There are n cities connected by some number of flights. You are given an array flights where flights[i] = [fromi, toi, pricei] indicates that there is a flight from city fromi to city toi with cost pricei.
You are also given three integers src, dst, and k, return the cheapest price from src to dst with at most k stops. If there is no such route, return **-1.
Example 1:
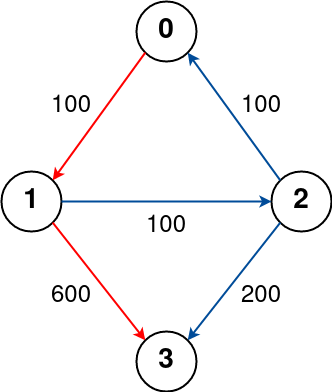
Input: n = 4, flights = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[2,0,100],[1,3,600],[2,3,200]], src = 0, dst = 3, k = 1
Output: 700
Explanation:
The graph is shown above.
The optimal path with at most 1 stop from city 0 to 3 is marked in red and has cost 100 + 600 = 700.
Note that the path through cities [0,1,2,3] is cheaper but is invalid because it uses 2 stops.
Example 2:
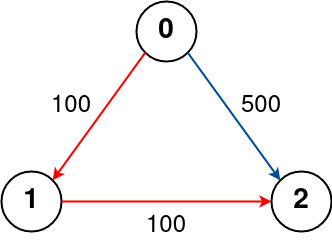
Input: n = 3, flights = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[0,2,500]], src = 0, dst = 2, k = 1
Output: 200
Explanation:
The graph is shown above.
The optimal path with at most 1 stop from city 0 to 2 is marked in red and has cost 100 + 100 = 200.
Example 3:
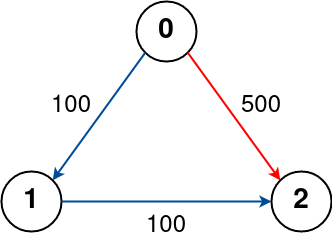
Input: n = 3, flights = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[0,2,500]], src = 0, dst = 2, k = 0
Output: 500
Explanation:
The graph is shown above.
The optimal path with no stops from city 0 to 2 is marked in red and has cost 500.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 1000 <= flights.length <= (n * (n - 1) / 2)flights[i].length == 30 <= fromi, toi < nfromi != toi1 <= pricei <= 104- There will not be any multiple flights between two cities.
0 <= src, dst, k < nsrc != dst
題目給定一個整數 n 代表有 0 到 n-1 的飛機站
給定一個 flights 矩陣 , 矩陣中每個 entry , flight[i] = [$source_i, target_i, price_i$]
代表從
給定一個整數 src 代表出發站
給定一個整數 dst 代表到達站
給定一個整數 k 代表最多只經過 k 個中繼站
要求在以上條件下實作一個演算法找出最便宜的從 src 到 dst 的票價
這題如果要使用 Dijkstra Algorithm
會需要注意有最多 k 中繼站的限制
也就是可能要跑 1 到 k 次 Dijkstra Algorithm 來處理
而這題剛好適合用 Bellman ford Algorithm
可以用每次從 src 出發透過可行的邊去更新 在level L 的限制之下的 prices
這樣只要更新 k+1 次(除了 source 之外有k+1個點)最後 prices[dst] 就是結果
這樣時間複雜度會是 O(E*k)
其中 E 代表邊的個數, k 是 level
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Solution {
public int findCheapestPrice(int n, int[][] flights, int src, int dst, int k) {
int[] prices = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(prices, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
prices[src] = 0;
for (int level = 1; level <= k+1; level++) {
int[] levelPrices = Arrays.copyOf(prices, n);
for (int[] flight: flights) {
int source = flight[0];
int target = flight[1];
int price = flight[2];
if (prices[source] == Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
continue;
}
if (levelPrices[target] > prices[source] + price) {
levelPrices[target] = prices[source] + price;
}
}
// copy current prices to prices
prices = Arrays.copyOf(levelPrices, n);
}
if (prices[dst] == Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
return -1;
}
return prices[dst];
}
}- 比一般的 shortest path 多了一個 最多 k 個中繼站的限制
- 理解如何逐步更新每個 level 的 prices
- 需要理解Bellman ford Algorithm
- 建立一個 prices 陣列來儲存當下 level 的 prices 更新結果
- 每次更新都需要用上一個 level 的更新結果來當做基準