With the increasing number of machine learning ap- plications, the security of machine learning models has attracted much attention. In the inferring phase, machine learning models are vulnerable to adversarial examples, i.e. legitimate examples with some imperceptible perturbation, and therefore prone to make wrong judgments. As an important stage in machine learning pipeline, feature selection techniques are mainly used to improve the generalization performance and training efficiency of machine learning model, but few works have focused on the robustness of machine learning models from the perspective of feature selection when dealing with adversarial attacks. In this paper, we propose the adversarial training (AT) based feature selection framework, i.e. AT based feature selection, to improve the robustness of machine learning model built on the feature selection result, which is inspired by using adversarial training to improve the robustness of deep learning model. AT based feature selection framework is the combination of adversarial training with some traditional feature selection algorithm, which can be divided into AT in-processing and AT post-processing feature selection. On the other hand, stability is also a very important property for feature selection. Then we experimentally analyze the relationship between robustness and stability of AT based feature selection, especially theoretically analyze the stability of l2 regularized AT in-processing feature selection algorithm in two different adversarial training forms. Our experimental results on benchmark data sets show that AT based feature selection algorithm is effective to improve the robustness of machine learning model, however, obtain lower stability than corresponding feature selection model without AT.
In this paper, the AT based feature selection framework is proposed. We discuss robustness and stability of feature selection algorithms under this framework. The main contributions of this paper are as follows,
- The robust feature selection framework based on AT is proposed to defense against adversarial attack;
- We theoretically analyze the stability bound of some AT based feature selections;
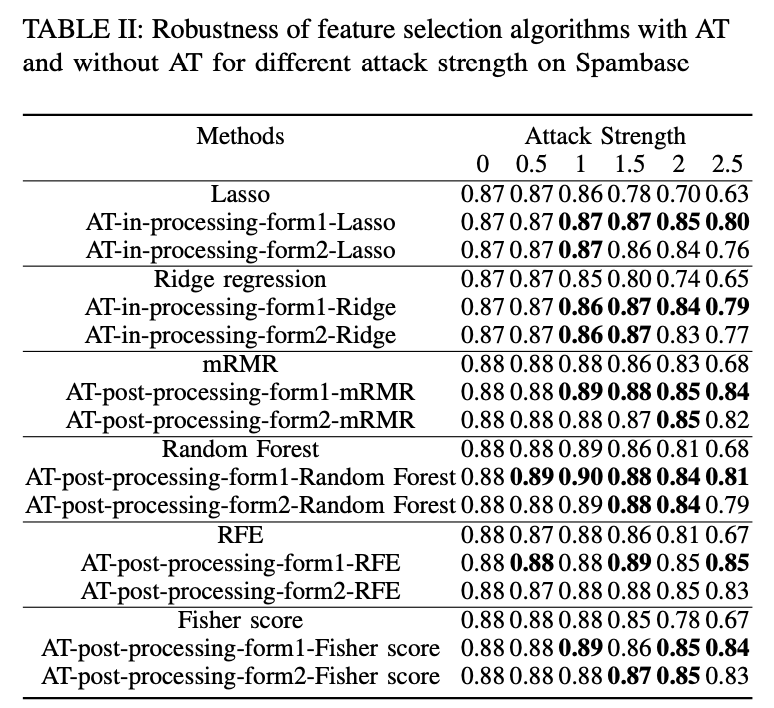
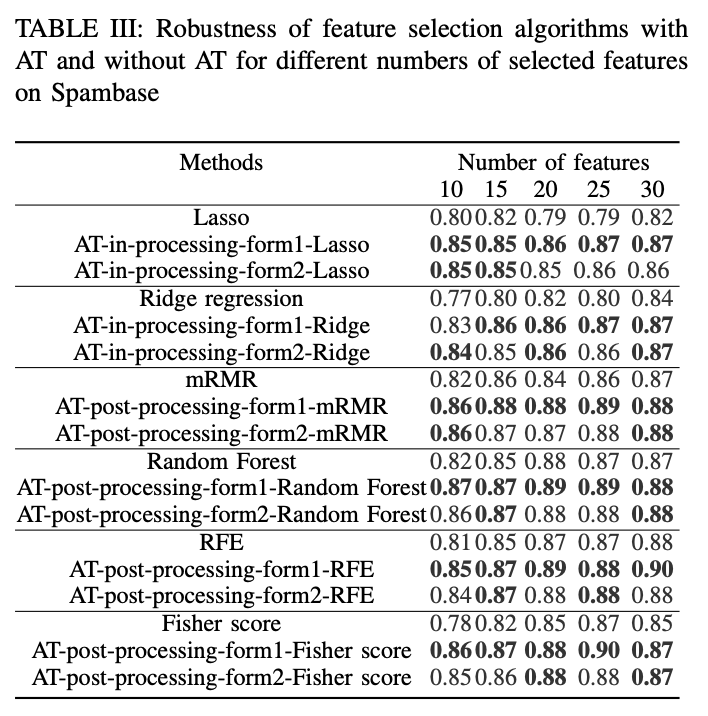
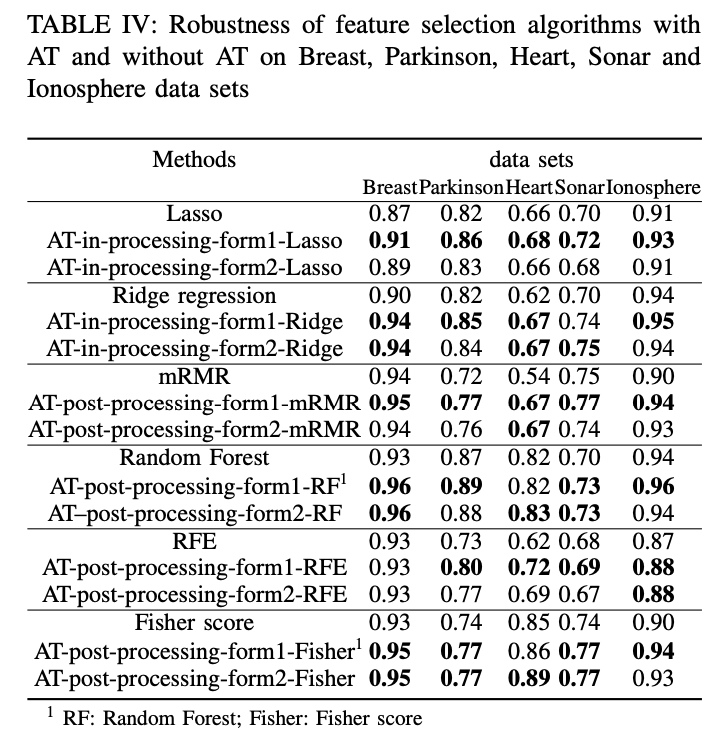
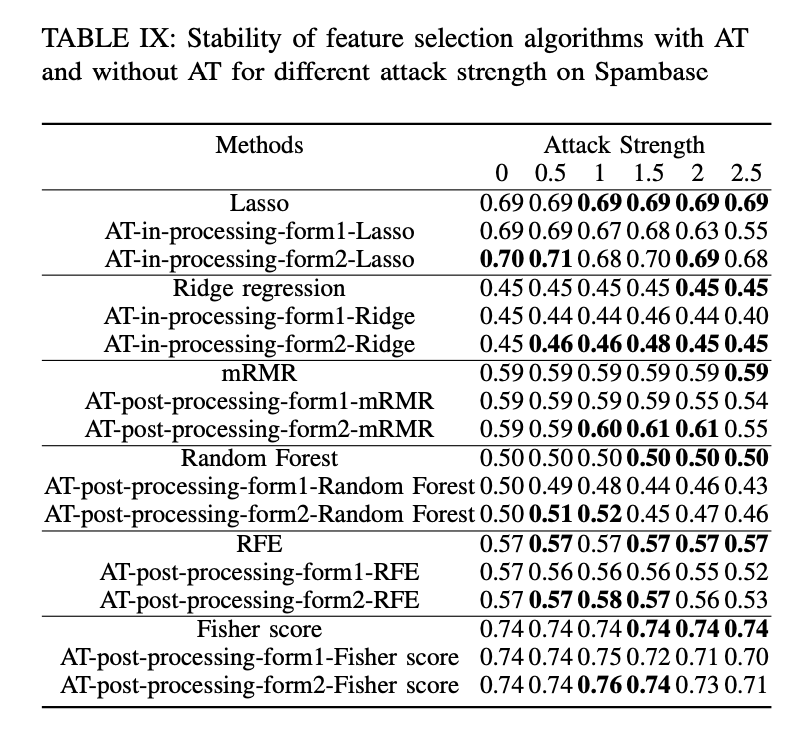
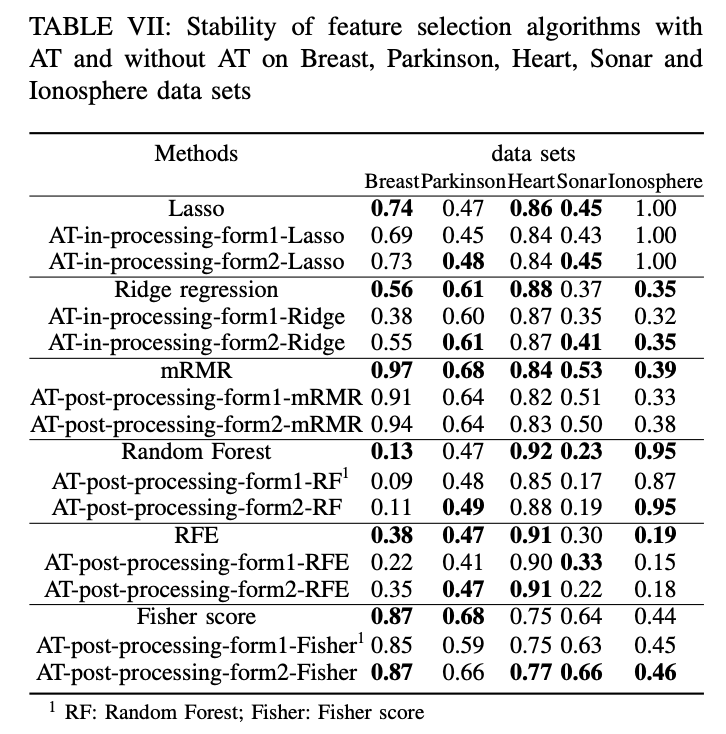
- The empirical results on benchmark data sets show the stability is at odds with robustness for AT based feature selection algorithms.
Participants:: LI-DATA Lab; Professor Yun Li, Ph.D, KeJi Han, Ph.D , WenQiong Zhang, Ph.D;
Referencing to the following projects:
- https://gitlab.com/secml/secml
- https://github.com/jundongl/scikit-feature
- https://github.com/smazzanti/mrmr
-
B. Biggio, Z. Akhtar, G. Fumera, G. L. Marcialis, and F. Roli, “Security evaluation of biometric authentication systems under real spoofing attacks,” IET biometrics, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 11–24, 2012.
-
D. Lowd and C. Meek, “Good word attacks on statistical spam filters.” in CEAS, vol. 2005, 2005.
-
J. Tang, S. Alelyani, and H. Liu, “Feature selection for classification: A review,” Data classification: Algorithms and applications, p. 37, 2014.
-
H.Xiao,B.Biggio,G.Brown,G.Fumera,C.Eckert,andF.Roli,“Isfeature selection secure against training data poisoning?” in InternationalConference on Machine Learning*. PMLR, 2015, pp. 1689–1698.
-
B. Li and Y. Vorobeychik, “Feature cross-substitution in adversarial classification,” Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems,vol. 27, 2014.
-
F. Zhang, P. P. Chan, B. Biggio, D. S. Yeung, and F. Roli, “Adver- sarial feature selection against evasion attacks,” IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, vol. 46, no. 3, pp. 766–777, 2015.
-
F.Wang,W.Liu,andS.Chawla,“Onsparsefeatureattacksinadversarial learning,” in 2014 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining. IEEE, 2014, pp. 1013–1018.
-
K. K. Budhraja and T. Oates, “Adversarial feature selection,” in 2015 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining Workshop (ICDMW). IEEE, 2015, pp. 288–294.
-
F. Trame`r, A. Kurakin, N. Papernot, I. Goodfellow, D. Boneh, and P. McDaniel, “Ensemble adversarial training: Attacks and defenses,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1705.07204, 2017.
-
G. Ditzler and A. Prater, “Fine tuning lasso in an adversarial environment against gradient attacks,” in 2017 IEEE Symposium Series on Compu- tational Intelligence (SSCI). IEEE, 2017, pp. 1–7.
-
V. Hamer and P. Dupont, “An importance weighted feature selection stability measure,” Journal of Machine Learning Research, vol. 22, no. 116, pp. 1–57, 2021.
-
Y. Saeys, T. Abeel, and Y. V. d. Peer, “Robust feature selection using ensemble feature selection techniques,” in Joint European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases. Springer, 2008, pp. 313–325.
-
A. Kalousis, J. Prados, and M. Hilario, “Stability of feature selection algorithms: a study on high-dimensional spaces,” Knowledge and Infor- mation Systems, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 95–116, 2007.
-
L. I. Kuncheva, “A stability index for feature selection.” in Artificial Intelligence and Applications, 2007, pp. 421–427.
-
P. Kˇr ́ızˇek, J. Kittler, and V. Hlava ́cˇ, “Improving stability of feature selection methods,” in International Conference on Computer Analysis of Images and Patterns. Springer, 2007, pp. 929–936.
-
Y. Li, J. Si, G. Zhou, S. Huang, and S. Chen, “Frel: A stable feature se- lection algorithm,” IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, vol. 26, no. 7, pp. 1388–1402, 2014.
-
T. Abeel, T. Helleputte, Y. Van de Peer, P. Dupont, and Y. Saeys, “Robust biomarker identification for cancer diagnosis with ensemble feature selection methods,” Bioinformatics, vol. 26, no. 3, pp. 392–398, 2010.
-
Y. Li, S. Gao, and S. Chen, “Ensemble feature weighting based on local learning and diversity,” in Twenty-Sixth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2012.
-
A. Woznica, P. Nguyen, and A. Kalousis, “Model mining for robust feature selection,” in Proceedings of the 18th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, 2012, pp.913–921.
-
Y. Han and L. Yu, “A variance reduction framework for stable feature selection,” Statistical Analysis and Data Mining: The ASA Data Science**Journal, vol. 5, no. 5, pp. 428–445, 2012.
-
L. Yu, Y. Han, and M. E. Berens, “Stable gene selection from microarray data via sample weighting,” IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational**Biology and Bioinformatics, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 262–272, 2011.
-
S. Loscalzo, L. Yu, and C. Ding, “Consensus group stable feature selection,” in Proceedings of the 15th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, 2009, pp. 567–576.
-
L. Yu, C. Ding, and S. Loscalzo, “Stable feature selection via dense feature groups,” in Proceedings of the 14th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, 2008, pp. 803–811.
-
R. Tibshirani, “Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso,” Jour- nal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Methodological), vol. 58, no. 1, pp. 267–288, 1996.
-
A. E. Hoerl and R. W. Kennard, “Ridge regression: Biased estimation for nonorthogonal problems,” Technometrics, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 55–67, 1970.
-
H. Zou and T. Hastie, “Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net,” Journal of the royal statistical society: series B (statistical methodology), vol. 67, no. 2, pp. 301–320, 2005.
-
A. Kalousis, J. Prados, and M. Hilario, “Stability of feature selection algorithms,” in Fifth IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM’05). IEEE, 2005, pp. 8–pp.
-
M. Consortium et al., “The microarray quality control (maqc) project shows inter-and intraplatform reproducibility of gene expression mea- surements,” Nature biotechnology, vol. 24, no. 9, p. 1151, 2006.
-
M.Zhang,L.Zhang,J.Zou,C.Yao,H.Xiao,Q.Liu,J.Wang,D.Wang, C. Wang, and Z. Guo, “Evaluating reproducibility of differential ex- pression discoveries in microarray studies by considering correlated molecular changes,” Bioinformatics, vol. 25, no. 13, pp. 1662–1668, 2009.
-
G. Jurman, S. Merler, A. Barla, S. Paoli, A. Galea, and C. Furlanello, “Algebraic stability indicators for ranked lists in molecular profiling,” Bioinformatics, vol. 24, no. 2, pp. 258–264, 2008.
-
S.NogueiraandG.Brown,“Measuringthestabilityoffeatureselection,” in Joint European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases. Springer, 2016, pp. 442–457.
-
S. Nogueira, K. Sechidis, and G. Brown, “On the stability of feature selection algorithms.” J. Mach. Learn. Res., vol. 18, no. 1, pp. 6345– 6398, 2017.
-
I. J. Goodfellow, J. Shlens, and C. Szegedy, “Explaining and harnessing adversarial examples,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6572, 2014.
-
C. Szegedy, W. Zaremba, I. Sutskever, J. Bruna, D. Erhan, I. Goodfellow, and R. Fergus, “Intriguing properties of neural networks,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1312.6199, 2013.
-
A. Madry, A. Makelov, L. Schmidt, D. Tsipras, and A. Vladu, “Towards deep learning models resistant to adversarial attacks,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1706.06083, 2017.
-
H. Zhang, Y. Yu, J. Jiao, E. Xing, L. El Ghaoui, and M. Jordan, “Theoretically principled trade-off between robustness and accuracy,” in International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, 2019, pp. 7472–7482.
-
L. Breiman, “Random forests,” Machine learning, vol. 45, no. 1, pp. 5–32, 2001.
-
I. Guyon, J. Weston, S. Barnhill, and V. Vapnik, “Gene selection for cancer classification using support vector machines,” Machine learning, vol. 46, no. 1, pp. 389–422, 2002.
-
Q.Gu,Z.Li,andJ.Han,“Generalizedfisherscoreforfeatureselection,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1202.3725, 2012.
-
H. Peng, F. Long, and C. Ding, “Feature selection based on mu- tual information criteria of max-dependency, max-relevance, and min- redundancy,” IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, vol. 27, no. 8, pp. 1226–1238, 2005.
-
D. Hendrycks and K. Gimpel, “Early methods for detecting adversarial images,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1608.00530, 2016.