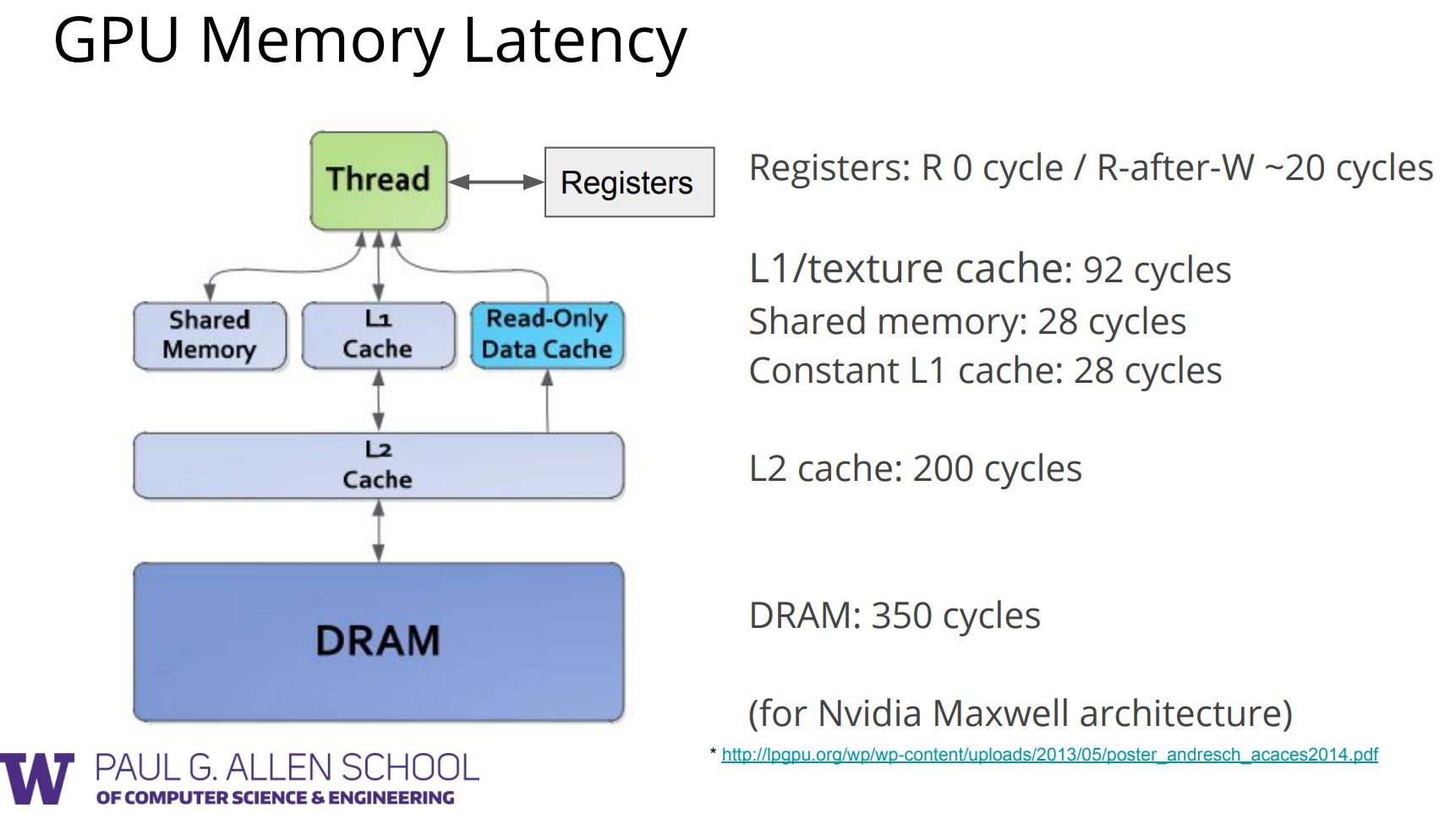
Latency is caused by not able to issue next instruction to execution unit
-
warp's context switching is free -> 通过大量warp来hide memory latency
-
一些单元
- SFU: special function unit
- Load/Store memory
-
-
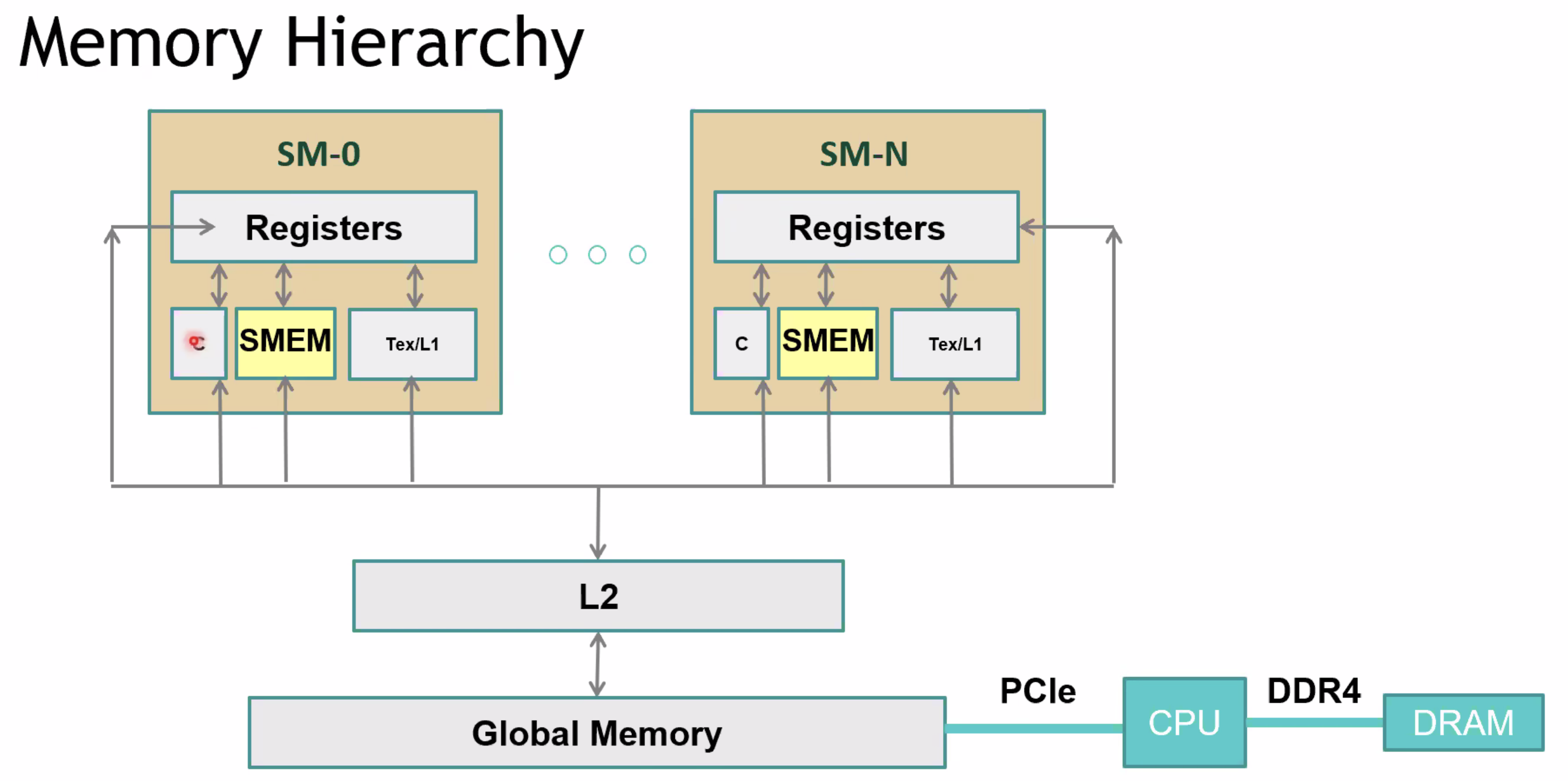
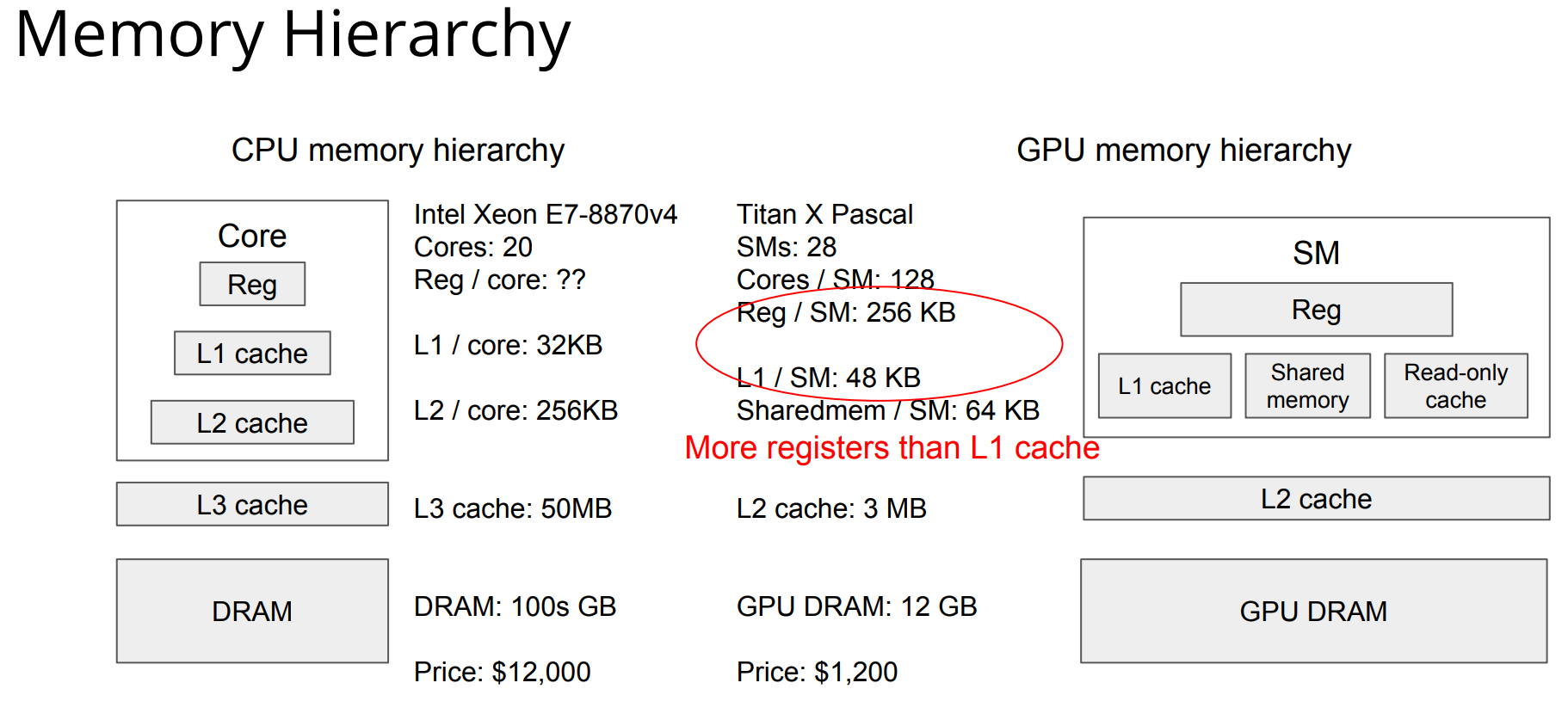
Registers / Shared Memory / L1 Cache
-
SMs share Global Memory
-
PCIe / NVLINk 与CPU Chipset交互
- More registers than L1 cache
- half gemm用32位寄存器做累加,input/output用16位寄存器
- SM片上单元比L2快3倍,比Global Memory快几十倍
cudaMallocManaged() 不注意的话开销大
cudaMalloc() 分配显存
cudaMemcpyHostToDevice- 编译器决定kernel内定义的变量是分配在寄存器上(没有超过上限的标量)还是per-thread local memory上
- 寄存器之间的值不一定是私有的,可以shuffle
- 左边的不是全连接结构,NV引入了NVSwitch单元,交换机芯片,支持最多16个GPU的直联
block size的选择,最小取64,通常取128、256
- SM的倍数
- 32的倍数, in depth coverage of SMs and warps
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int deviceId;
cudaGetDevice(&deviceId);
cudaDeviceProp props;
cudaGetDeviceProperties(&props, deviceId);
int computeCapabilityMajor = props.major;
int computeCapabilityMinor = props.minor;
int multiProcessorCount = props.multiProcessorCount;
int warpSize = props.warpSize;
printf("Device ID: %d\nNumber of SMs: %d\nCompute Capability Major: %d\nCompute Capability Minor: %d\nWarp Size: %d\n", deviceId, multiProcessorCount, computeCapabilityMajor, computeCapabilityMinor, warpSize);
}dynamic parallelism in cuda: kernel内执行kernel,但launch kernel开销较大,有几微秒
-
Host<->device data transfer has much lower bandwidth than global memory access.
- 16 GB/s (PCIe x16 Gen3) vs 250 GB/s & 10.6 T inst/s (GP100)
-
Minimize transfer
-
Intermediate data can be allocated, operated, de-allocated directly on GPU
-
Sometimes it’s even better to re-compute on GPU
-
-
Group transfer
- One large transfer much better than many small ones
- Overlap memory transfer with computation
unmanaged memory allocation and migration; pinning, or page-locking host memory; and non-default concurrent CUDA streams.
优化思路:
-
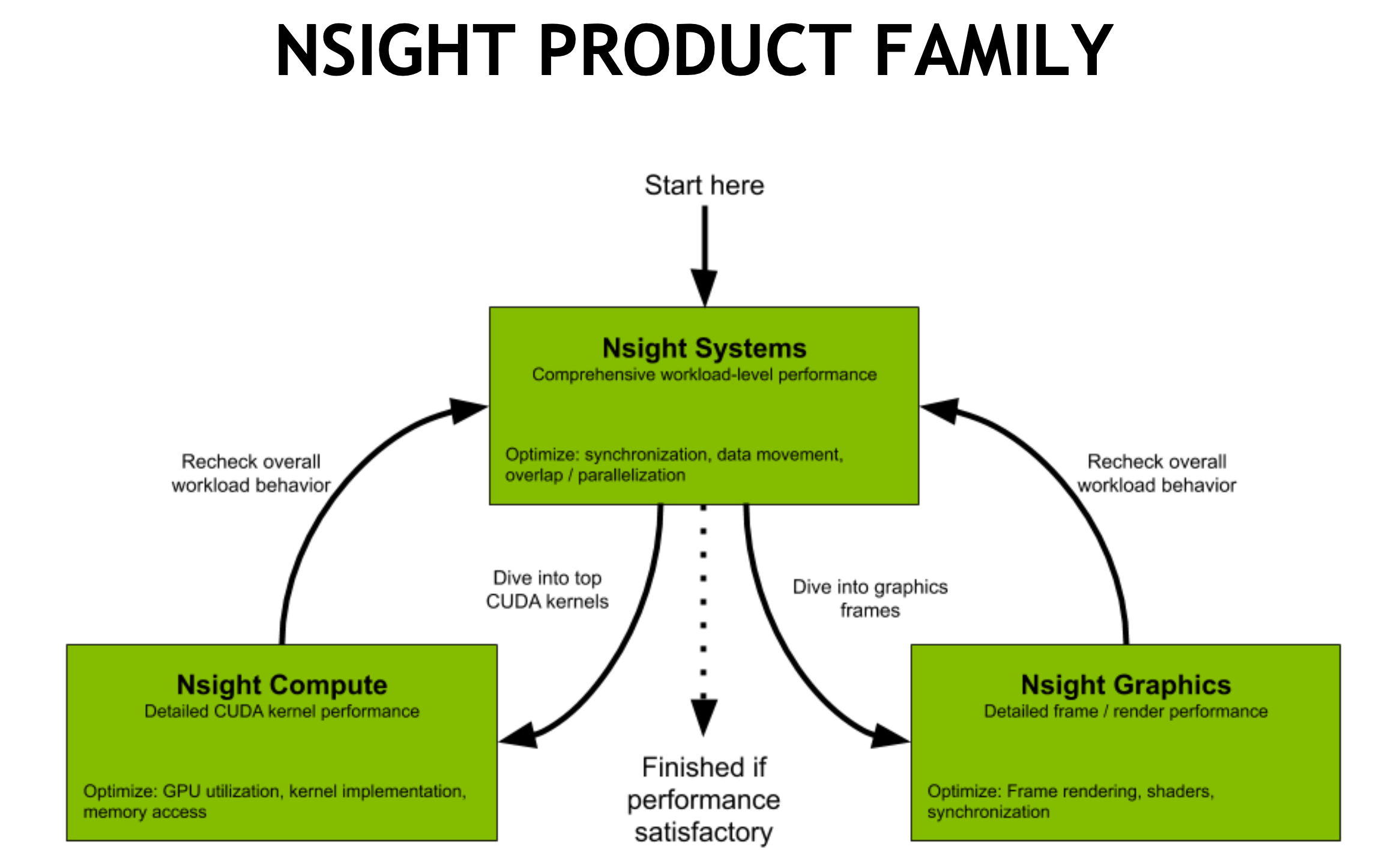
NVVP & nvprof (legacy)
-
Nsight System & Nsight Compute
-
Use existing libraries, which are highly optimized, e.g. cublas, cudnn.
-
Use high level language to write GPU kernels.
-
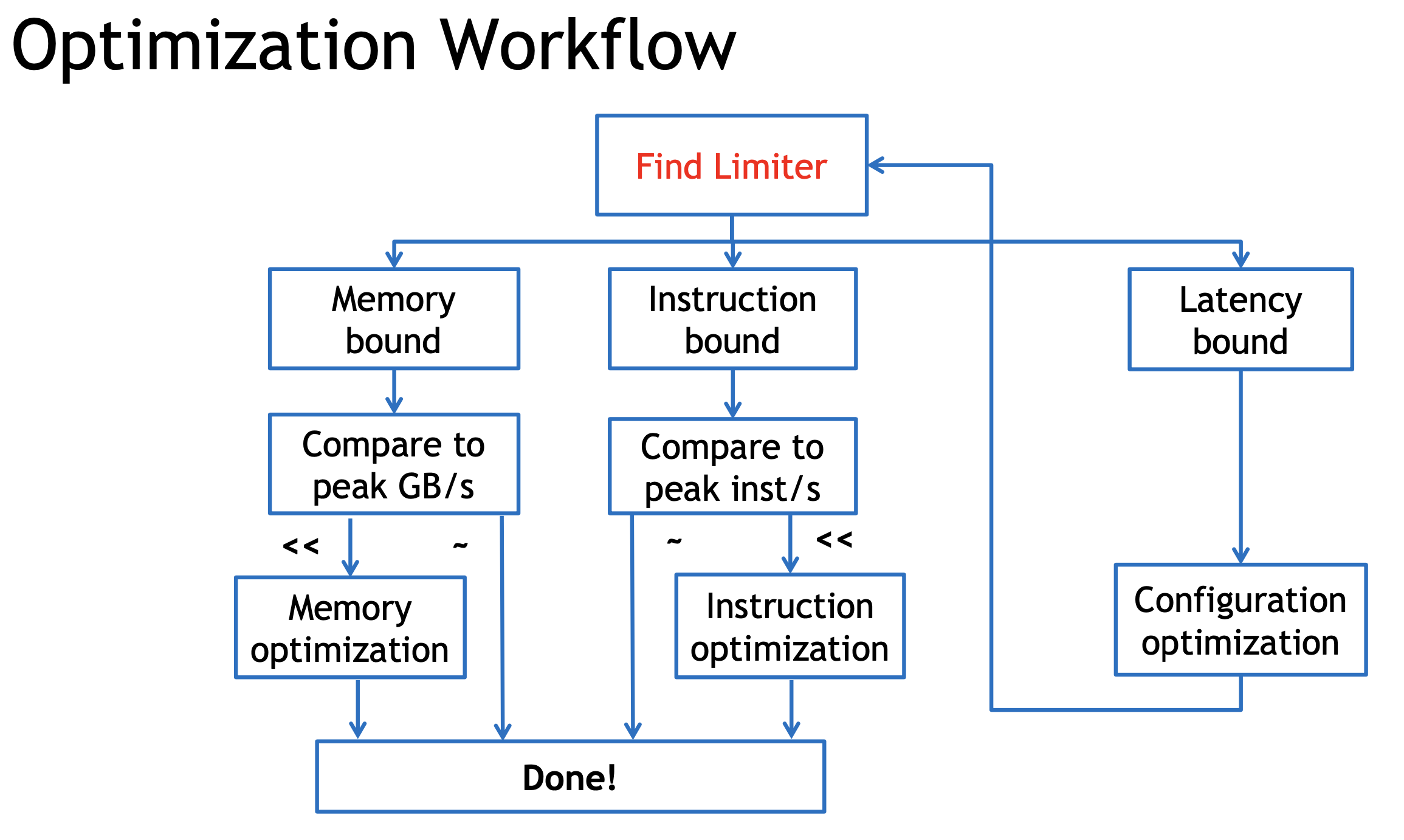
Choose the right metric:
- GFLOP/s: for compute-bound kernels
- Bandwidth: for memory-bound kernels
- Will use G80 GPU for this example
- 384-bit memory interface(数据总线位数), 900 MHz DDR
- 384 * 1800 / 8 = 86.4 GB/s
- 由于DDR的时钟脉冲上升沿和下降沿都传输数据,因此倍增系数为2
-
Understand CUDA performance characteristics
- Memory coalescing
- Divergent branching
- Bank conflicts
- Latency hiding
-
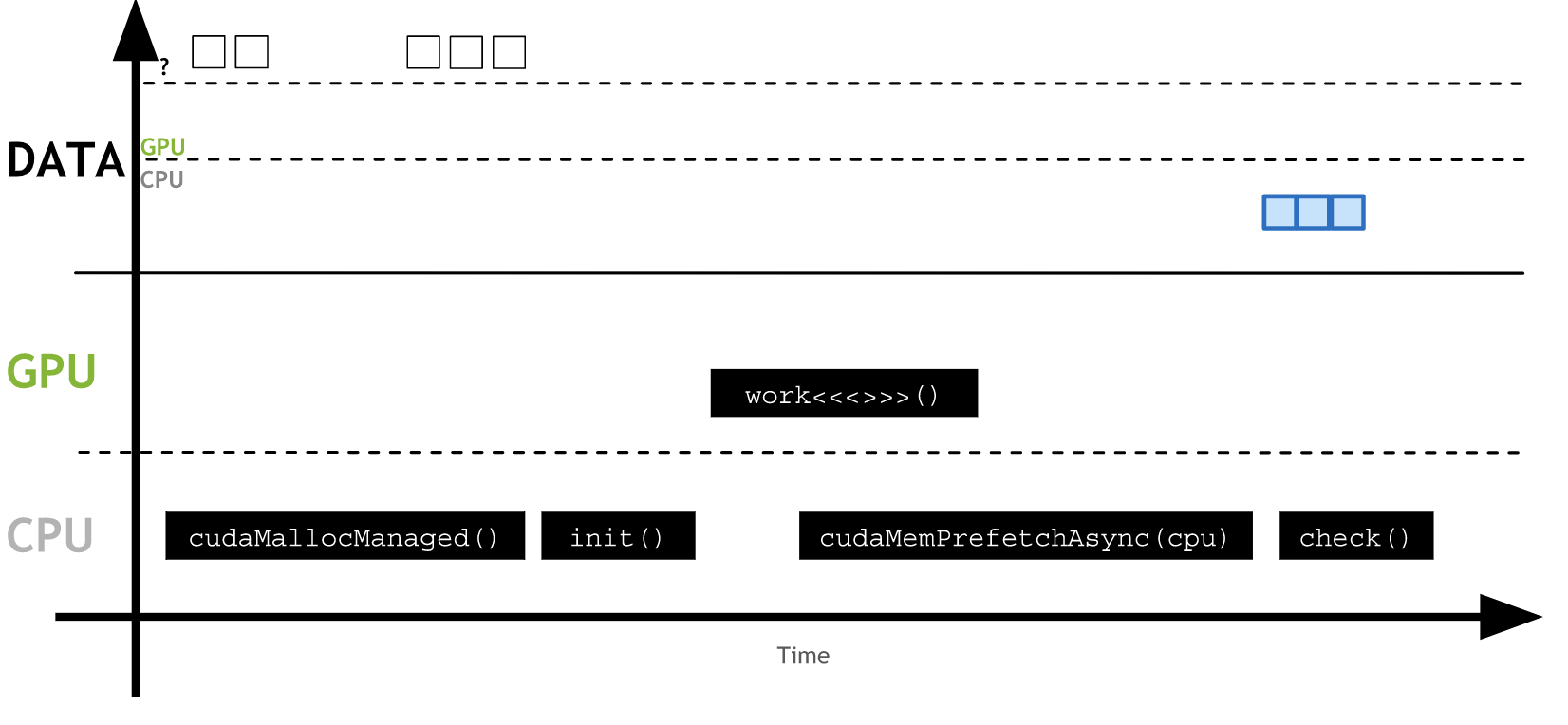
prefetch: 减少HtoD耗时(因为larger chunks),大幅减少kernel耗时(不再page fault)
-
init-kernel: 不再有HtoD,OS耗时也没了
https://developer.nvidia.com/blog/maximizing-unified-memory-performance-cuda/
- Kernels within any single stream must execute in order
- Kernels in different, non-default streams can interact concurrently
- The default stream is special: it blocks all kernels in all other streams
- 这一规则有副作用,因此推荐用non-default streams
cudaStream_t stream; // CUDA streams are of type `cudaStream_t`.
cudaStreamCreate(&stream); // Note that a pointer must be passed to `cudaCreateStream`.
someKernel<<<number_of_blocks, threads_per_block, 0, stream>>>(); // `stream` is passed as 4th EC argument.
// 3th argument: the number of bytes in shared memory
cudaStreamDestroy(stream); // Note that a value, not a pointer, is passed to `cudaDestroyStream`.
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i){
cudaStream_t stream;
cudaStreamCreate(&stream);
printNumber<<<1, 1, 0, stream>>>(i);
cudaStreamDestroy(stream);
}
cudaDeviceSynchronize();- Exericise: Accelerate and Optimize an N-Body Simulator
- nbody-raw.cu -> nbody-optimized.cu
- Improve memory access pattern to reduce wasted transactions,提高bus utilization
- per warp (coalesced, 32/64/128B)
- 线程访问可以不连续,但内存需要连续
- in discrete chunks (transported in segments: L2 cache line, 32B)
- 长度和index均需对齐
- per warp (coalesced, 32/64/128B)
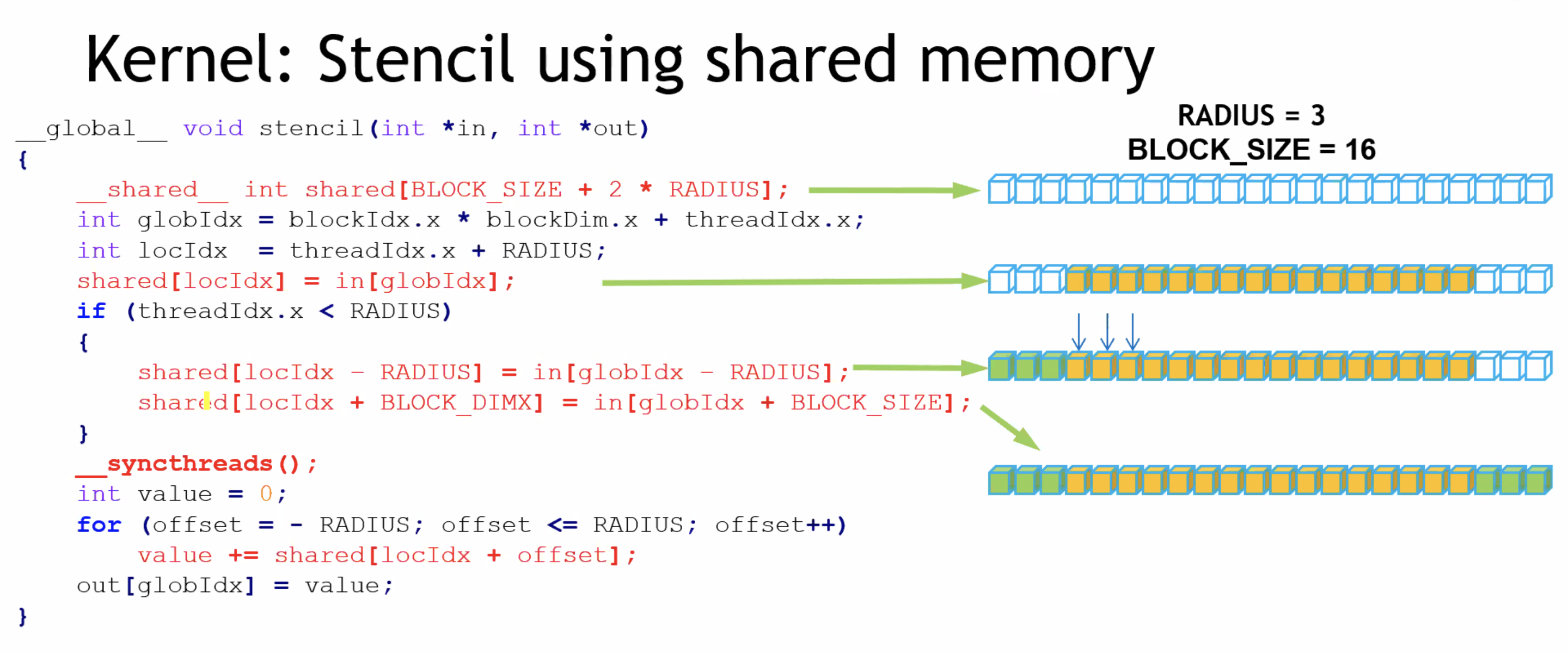
- Reduce redundant access: shared memory
- Inter-block communication
- User-managed cache to reduce redundant global memory accesses
- Avoid non-coalesced access: shared memory没有cache line的概念,e.g. matrix-transposition.cu
- Shared memory应用于矩阵乘法,见【code/gemm.cu】
- 双buffer的思路:prefetch和计算并行
- Reduction优化,见【code/reduction.pdf】
- Parallel Reduction
- Problem: Global Synchronization
- Solution: decompose into multiple kernels Kernel launch serves as a global synchronization point
- Kernel launch has negligible HW overhead, low SW overhead
- Solution: Kernel Decomposition
- Recursive kernel invocation
- Manual Device Memory Allocation and Copying
int *host_a, *device_a; // Define host-specific and device-specific arrays.
cudaMalloc(&device_a, size); // `device_a` is immediately available on the GPU.
cudaMallocHost(&host_a, size); // `host_a` is immediately available on CPU, and is page-locked, or pinned.
initializeOnHost(host_a, N); // No CPU page faulting since memory is already allocated on the host.
// `cudaMemcpy` takes the destination, source, size, and a CUDA-provided variable for the direction of the copy.
cudaMemcpy(device_a, host_a, size, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
kernel<<<blocks, threads, 0, someStream>>>(device_a, N);
// `cudaMemcpy` can also copy data from device to host.
cudaMemcpy(host_a, device_a, size, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
verifyOnHost(host_a, N);
cudaFree(device_a);
cudaFreeHost(host_a); // Free pinned memory like this.cudaHostAlloc: Pinned(Non-pageable) Memory, very expensive
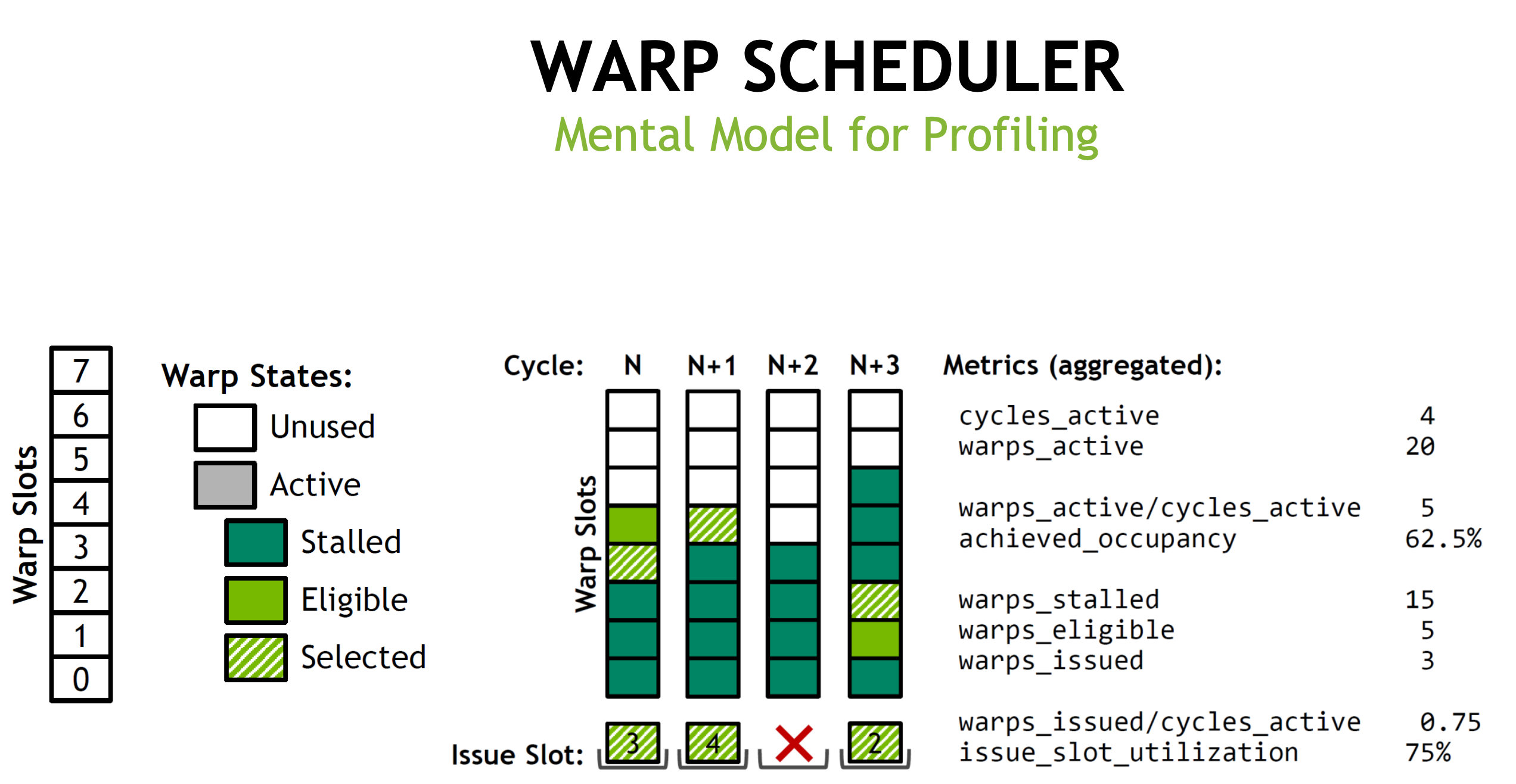
Warp State
- Active: warps inside the pool which has non-exiting threads
- Eligible: active warps that are not stalled
- Issued: a single eligible warp that the warp scheduler choose to issue one or more instructions on this cycle
Latency
-
bound: for many cycles, lack of eligible warps to issue instructions
-
hiding: switching warp
-
technique: increase active warps
Occupancy & Active Warps
- Occupancy: ratio of active warps per SM to the maximum number of allowed warps
- Hardware limit: 64 in Volta GV100 Per SM(16 per sub-partition), but 32 in Turing
- We need the occupancy to be high enough to hide latency
- Theoretical occupancy is limited by resource usage (shared memory/registers/blocks per SM)
Achieved occupancy can be significantly lower than theoretical occupancy when:
- Unbalanced workload within blocks
- Unbalanced workload across blocks
- Too few blocks launched
Occupancy Optimization
-
Know the occupancy: NVIDIA Visual profiler / Nsight Compute
-
Adjust resource usage to increase theoretical occupancy
-
Change block size
-
Limit register usage
-
Compiler option –maxregcount=n: per file
-
__launch_bounds__: per kernel
-
-
Limit shared memory usage.
-
-
Launch enough load-balanced blocks to increase achieved occupancy
__global__ void
__launch_bounds__(maxThreadsPerBlock, minBlocksPerMultiprocessor)
MyKernel(...){
...
}Using Streams to Overlap Data Transfers and Code Execution
- cudaMemcpyAsync:
manual-malloc.cu,memcpy-async.cu
-
Use float if precision allow
- Adding “f” to floating literals (e.g. 1.0f) because the default is double
-
Fast math functions
- Two types of runtime math library functions
- func(): slower but higher accuracy (5 ulp or less)
- __func(): fast but lower accuracy (SFU做,see prog. guide for full details)
- -use_fast_math: forces every func() to __func ()
- Two types of runtime math library functions
-
High-throughput function:
- DP4A and DP2A for int8 and int16 dot productions
- Warp matrix function for tensor core operations
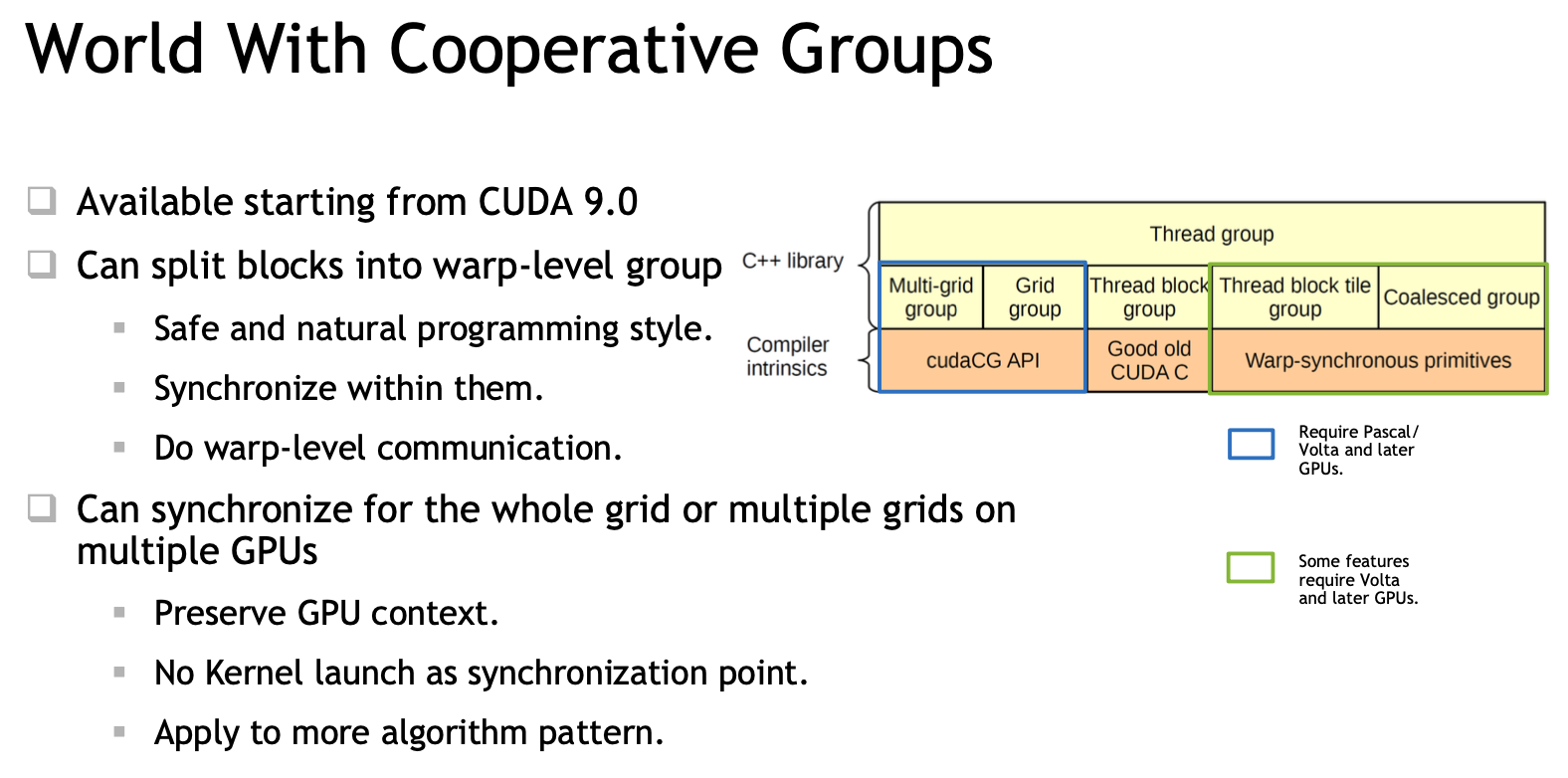
namespace cooperative_groups{
class thread_group{
public:
__device__ unsigned int size() const;
__device__ unsigned int thread_rank() const;
__device__ void sync() const;
};
thread_block myblock = this_thread_block();
// intra-block groups
thread_group tile32 = tiled_partition(myblock, 32);
thread_group tile4 = tiled_partition(tile32, 4);
thread_block_tile<8> tile8 = tiled_partition<8>(this_thread_block());
// Warp collectives
template <unsigned int Size>
class thread_block_tile : public thread_group{
public:
__device__ unsigned int size() const;
__device__ unsigned int thread_rank() const;
__device__ void sync() const;
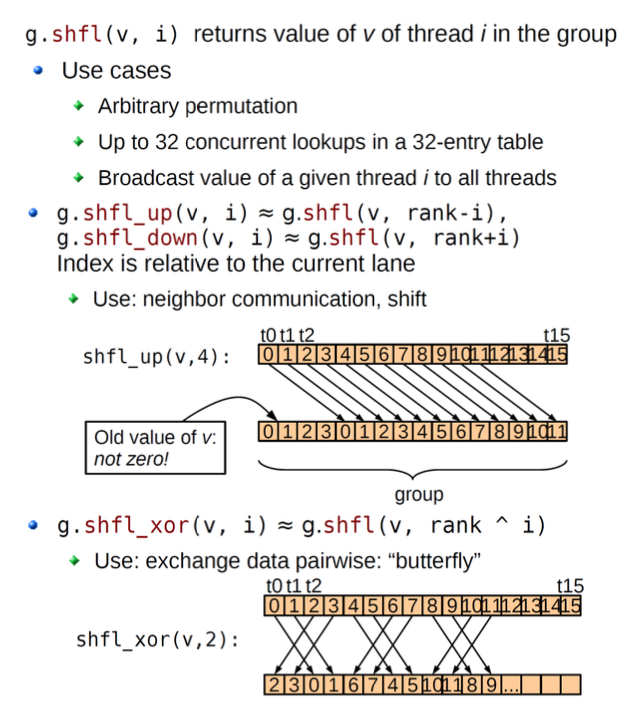
// Shuffle collectives
__device__ int shfl(int var, int srcRank) const;
__device__ int shfl_down(int var, unsigned int delta) const;
__device__ int shfl_up(int var, unsigned int delta) const;
__device__ int shfl_xor(int var, unsigned int laneMask);
// Vote collectives
__device__ int any(int predicate) const;
__device__ int all(int predicate) const;
__device__ unsigned int ballot(int predicate) const;
// Match collectives
__device__ unsigned int match_any(int val);
__device__ unsigned int match_all(int val, int &pred);
};
}目标:
-
使 GPU 计算与 GPU 上的内存传输重叠
-
在多个 GPU 上并发执行计算
nsys profile -t cuda,osrt,nvtx -o baseline -w true python main.pySupport:
-
OS Thread state and CPU utilization, pthread, file I/O, etc.
-
User annotations API (NVTX)
-
Compute
- CUDA API: Kernel launch and execution correlation
- Libraries and directive: cuBLAS, cuDNN, OpenACC
-
Graphics
- Vulkan, OpenGL, DX11, DX12, DXR, V-sync
-
nvtx记录kernel信息
- "//tensorflow/core/profiler:nvtx_utils"
- nvtxDomainRangeStartEx 和 nvtxDomainRangeEnd
- export TF_ENABLE_NVTX_RANGES=1、export TF_ENABLE_NVTX_RANGES_DETAILED=1
Key features
- section is a group of metrics
线上推理加速的思路
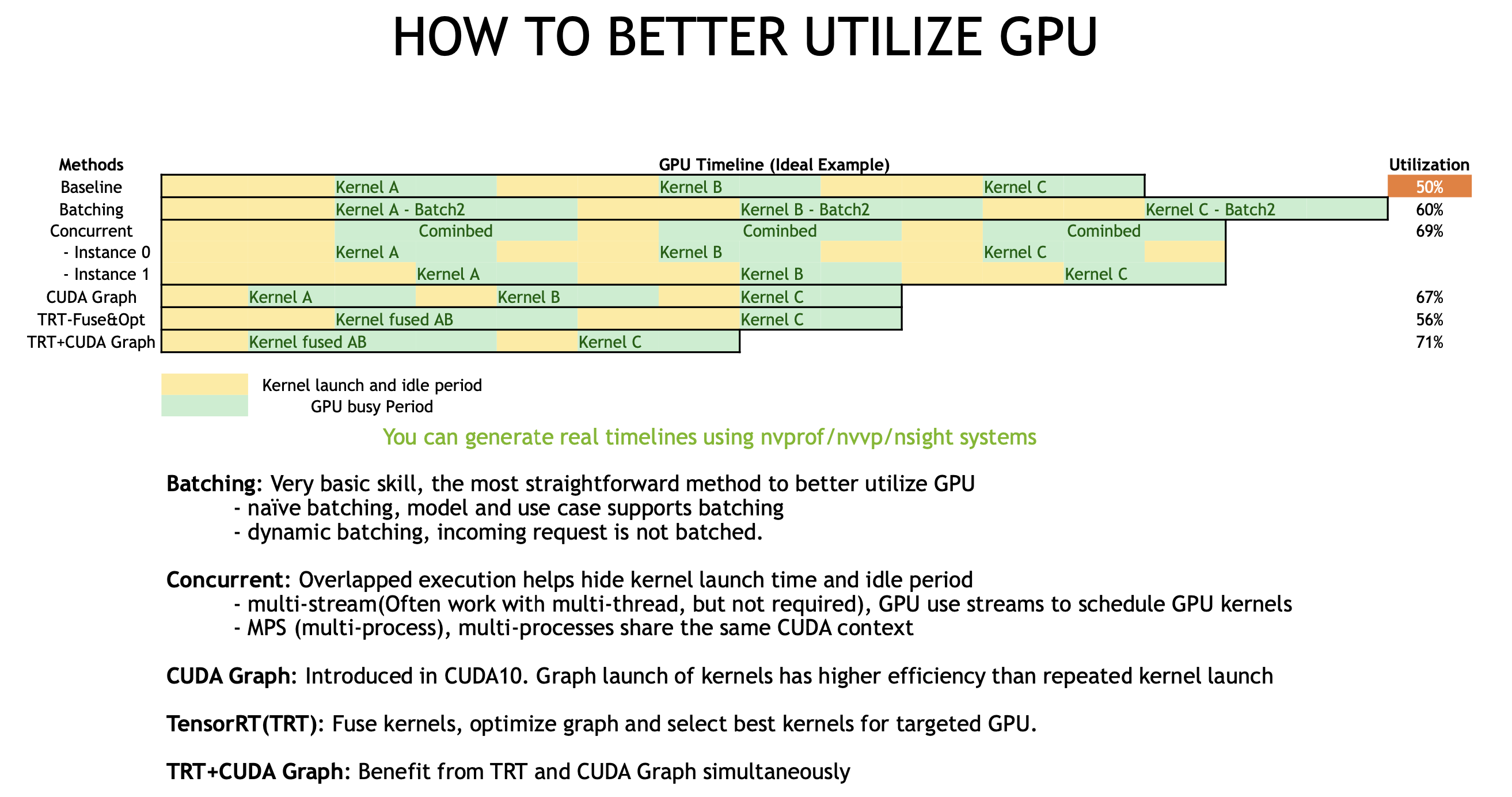
- 模型本身的加速,TensorRT、DL complier
-
Layer & Tensor Fusion: 横向/纵向的融合,减少copy显存; layer merge (concatforward)
-
Weights & Activation Precision Calibration
- Symmetric quantization: 超参threshold,超过会截断,提高转换精度
- 用KL-divergence来衡量threshold
-
Kernel Auto-Tuning: 找当前硬件下最优的卷积算法、kernels、tensor layouts
-
Dynamic Tensor Memory: 给层加引用计数
-
IBuilderConfig * config = builder->createBuilderConfig();
config->setFlag(BuilderFlag::kFP16); //INT8 and FP16 can be both set-
部署服务,CPU or GPU
-
Model Parser 解析TensorFlow/Caffe模型
-
TensorRT Network Definition API
- 自定义算子需要自己写
IBuilder* builder = createInferBuilder(gLogger.getTRTLogger());
INetworkDefinition* network = builder->createNetwork();
ITensor* data = network->addInput(INPUT_BLOB_NAME, dt, Dims3{1, INPUT_H, INPUT_W});
IScaleLayer* scale_1 = network->addScale(*data, ScaleMode::kUNIFORM, shift, scale, power);
IConvolutionLayer* conv2 = network->addConvolution(*scale_1->getOutput(0), 50, DimsHW{5, 5}, weightMap["conv2filter"], weightMap["conv2bias"]);
conv2->setStride(DimsHW{1, 1});
ISoftMaxLayer* prob = network->addSoftMax(*conv2->getOutput(0));
prob->getOutput(0)->setName(OUTPUT_BLOB_NAME); // set output
network->markOutput(*prob->getOutput(0)); // mark output
//序列化反序列化
IHostMemory* trtModelStream = engine->serialize(); //store model to disk
//<...>
IRuntime* runtime = createInferRuntime(gLogger.getTRTLogger());
ICudaEngine* engine = runtime->deserializeCudaEngine(trtModelStream->data(), trtModelStream->size(), nullptr);
IExecutionContext* context = engine->createExecutionContext();TF-TRT (TensorFlow integration with TensorRT) parses the frozen TF graph or saved model, and converts each supported subgraph to a TRT optimized node (TRTEngineOp), allowing TF to execute the remaining graph.
# Set Precision
conversion_params = trt.DEFAULT_TRT_CONVERSION_PARAMS._replace(
precision_mode=trt.TrtPrecisionMode.INT8)
# Convert to TF-TRT Graph
converter = trt.TrtGraphConverterV2(input_saved_model_dir=input_saved_model_dir, conversion_params=conversion_params)
# INT8 Calibration
converter.convert(calibration_input_fn=my_calibration_fn)
# Run Inference
converter.save(output_saved_model_dir)Triton Inference Server
- Client/server在本地:Inputs/outputs needed to be passed to/from Triton are stored in system/CUDA shared memory. Reduces HTTP/gRPC overhead
dynamic_batching {
preferred_batch_size:[4,8],
max_queue_delay_microseconds: 100,
}
Case Study: NVIDA BERT Solution: FasterTransformer2.0 and TensorRT
ASR Pipeline
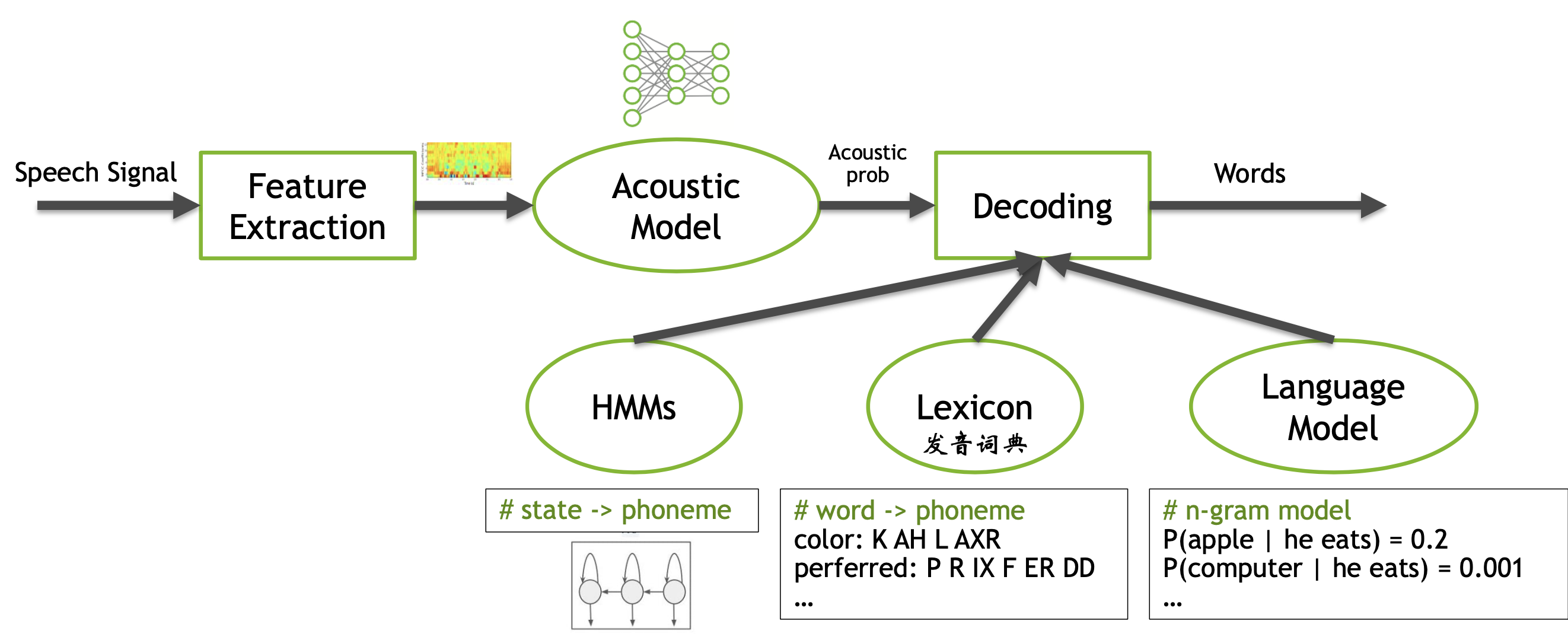
- 多级的转换:speech -> phoneme -> character -> word -> sentence
- 即使是深度学习兴起,工业界少有用e2e
- 多级带来海量choices,需要构建一个decoder解决识别任务(a search problem)
- ASR system overview
Q: How do we combine HMM, Lexicon & LM together?
A: WFST (Weighted Finite State Transducer)
WFST是一种图的表示方式,能通用地表示上述三种模型,然后这三张图可以合并。
-
HMM的输出是phoneme的输入,phoneme的输出是language model的输入
-
WFST Decoding: 图的最短路径问题,Token Pathing,Traverse the graph by copying token
Kaldi CUDA decoding pipeline
- WFST Decoding逻辑判断和对象copy较多,之前很长时间之后CPU实现
- GPU DECODE CHALLENGES
- Dynamic workload
- Amount of parallelism varies greatly throughout decode process
- Can have few or many candidates moving from frame to frame
- Limited parallelism
- Even with many candidates, the amount of parallelism is still far smaller to saturate a GPU
- Complex data structure
- Need a GPU-friendly data layout to obtain high performance on GPU
- Dynamic workload
- CUDA DECODER
- Operate FST on GPU
- CudaFst takes ~1/3 of its original size
- Accelerate decoding by parallelization
- Batch processing: batch不同语句的chunks,支持context switch
- Token Passing in parallel
- Process in streaming manner
- Operate FST on GPU
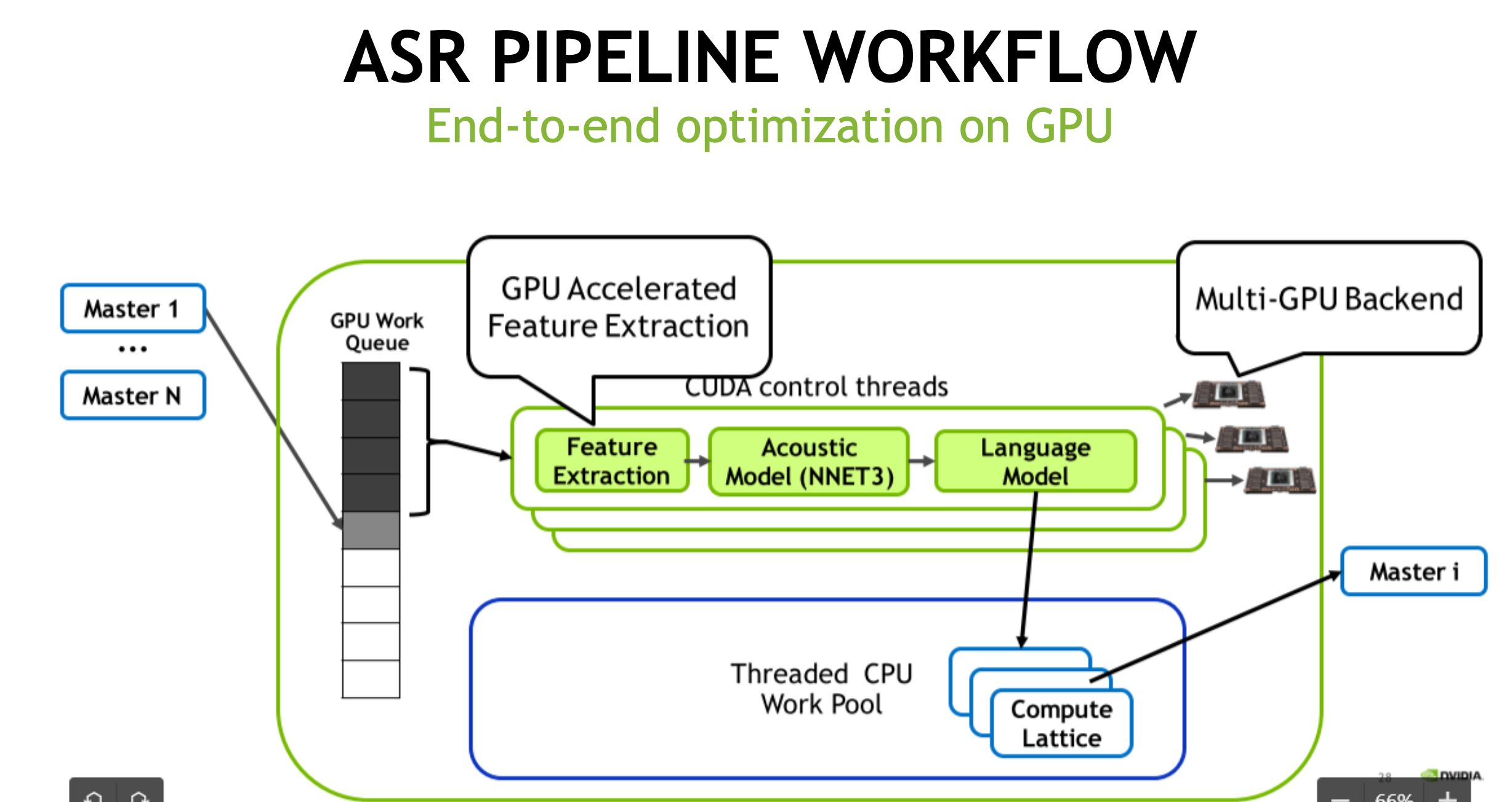
- ASR GPU PIPELINE: e2e acceleration, feature extraction + Acoustic Model + Language Model
- 结合Triton Inference Server
Reference:
- Blogs: https://developer.nvidia.com/blog/gpu-accelerated-speech-to-text-with-kaldi-a-tutorial-on-getting-started/
- Kaldi integration with Triton: https://github.com/NVIDIA/DeepLearningExamples/tree/master/Kaldi/SpeechRecognition
- Kaldi GPU decoder
- NGC: nvcr.io/nvidia/kaldi:20.08-py3
- Kaldi github: github.com/kaldi-asr/src/cudadecoder
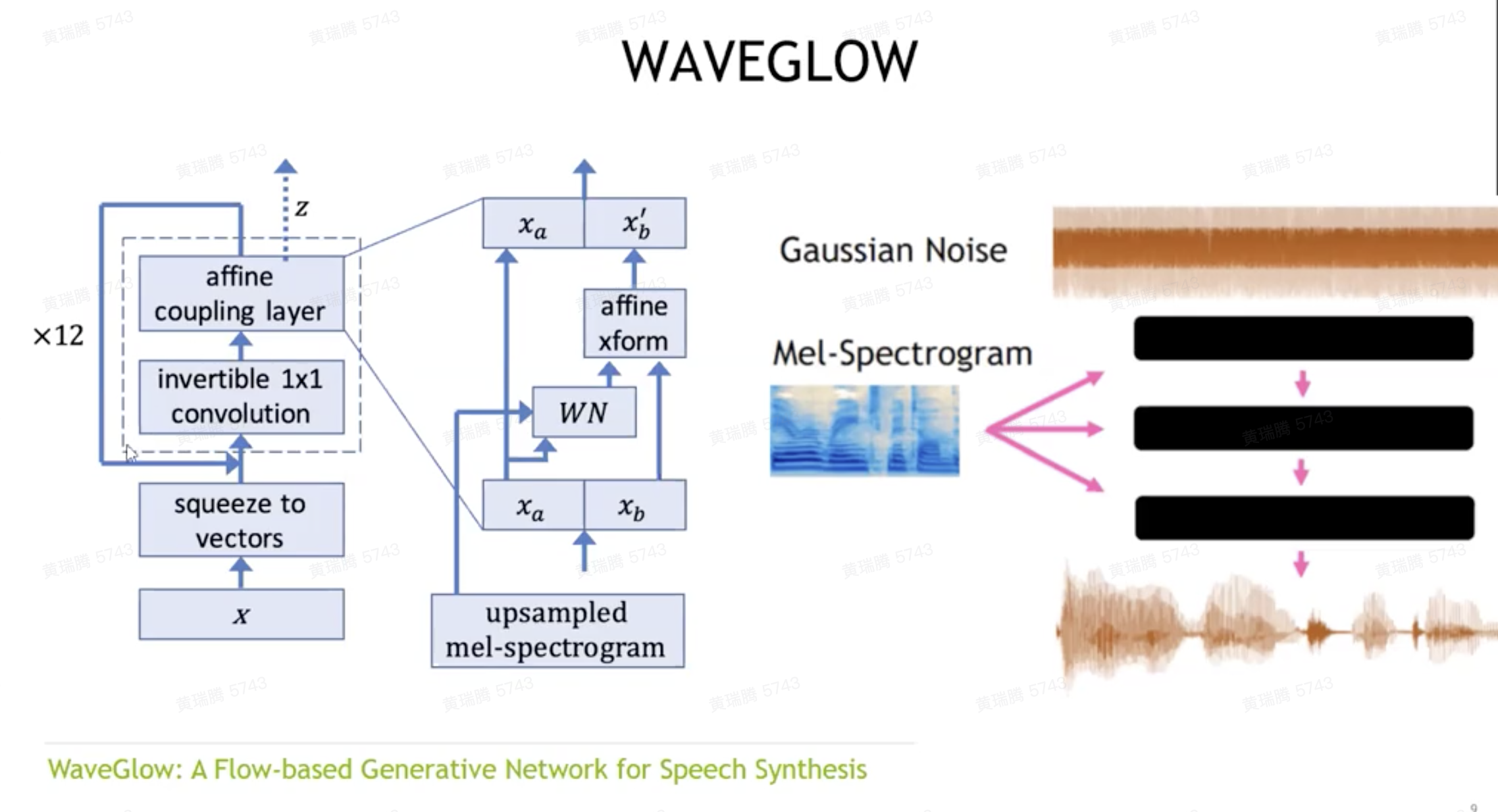
Modern TTS Solution
- Synthesizer: TACOTRON 2模型,合成发音特征
- Vocoder:声码器 WAVENET、WAVEGLOW
- 思路:利用可逆网络生成声音, affine coupling layer很关键
APEX ~ Mixed Precision Training
BERT
-
Challenge: polyphone disambiguation, prodisic structure prediction
-
BERT Optimization: 对self-attention layer做kernel fusion
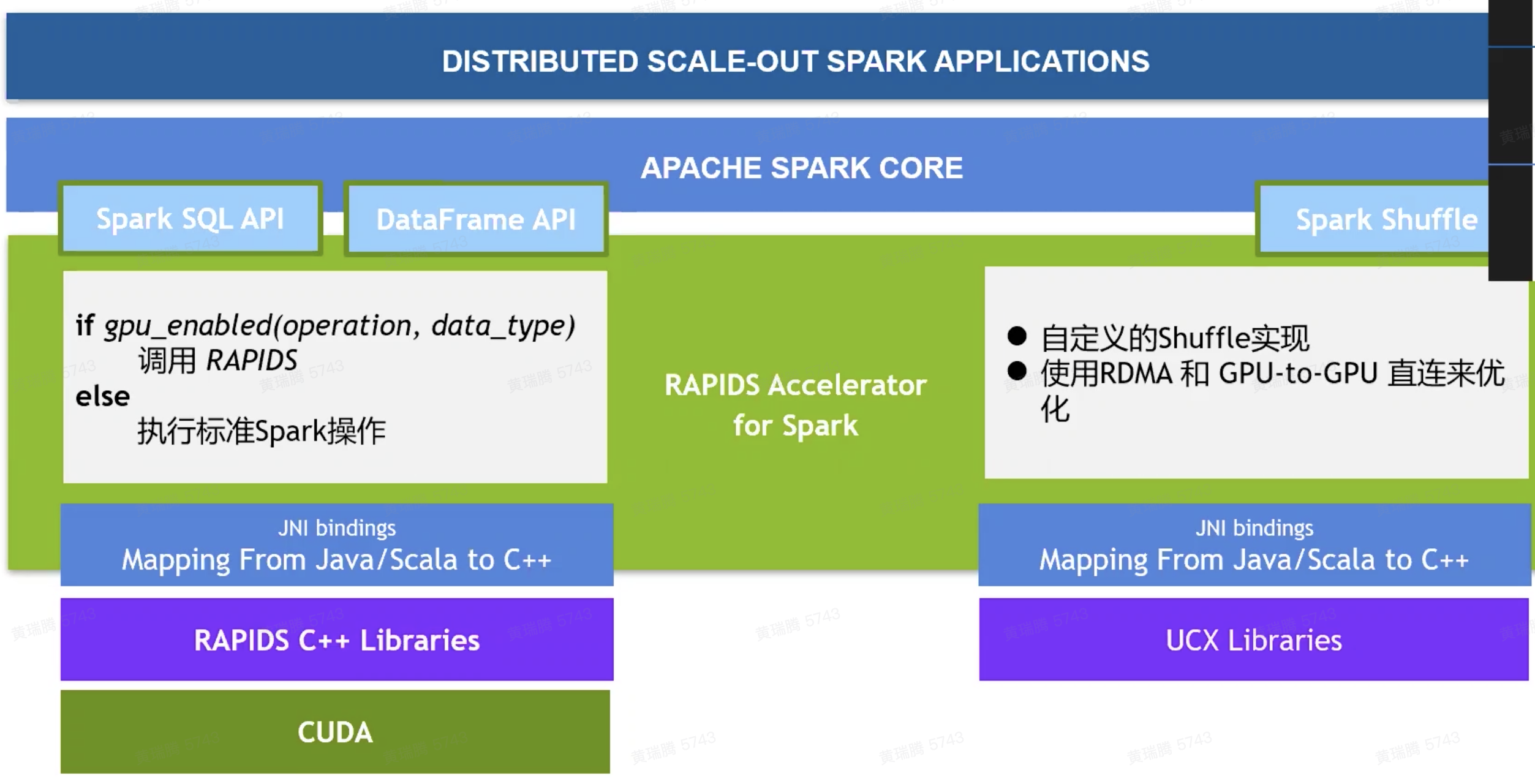
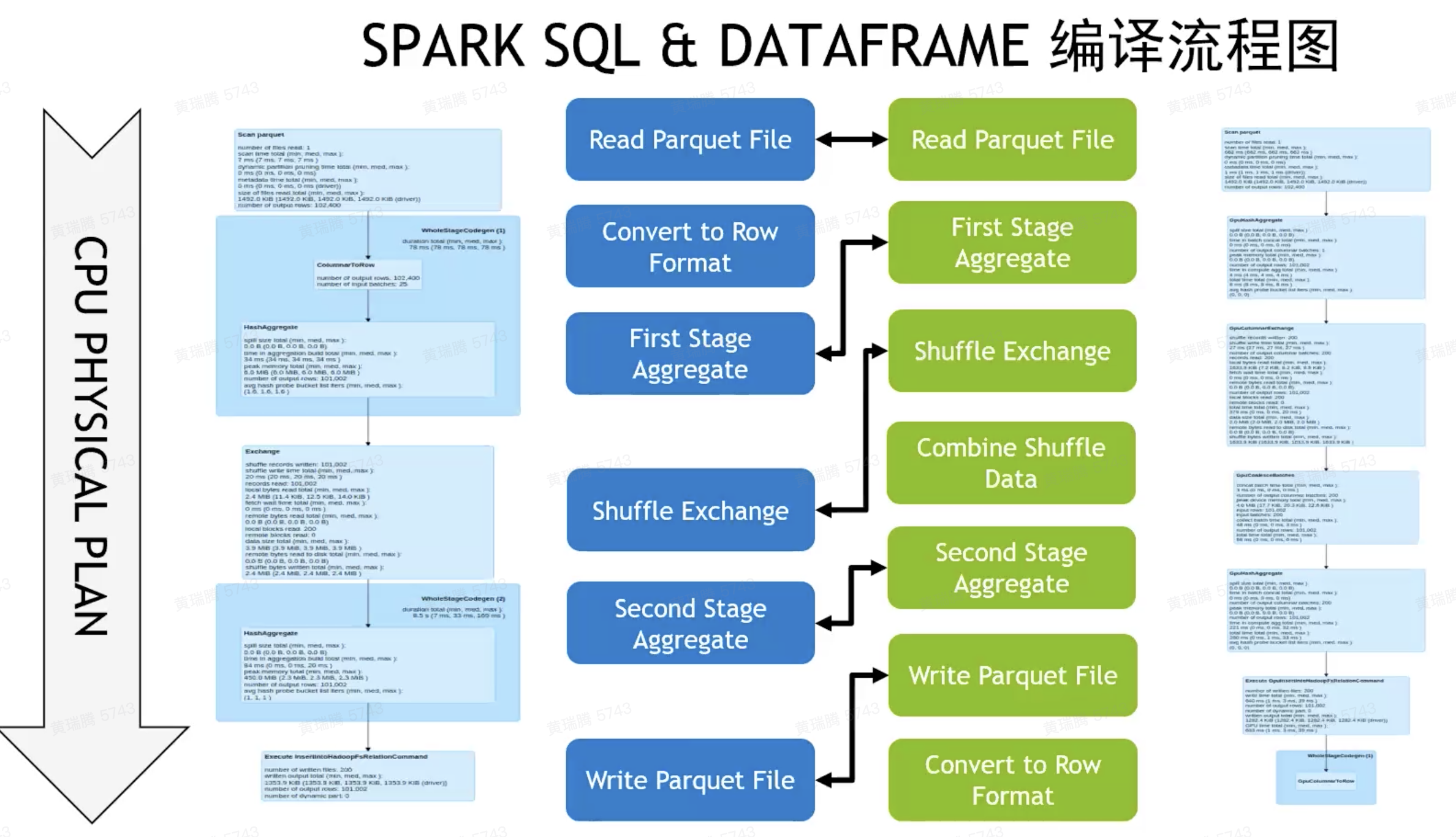
用于Apache Spark的RAPIDS加速器
- 不适合GPU大数据处理的场景
- 数据规模小:仅百兆
- 高缓存一致性的操作
- 数据移动:缓慢I/O,与CPU的不断交互(UDFs),Shuffle
- 有限的GPU内存
- SQL plugin擅长于
- 高散列度数据的joins、aggregates、sort
- Window operations、复杂计算、数据编码(创建Parquet和ORC文件,读取CSV)
Spark Shuffle: 前后stages间的数据交换
- CPU-Centric Data Movement: GPU0->CPU->GPU1;PCIe总线(GPU and CPU)、Network(远端CPU),CPU参与调度
- GPU-Centric Data Movement: NVLink(同节点GPU), RDMA(远端GPU), GPU Direct Storage(落盘)
- Shuffling Spilled Data: 溢出到cpu的host memory;如果无法满足,host memory内数据落盘或者通过RDMA传输到远端
- UCX Library: https://www.openucx.org/
Spark 0.2的亮点
- 支持原生Spark、Databricks 7.0ML、Dataproc 2.0
- 读取大量小的Parquet文件的优化:并行化处理文件Buffer,CPU与GPU无缝衔接
- 初步支持SCALA UDF
- 加速PANDAS UDFs
- 实现对Python进程的GPU资源管理,使JVM进程与Python进程共享一个GPU,以安全地在Pandas UDF里使用GPU
- 优化JVM与Python之间的数据交换,避免不必要的行列转换
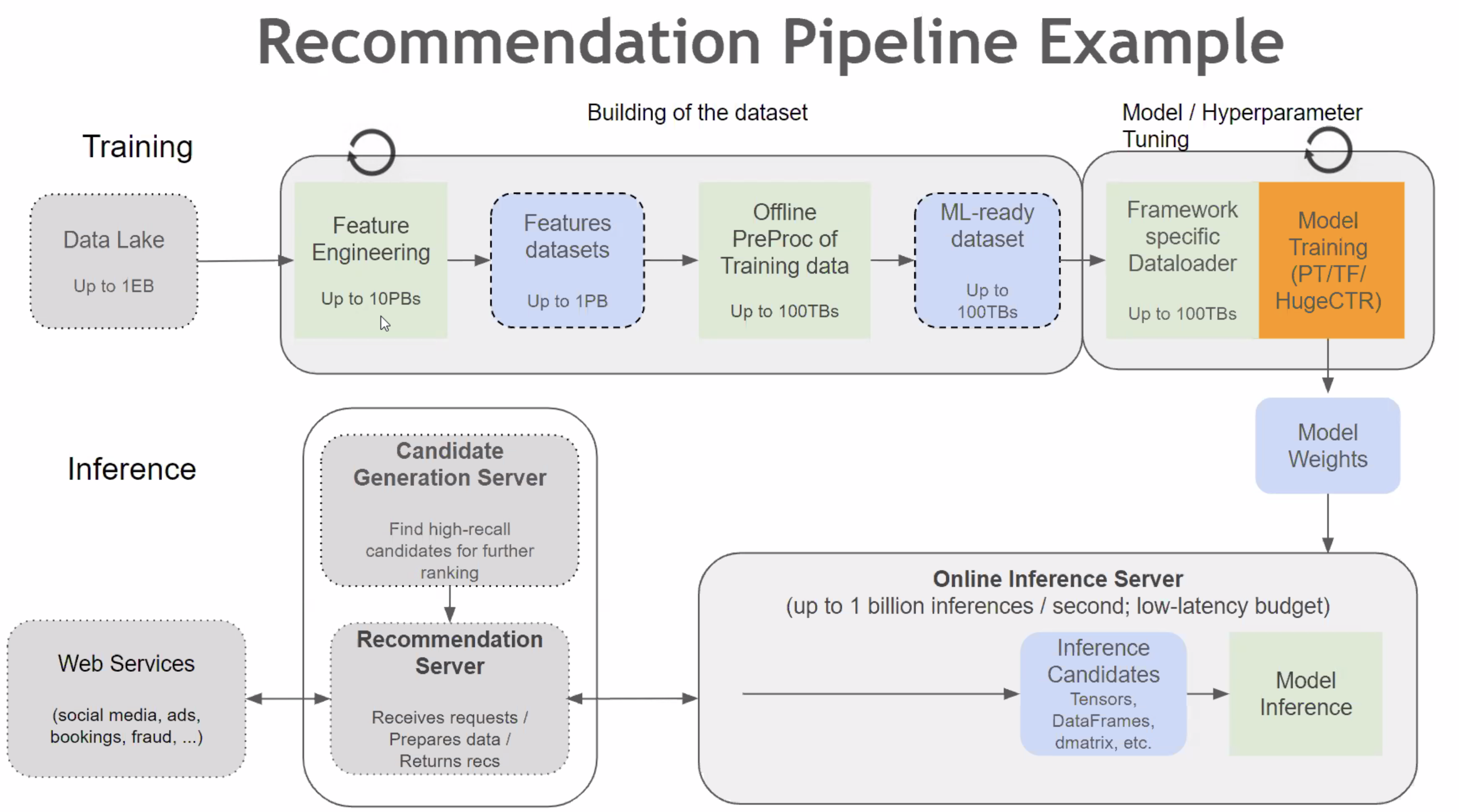
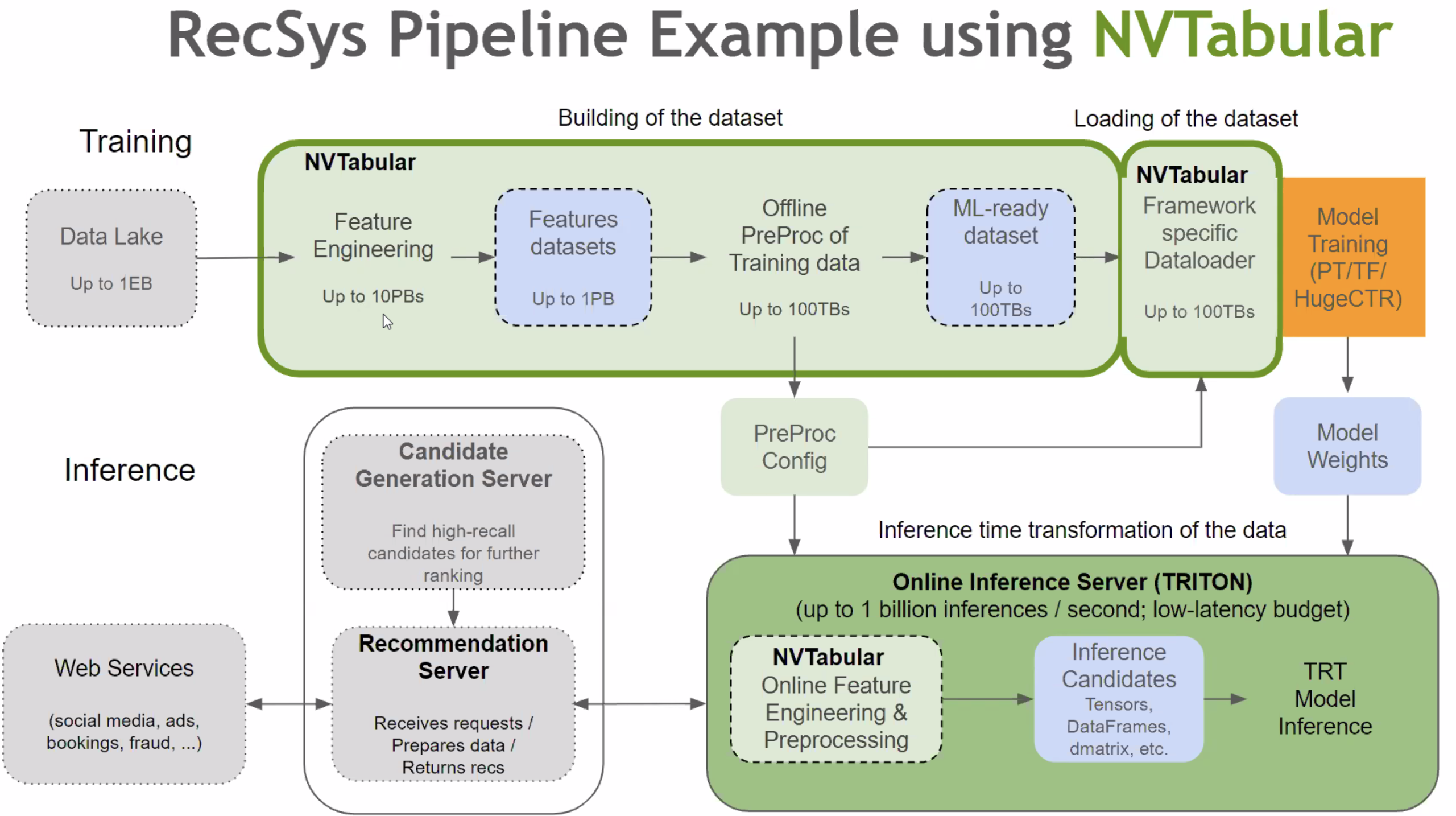
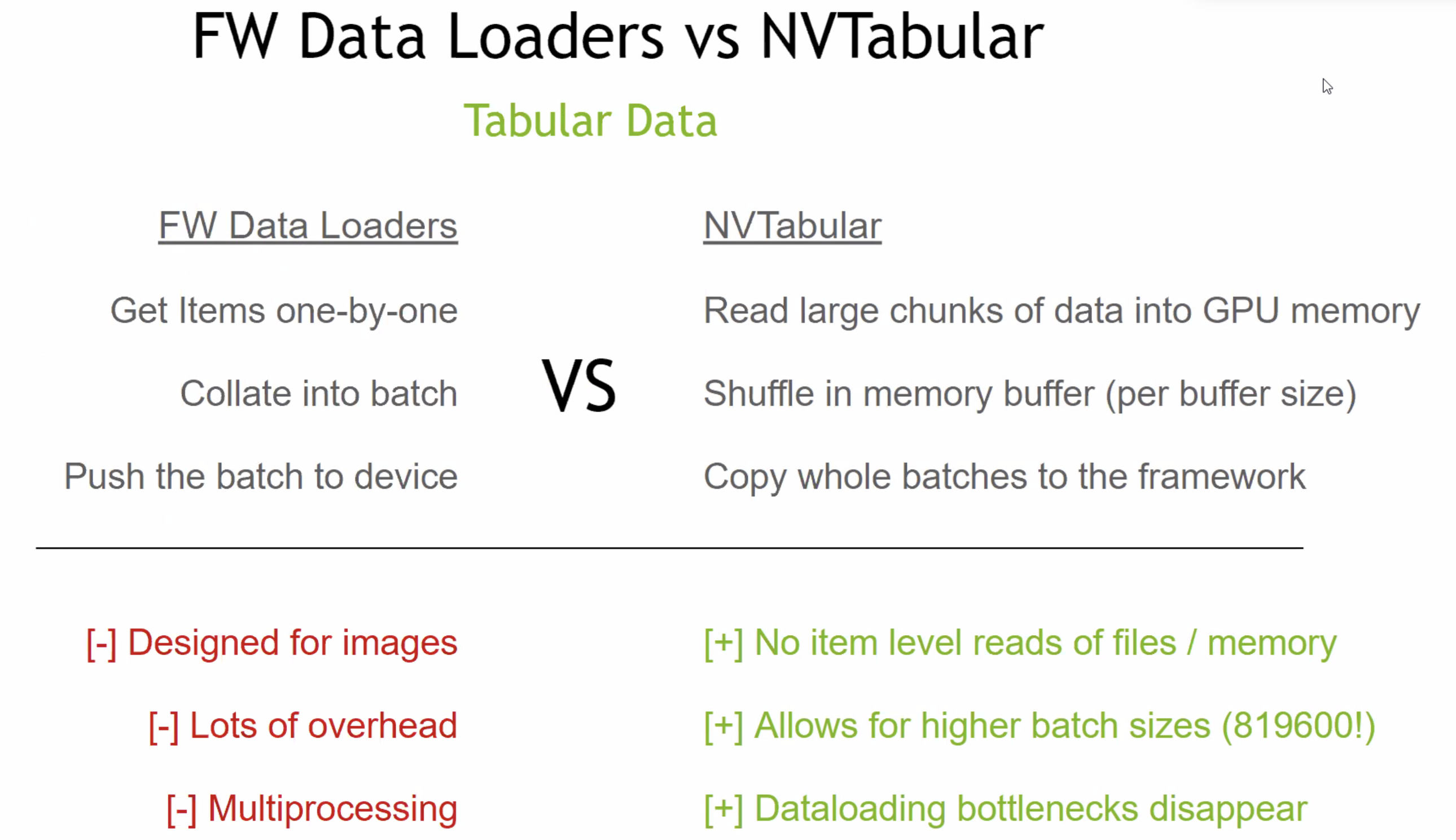
NVTabular,基于RAPIDS的Recommendation ETL,底层是RAPIDS
-
Embedding Table入显存:unified memory management,节点间交换不再layer by layer,可以一次交换所有PS
- 高效的GPU HashTable实现,解决冲突
-
Multi-nodes Model Parallel
-
Model Subscription: per req load PS to Embedding Cache in GPU
-
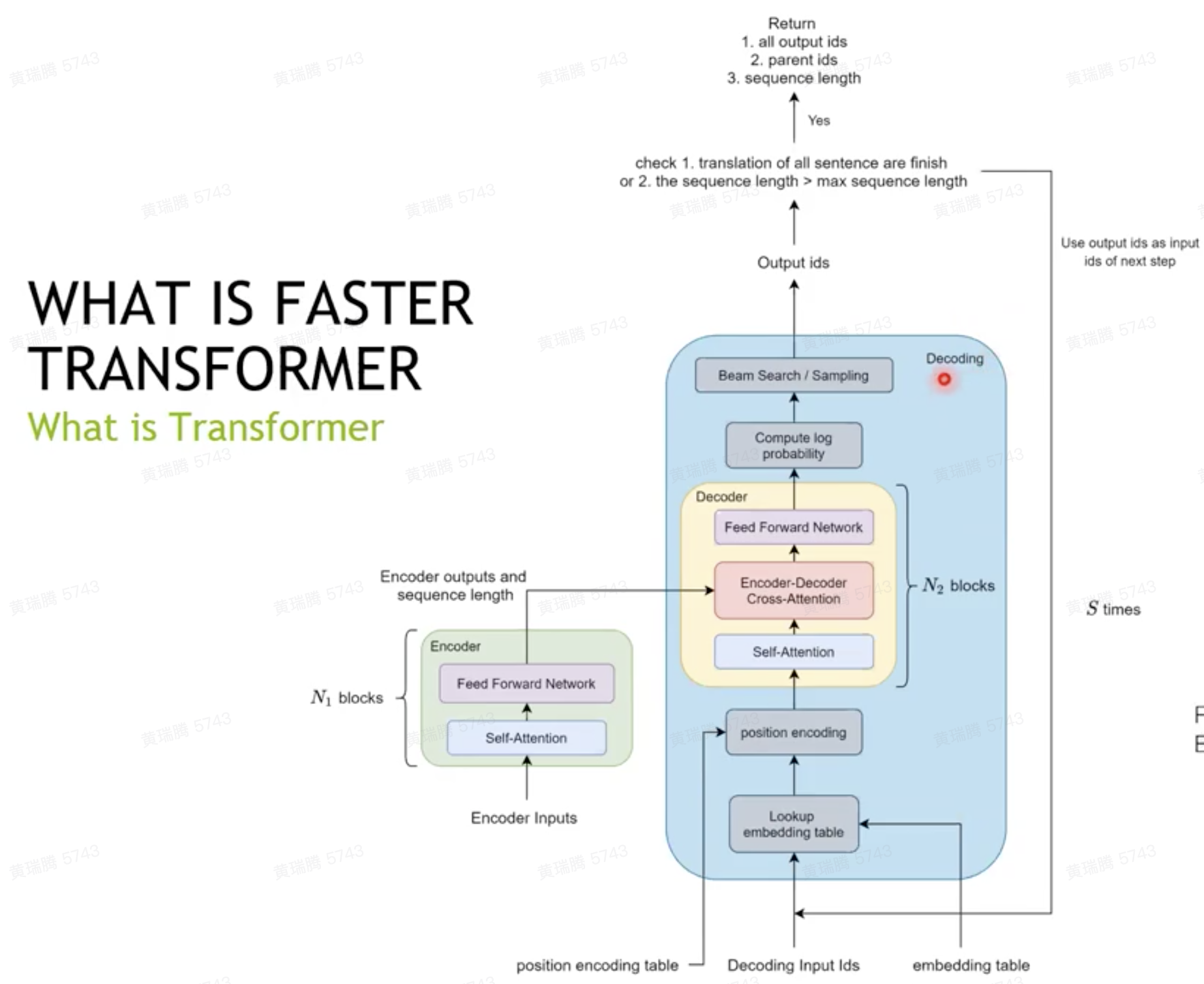
decoder和decoding两层抽象,适用于不同灵活性的场景
-
GPT-2 model
- Only one attention block
- No beam search
- Support sequence length <= 4096
-
encoder和decoder的讨论
- encoder一次输入的词多、运行次数少、对GPU更友好
- decoder和上述相反,但依据Amdahl's Law,在encoder和decoder共用的场景,decoder是瓶颈
- Faster Transformer的实现:encoder参考BERT、decoder和decoding参考OpenNMT-tf (Attention is all you need)、GPT-2
-
优化的讨论
- encoder:瓶颈是kernel launch bound,kernels are too small
- Fused Encoder: Fuse the kernels except GEMMs (General Matrix Multiplication) as much as possible,GEMM用tensorcore优化。更进一步可以利用cutlass工具fuse multi-head attention
- decoder:更多small kernels
- Fuse multi-head attention:原因是decoder的batch size是1,不必要对GEMM优化
- decoding :
- fuse the softmax and top k operations by online-softmax
- use CUB to accelerate the reduce operations
- beam search 之前要 FP16 转 FP32
- Beam width
- effective_transformer by ByteDance: 记录每个sentence的padding前缀和,矩阵计算前移除无用的padding,做attention时再映射回来,本质上是追求tensor的紧致组织。
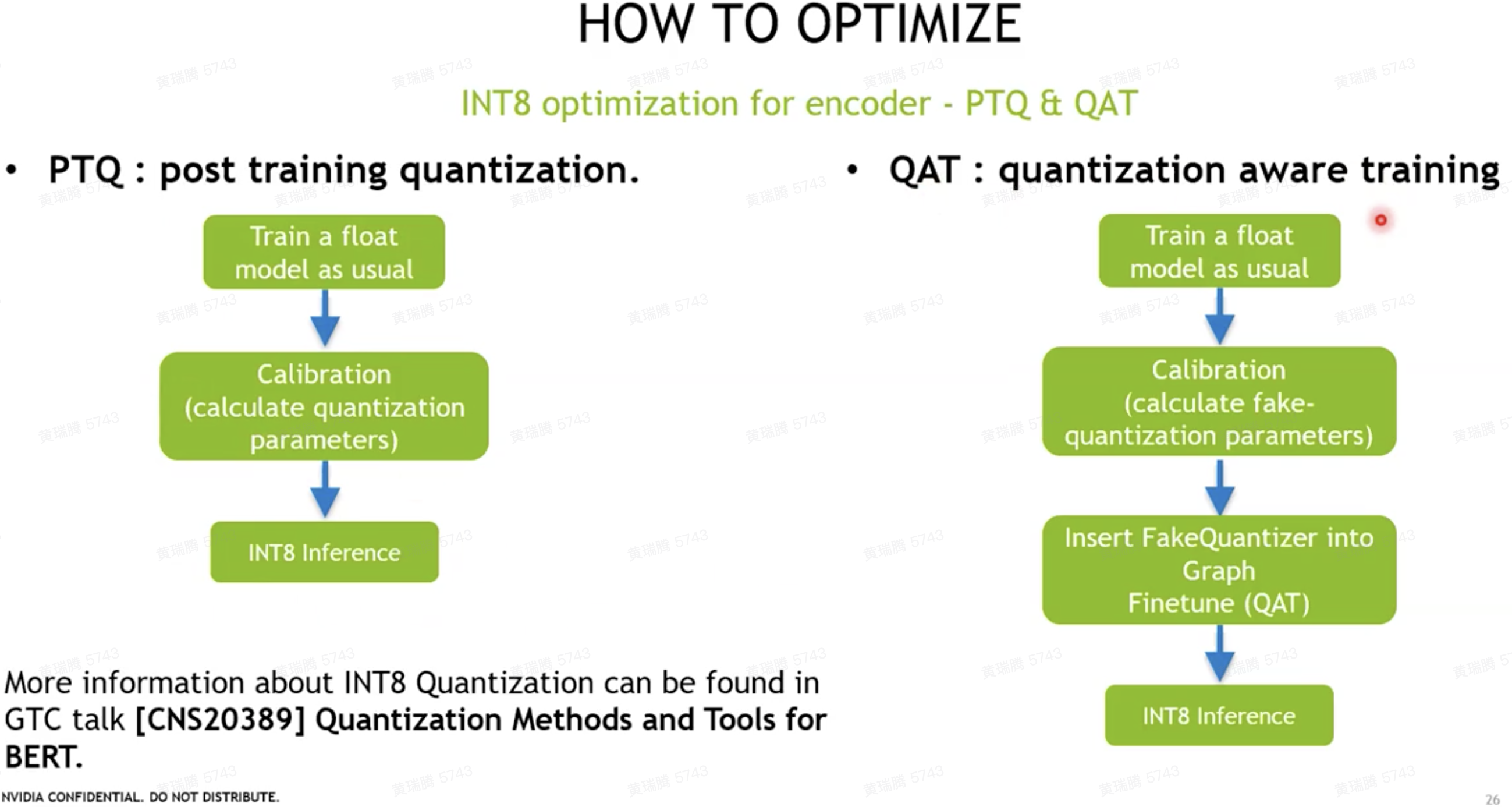
- INT8 optimization:QAT + without quantizing residuals => 精度损失少
- encoder:瓶颈是kernel launch bound,kernels are too small