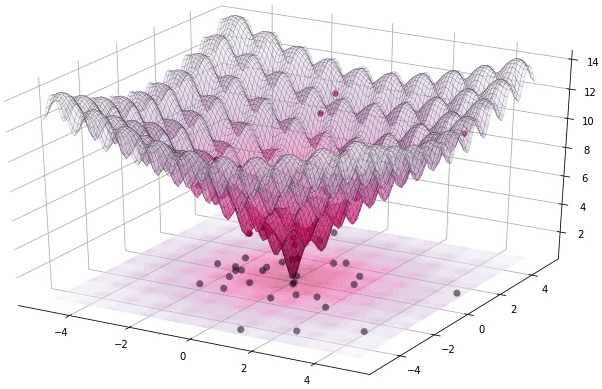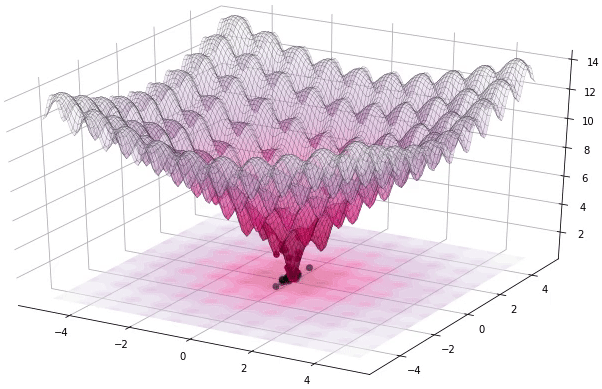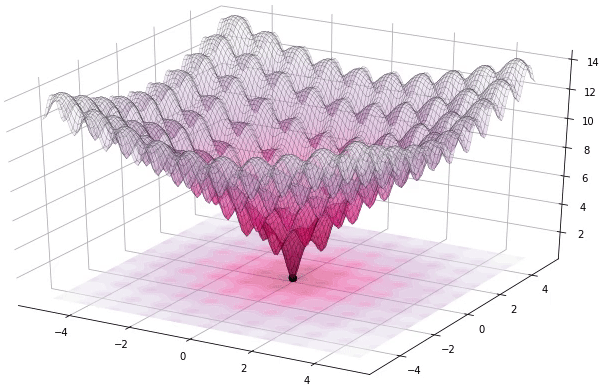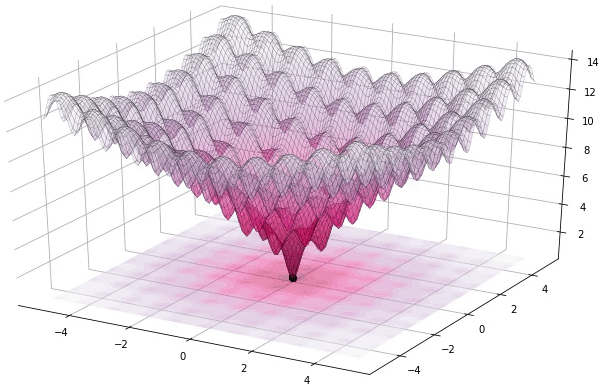
diff_evo is a simple Differential Evolution C++ library with no external dependencies.
To add diff_evo to your project, clone the repo, compile it and link against it in your CMakeLists.txt:
# clone the repo
git clone https://github.com/iibrahimli/diff_evo.git
# compile
cd diff_evo
mkdir build
cmake ..
makeThen, copy build/diff_evo/libdiff_evo.a into your libs directory and diff_evo/include/diff_evo.h into your include directory. An example CMakeLists.txt file using diff_evo might look like this:
project( myProject )
set( SOURCE_FILES main.cpp )
add_library( diff_evo STATIC IMPORTED )
set_property( TARGET diff_evo PROPERTY IMPORTED_LOCATION /path/to/your/libs/libdiff_evo.a )
include_directories( /path/to/your/include/ )
add_executable( myProject ${SOURCE_FILES} )
target_link_libraries( myProject diff_evo )The parameters of the diff_evo class constructor are the following:
| type | name | default | definition |
|---|---|---|---|
size_t |
num_params | Number of parameters of the function, i.e. dimensionality of the problem | |
dvec |
param_min | Minimum bounds for each parameter | |
dvec |
param_max | Maximum bounds for each parameter | |
size_t |
np | 0 | Population size (0: choose automatically) |
double |
cr | 0.8 | Crossover probability |
double |
f | 0.9 | Differential weight |
bool |
dither | true | Randomly choose f for each generation |
double |
dither_min | 0.5 | Minimum to use when dither is true |
double |
dither_max | 1.0 | Maximum to use when dither is true |
and for the member function optimize, you have to specify:
| type | name | default | definition |
|---|---|---|---|
std::function<double(dvec)> |
obj | Objective (fitness) function | |
de::opt_mode |
mode | de::MINIMIZE |
Optimization mode |
double |
delta | 1e-4 | Maximum difference in objective function to stop (tolerance) |
size_t |
max_iter | 100000 | Maximum number of iterations |
de::dvec is std::vector<double>, typedef'd for convenience.
#include <iostream>
#include "diff_evo.h"
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
// Beale function (R^2 -> R)
double beale(de::dvec x){
return pow((1.5 - x[0] + x[0]*x[1]), 2)
+ pow((2.25 - x[0] + x[0]*x[1]*x[1]), 2)
+ pow((2.625 - x[0] + x[0]*x[1]*x[1]*x[1]), 2);
}
int main(){
auto evo = de::diff_evo(
2,
{-4.5, -4.5},
{4.5, 4.5}
);
auto sol = evo.optimize(
beale,
de::MINIMIZE,
1e-14
);
cout << "optimal solution:" << endl;
for(int i=0; i<sol.size(); ++i){
cout << sol[i] << endl;
}
cout << "obj: " << obj(sol) << endl;
return 0;
}which prints
optimal solution:
3
0.5
obj: 1.8674e-15