This is a connected open-source repository for the publication "Communities in C.elegans connectome through the prism of non-backtracking walks" published in Scientific Reports (2023) DOI
Authors: Arsenii Onuchin, Alina Chernizova, Mikhail Lebedev, Kirill Polovnikov
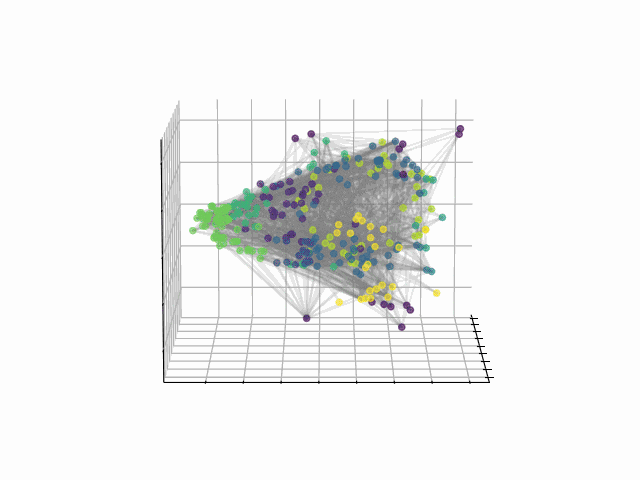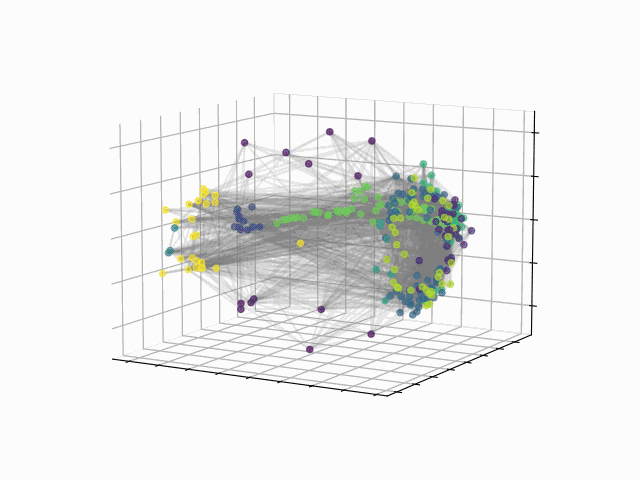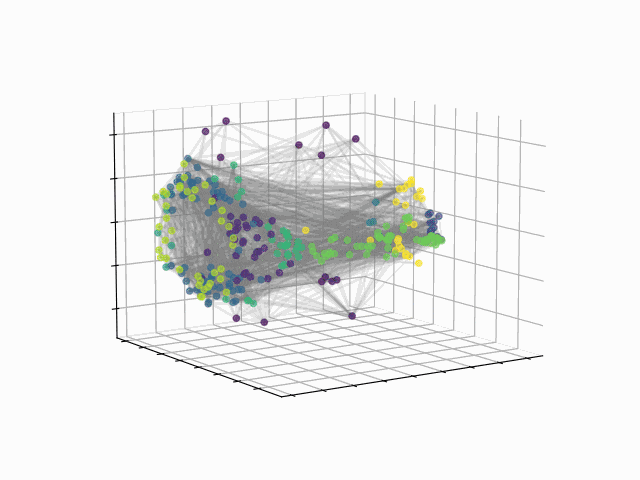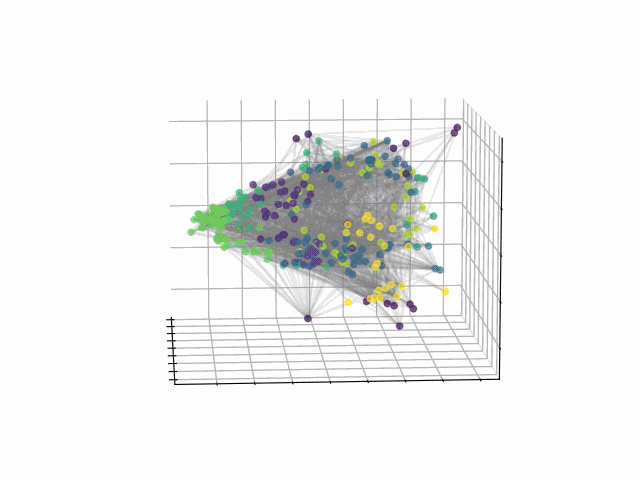
Abstract: The fundamental relationship between the mesoscopic structure of neuronal circuits and organismic functions they subserve is one of the major challenges in contemporary neuroscience. Formation of structurally connected modules of neurons enacts the conversion from single-cell firing to largescale behaviour of an organism, highlighting the importance of their accurate profiling in the data. While connectomes are typically characterized by significant sparsity of neuronal connections, recent advances in network theory and machine learning have revealed fundamental limitations of traditionally used community detection approaches in cases where the network is sparse. Here we studied the optimal community structure in the structural connectome of Caenorhabditis elegans, for which we exploited a non-conventional approach that is based on non-backtracking random walks, virtually eliminating the sparsity issue. In full agreement with the previous asymptotic results, we demonstrated that non-backtracking walks resolve the ground truth annotation into clusters on stochastic block models (SBM) with the size and density of the connectome better than the spectral methods related to simple random walks. Based on the cluster detectability threshold, we determined that the optimal number of modules in a recently mapped connectome of C. elegans is 10, which precisely corresponds to the number of isolated eigenvalues in the spectrum of the non-backtracking flow matrix. The discovered communities have a clear interpretation in terms of their functional role, which allows one to discern three structural compartments in the worm: the Worm Brain (WB), the Worm Movement Controller (WMC), and the Worm Information Flow Connector (WIFC). Broadly, our work provides a robust network-based framework to reveal mesoscopic structures in sparse connectomic datasets, paving way to further investigation of connectome mechanisms for different functions.
Contact: Kirill Polovnikov kipolovnikov@gmail.com
data folder desciption:
- 3D_coordinates_celegans.csv is a 3D coordinates reconstruction from the article "Toward a more accurate 3D atlas of C. elegans neurons" (2022)
- C.elegans_connectome_updated.graphml is an old connectivity data from the "Wiring optimization can relate neuronal structure and function" (2006)
- NeuronType.xls is a list of neuron types from www.wormwiring.org
- SI 5 Connectome adjacency matrices.xlsx is a connectome data from the "Whole-animal connectomes of both Caenorhabditis elegans sexes" (2019)
- Virtual_Worm_February_2012_with_cluster_colors.blend is a blender 3D model of the C.elegans connectome from the http://canopus.caltech.edu/virtualworm/
- clusters_and_stratas.xlsx is a resulting Flow Matrix clusters and contactome strata tables from "A multi-scale brain map derived from whole-brain volumetric reconstructions" (2021) and "Structural and developmental principles of neuropil assembly in C. elegans" (2021)