-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Implementing Custom Spring Events ☃️
Table Of Contents
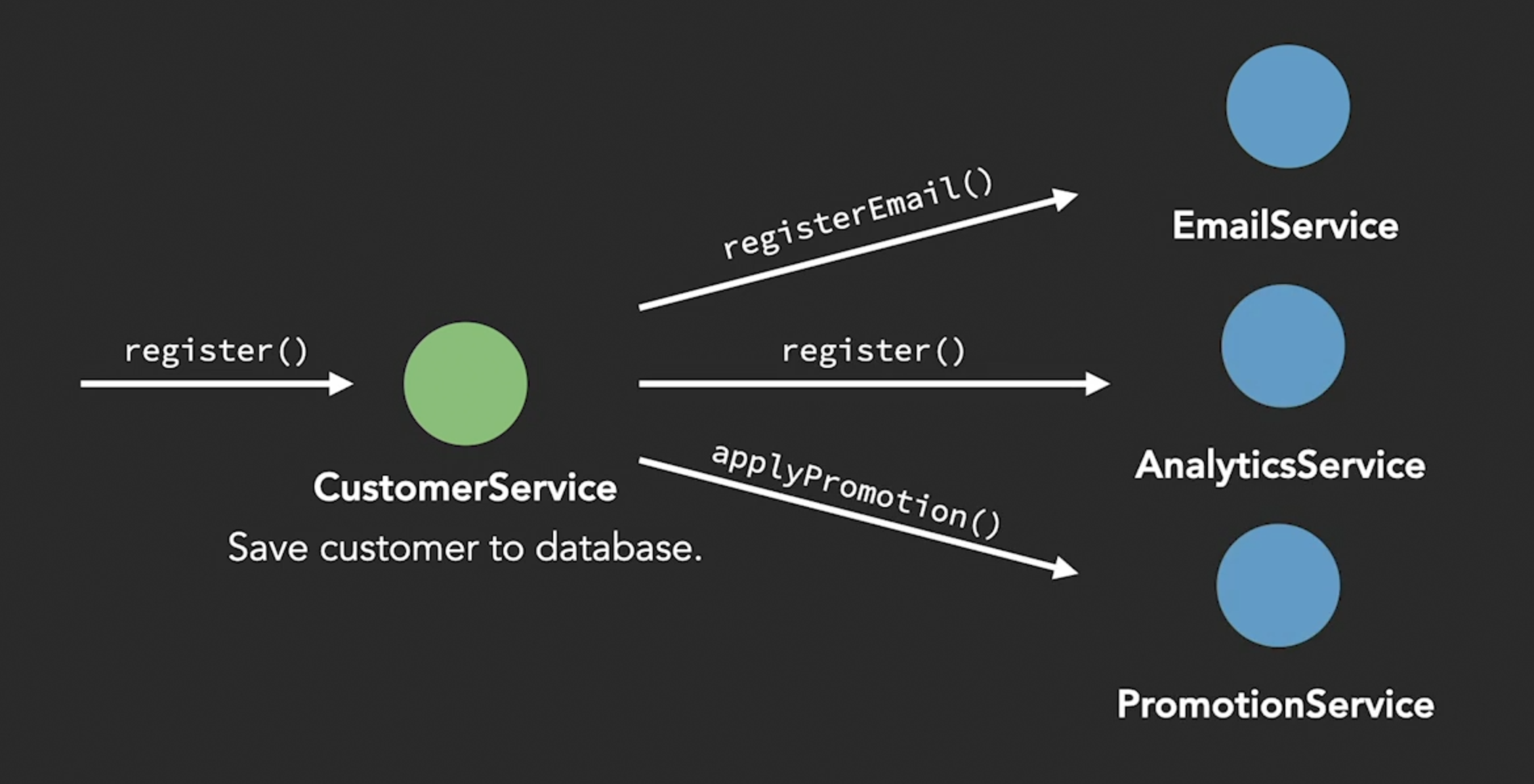
Imagine a customer has initiated registration, such a use case would persist a customer in the database and trigger an email service, may be invoke external CRM registration system and many other things.
 Ref.:[1]
Ref.:[1]
In a typical imperative style, the CustomerService class would call CustomerRepository to store a customer in the database and trigger an EmailService as shown in the following code.
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEventPublisher;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class CustomerService {
private final CustomerRepository customerRepository;
private final EmailService emailService;
public void register(Customer customer) {
customerRepository.save(customer);
emailService.sendRegistration(customer)
}
public void remove(Customer customer){
customerRepository.delete(customer);
}
}Q1 : Why should the customer registration process know about email registration and/or any other functionalities ?
- This could create a cyclic dependencies and Single Responsibility Principle violation. Testing becomes much more harder as we might need to mock different dependencies.
Let's create an Event : CustomerRegisteredEvent (we can extends an 'ApplicationEvent' base class, however since Spring 4.2 this is no longer required).
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class CustomerRegisteredEvent {
private final Customer customer;
}In CustomerSerice class, to publish an event, we need to inject 'ApplicationEventPublisher' bean and call 'publishEvent' method and provide 'CustomerRegisteredEvent' as argument.
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEventPublisher;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class CustomerService {
private final CustomerRepository customerRepository;
private final ApplicationEventPublisher publisher;
public void register(Customer customer) {
customerRepository.save(customer);
publisher.publishEvent(new CustomerRegisteredEvent(customer));
}
public void remove(Customer customer) {
customerRepository.delete(customer);
}
}Let's implement an event listener
- ApplicationListener Interface Usage Limitations
- Only used for objects extending 'ApplicationEvent'
- Listener can only have one method for event type
- Supports void return type
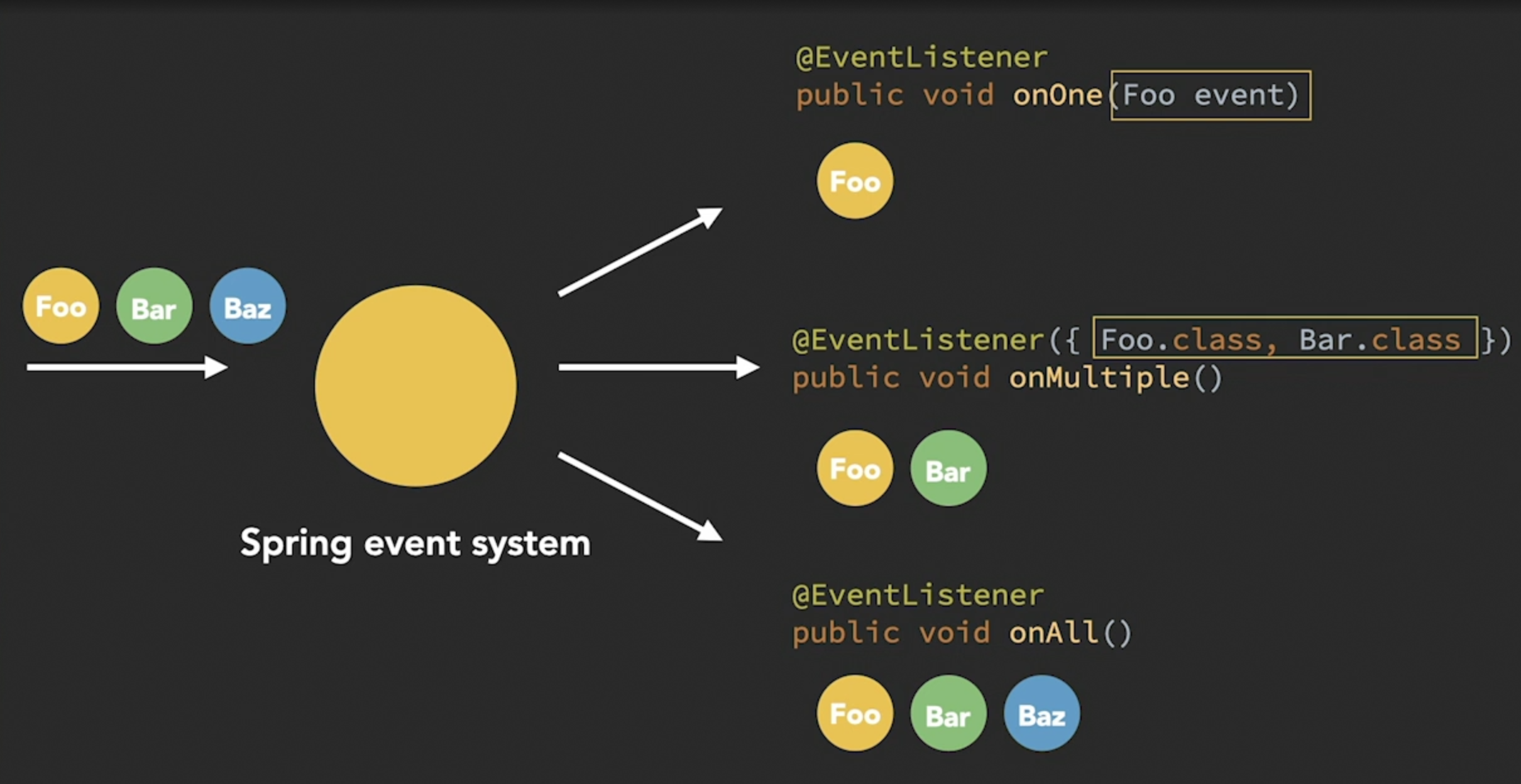
Starting Spring 4.2, it's possible to annotate a method over Spring bean with @EventListener. Each method will be automatically registered as a new application listener to listen for one or many events depending on the signature of the method.
 Ref.:[1]
Ref.:[1]
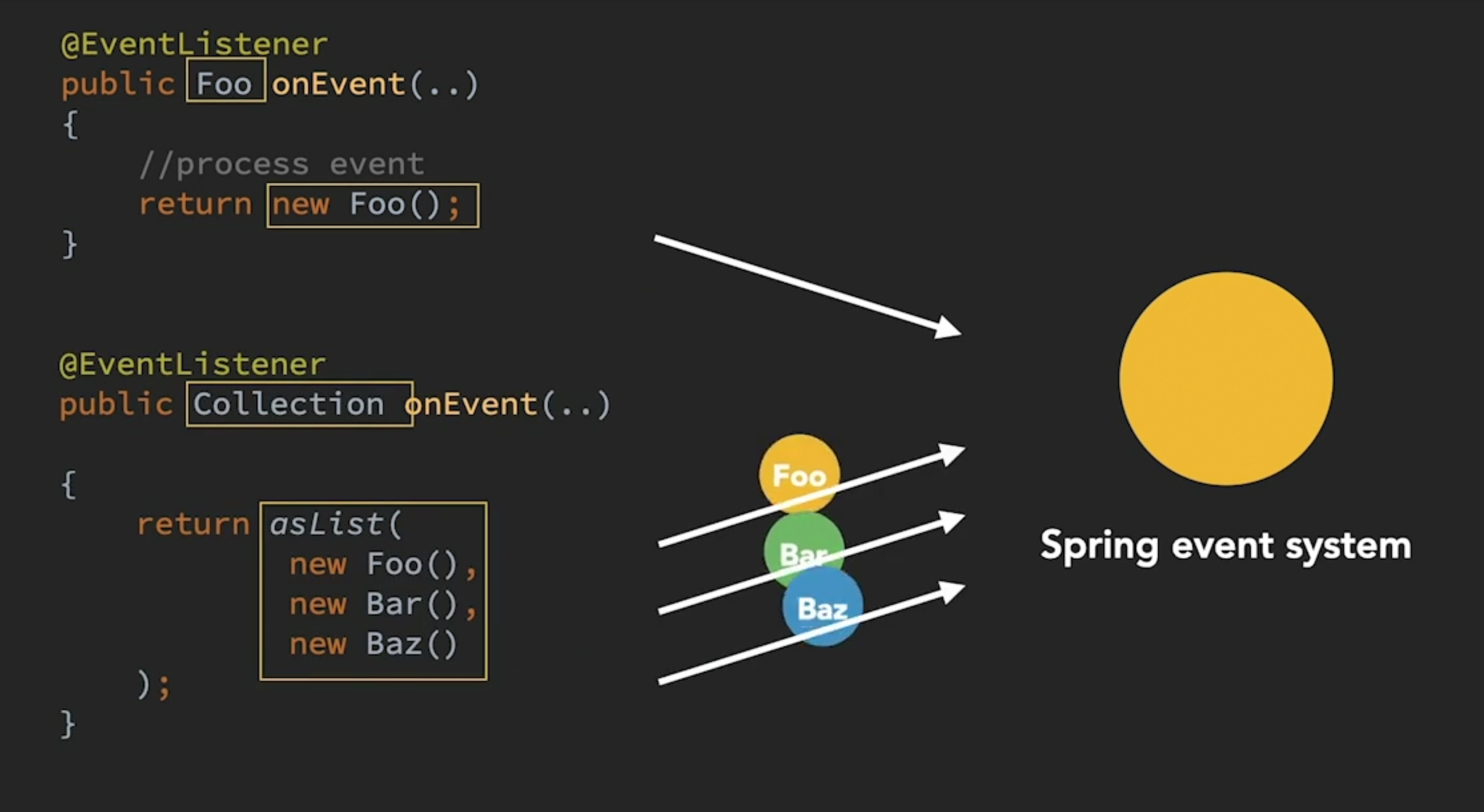
Annotated methods may have a non-void return type (unlike ApplicationListener interface). When they do, the result of the method is sent as new event. If the return type is either an array or a collection, each element is sent as a new individual event.
 Ref.:[1]
Ref.:[1]
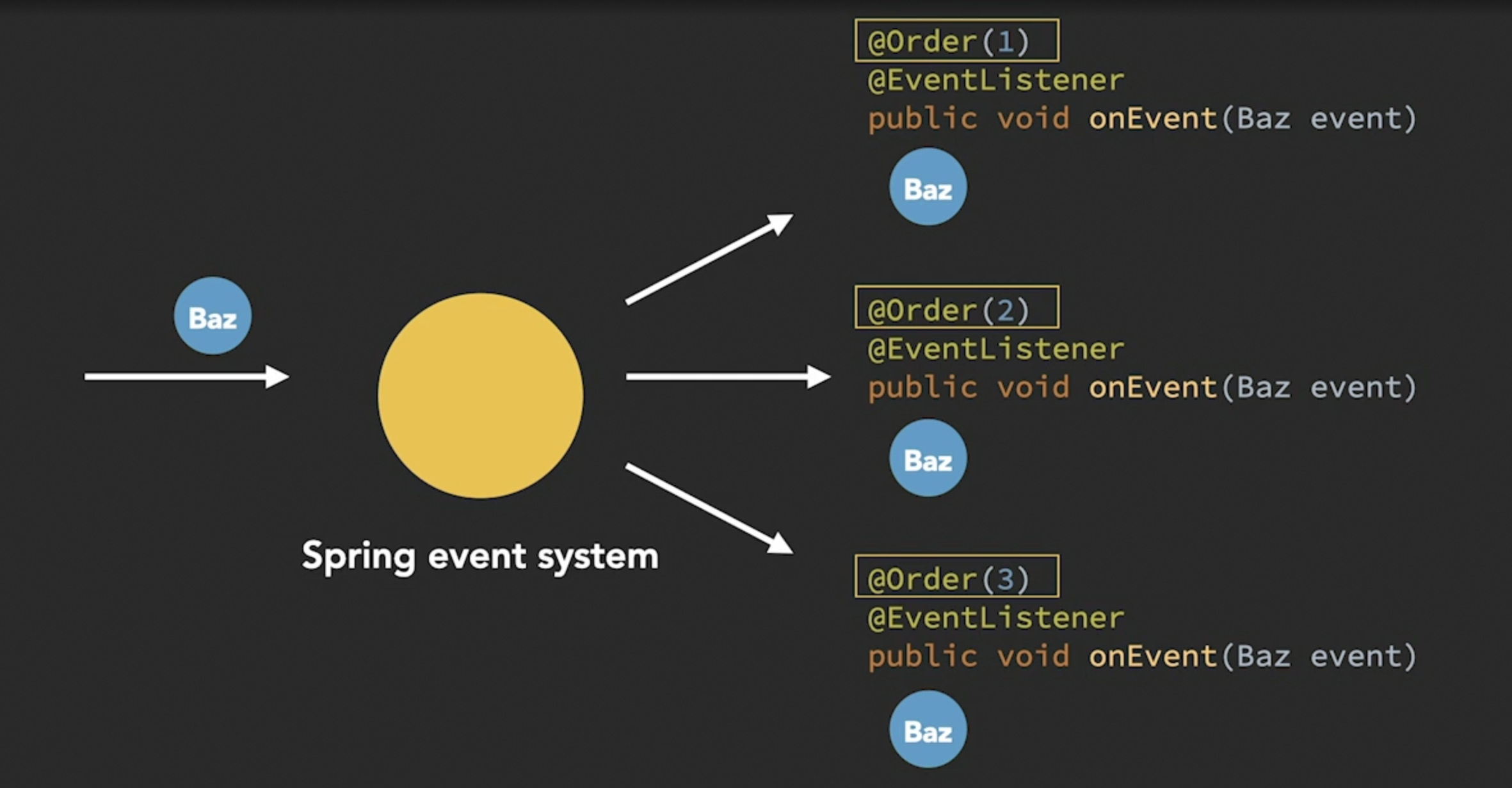
It is also possible to define the order in which listeners for the same event are to be invoked (add @Order(i) where i is an integer, on the method signature along with @EventListener annotation).
 Ref.:[1]
Ref.:[1]
- Let's create EmailListener class
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.context.event.EventListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class EmailListeners
{
private final EmailService emailService;
@EventListener
public void onRegisterEvent(CustomerRegisteredEvent event) {
emailService.sendRegisterEmail(event.getCustomer());
}
}"A time for everything, and to everything its place
Return what has been moved through time and space."
[Charmed]