🎯Motivation: The aim of the project is, to create E-Portfolio for the lab work we prepare week by week. Each week has its own articles and report. You can review all articles and exercises week by week. Some of them may include external links for blog posts. You can check and get more information.
Week one was all about Digitalization and Energy Crisis in 2022. We have an article written by 3 authors about the security implications of the digital economy. Week 1 basically all about finding answers to the following questions:- What is the definition of a fully digital enterprise?
- What are the cyber-security challenges/concerns with a fully digital enterprise?
- What are the cyber security challenges for bricks and mortar SMEs wanting to become digital enterprises?
I read the article and found external references for answering those questions properly. You can find the reference links down below the word document.
Week two was all about Scanning Activity which means we used some CMD commands to check following tasks:-
How many hops do we have from our machine to target website?
tracert [target website link] -
Which step causes the biggest delay in the route?
tracert [target website link] -
What is the average duration of that delay?
ping [target website link] -
Checking main nameservers for the target website
nslookup [target website link] -
Details of the MX Record for the target website
nslookupset q=MX[target website link]
-
Who is the registered contract?
whois [target website address] -
Find out where the target website is hosted.
nslookup [target website link]
My Reflection: This exercise was quite informative and enjoyable for me. I love to work with CMD commands as a programmer. It is lifesaver most of the time. Our exercise’s aim for checking network details in general. In first question we checked our hops path from ISP to target website and observed the biggest delay in the route. In rest of the questions we used nslook up commands to check server names , addresses and MX records for our target website.
Challange i faced & solution i found: I faced an issue while I was trying to check the MX record for the target website. I was not able to check MX records via the command line.
Since I have been using ubuntu for almost 1 year I decided to use ubuntu for this task instead of LINUX.
I found useful documentation on cloudflare.com and I executed the following code.
First, I entered nslookup command then set a filter to only collect MX records and related information (q=MX) and added the target website.
At the end I was able to check MX records and SMTP email address of the target website.
At the end of the week 2 we have also some end of unit activitiy questions.The questions and summariezed answers are the followings.
-
Question: Cloud platforms are becoming a very common commodity in the digital system. What are the benefits and draw backs in Cloud solutions with respect to cyber security? Present an argument with minimum 500 words in favour of or against cloud storage. What are the security risks involved in cloud vs local store . You should post your solution in the discussion group and provide at least two references
Answer: Cloud storage solutions offer scalability, cost-effectiveness, automatic updates, and data backup and recovery, but also have drawbacks such as dependence on internet connection, security concerns, limited control, limited customization, vendor lock-in, and security risks. Local storage has the risk of physical damage or theft and is vulnerable to natural disasters, but also offers more control. Businesses must weigh the benefits and drawbacks and consider their specific needs when deciding between cloud and local storage for cyber security.
-
Question: In 2017 a ransomware termed as WannaCry unleased its malicious attack on a global scale. What cautions and safeguards should have been in place that could have averted this attack?
Answer: The WannaCry ransomware attack in 2017 exploited a vulnerability in older versions of Windows and encrypted users' data. To prevent similar attacks, it is important to keep software and operating systems up to date, use antivirus software, implement a firewall, use strong passwords, regularly back up data, educate employees about cyber security, and use multi-factor authentication.
-
Question:Why is it important to have a backup system in place that works closely with cyber security framework? How are these two components are related? Please use your own personal computer as hypothetical machine and list the steps that you will adopt to backup your data.
Answer: Having a backup system in place is important for protecting against data loss due to cyber attacks, hardware failures, or other disasters. To create a backup system for a personal computer, identify the data that needs to be backed up, choose a backup method, set up a schedule for backups, test the system to ensure it is working properly, and store the backup in a secure location. This will create a backup system that works closely with the cyber security framework to protect against data loss.
On week 3 and 4 we discussed Cyber Kill Chain. Understanding the Cyber Kill Chain can help organizations to develop defenses at each stage of an attack and to implement effective cybersecurity measures to reduce the risk of a successful attack.
Understanding the Cyber Kill Chain can help organizations to develop defenses at each stage of an attack and to implement effective cybersecurity measures to reduce the risk of a successful attack.
| Phase | Description | SolarWinds Exploit | Mitigations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reconnaissance | The attacker gathers information about the target to plan the attack. | It is not clear at this time how the attacker obtained information about SolarWinds and its customers |
|
| Weaponization | The attacker creates a tool or payload to deliver the attack. | The attacker created a malicious update for the SolarWinds Orion software, which was then distributed to customers through the normal update process. |
|
| Delivery | The attacker delivers the weapon to the target. | The attacker delivered the malicious update to SolarWinds customers through the normal update process. |
|
| Exploitation | The attacker exploits a vulnerability in the target system. | The attacker exploited a vulnerability in the SolarWinds Orion software to gain access to the systems of customers who installed the malicious update. |
|
| Installation | The attacker installs the payload on the target system. | The attacker installed a backdoor on the systems of customers who installed the malicious update. |
|
| Command and control | The attacker establishes a connection to the payload and gains control of the target system. | The attacker established a connection to the backdoor on the compromised systems and gained control of them. |
|
| Actions on objectives | The attacker performs their desired actions on the target system. | The attacker used the compromised systems to access other networks and gather information. |
|
Tools used to utilize in each phase:
-
Reconnaissance phase:
-
Access control systems: These systems can limit the information that is available to potential attackers.
-
Network monitoring tools: These tools can detect signs of reconnaissance activity, such as scans or probes of a network.
-
Threat intelligence platforms: These platforms provide information about potential threats and the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) used by attackers
-
-
Weaponization phase:
-
Code signing tools: These tools verify the authenticity of software updates and can prevent the distribution of malicious updates.
-
Multi-factor authentication systems: These systems can be used to secure update servers and processes, making it more difficult for attackers to deliver malware.
-
Supply chain management tools: These tools can help ensure that software is not tampered with during the development and distribution process.
-
-
Delivery phase:
-
Network segmentation tools: These tools can isolate systems and limit the spread of an attack.
-
Network monitoring tools: These tools can detect unusual or unauthorized traffic that could indicate an attack.
-
Email filtering tools: These tools can prevent the delivery of malicious emails by blocking or quarantining suspicious messages.
-
-
Exploitation phase:
-
Vulnerability management tools: These tools can help identify and address vulnerabilities in a timely manner, reducing the risk of exploitation.
-
Firewall systems: These systems can block access to known vulnerabilities, helping to prevent exploitation.
-
-
Installation phase:
-
Endpoint security tools: These tools can detect and block malware from being installed on systems.
-
System monitoring tools: These tools can alert administrators to unusual activity that could indicate an attempt to install malware.
-
Application whitelisting tools: These tools allow only trusted applications to run on systems, which can prevent malware from being installed or executed.
-
-
Command and Control (C2) phase:
-
Network monitoring tools: These tools can help detect C2 traffic, such as outbound connections to known C2 servers or unusual traffic patterns.
-
Threat intelligence platforms: These platforms provide information about known C2 servers and tactics used by attackers.
-
Firewall systems: These systems can block access to known C2 servers.
-
-
Actions on Objectives phase:
-
Data backup tools: These tools enable the restoration of affected systems and data.
-
Data loss prevention (DLP) systems: These systems detect and prevent the exfiltration of sensitive data.
-
Access control systems: These systems limit the ability of unauthorized users to access and modify critical systems and data.
-
My Summarized reflection about Solar Winds hack from the blog post: The SolarWinds hack was a worst nightmare for many organizations, as it allowed cybercriminals to gain access to sensitive information on a massive scale. The hack, which was discovered in December 2020, affected hundreds of government agencies and private businesses around the world. One of the most alarming aspects of the SolarWinds hack was the level of sophistication involved. The hackers used a sophisticated supply chain attack to insert malicious code into software updates that were distributed to SolarWinds customers. This allowed them to gain access to the networks of the organizations that installed the updates, giving them the ability to steal sensitive data and potentially even disrupt operations. The fact that the hack went undetected for so long was also a major concern. It is believed that the hackers had been active for months before the breach was discovered, giving them ample time to steal data and plant malware on the affected systems. The SolarWinds hack serves as a reminder of the importance of cybersecurity in today's digital age. It is crucial for organizations to take steps to protect their systems and data, including implementing strong passwords, regularly updating software and systems, and training employees on how to recognize and report potential threats. Overall, the SolarWinds hack was a worst nightmare for those affected by it, highlighting the need for increased vigilance and proactive measures to protect against cyberattacks.
This week, we are asked to create brief reflection report based on the usage and installation of Kali Linux to show what we have learnt, problems we faced and solutions we provide (challanges). Also our instructor provided us two links to read related to the Kali Linux. You can see links in the associated word document.
Summary: Linux is a free and open-source operating system that was first released in 1991 by Linus Torvalds. It is based on the Unix operating system and is often used as an alternative to proprietary operating systems such as Microsoft Windows or MacOS. One of the key benefits of Linux is that it is highly customizable and can be tailored to meet the specific needs of an individual or organization. It is also known for being stable, secure, and efficient.
Linux is used in a wide range of applications, including personal computers, servers, mobile devices, and embedded systems. It is also a popular choice for programming and development due to the availability of a wide range of tools and resources. Overall, Linux is a powerful and versatile operating system that has gained widespread adoption in the technology industry. It has a strong community of users and developers who contribute to its ongoing development and improvement.
Why Kali?
- Includes more than 600 Penetration Testing Tools
- Free to use (if your time has no value)
- Operates on Open-Source Development Model
- Gives freedom to customize completely
- Developed in a secure environment
- Custom kernel, patched for injection
- ARMEL and ARMHF support
- Diverse and vibrant community
My Reflection: Kali Linux is a popular open-source operating system that is widely used for penetration testing and security assessments. It is a distribution of Linux that is specifically designed for these tasks and includes a wide range of tools and resources for identifying and addressing vulnerabilities in computer systems and networks. Whether or not Kali Linux is the right operating system for a particular individual or organization will depend on their specific needs and goals. It is important to carefully evaluate the benefits and limitations of any operating system before deciding to use it.
Challange i faced & solution i found: As far as I searched, after installation is successful, GRUB is installed to MBR, but when I rebooted the system there was no grub splash screen; just a text based booting menu. After Kali booted up, there was no GUI; but only a text-based login option. By spending some time googling it, I found that there is bug in 2020.1 installer ISO and about 140+ packages are missing in offline installer. Also, there are a few packages that are missing in APT package manager. To install Kali Linux with default options (XFCE DE), the installer needs an Internet connection to download missing packages from Kali repository. If you try to install Kali Linux offline, you will end up with text mode installation.
What is Honepot Attack ?
Honey pot is a computer system that is set up to trap cyber attackers who try to gain unauthorized access to information systems.Here are the simulated each step of attack.
- A hacker begins by scanning the internet for vulnerable systems to target.
- The hacker comes across a network that appears to have multiple servers and many open ports, indicating that it may be a valuable target.
- Upon further investigation, the hacker discovers that the network is a honeypot - a trap set up by cybersecurity professionals to attract and monitor potential attackers.
- The hacker attempts to gain access to the honeypot by entering various login credentials and attempting to exploit known vulnerabilities.
- As the hacker continues to try and gain access to the honeypot, they are being monitored by cybersecurity professionals. The professionals can track the hacker's IP address, the methods they are using to try and gain access, and any other information that may be useful in identifying and prosecuting the attacker.
- Eventually, the hacker realizes that they have been caught in a honeypot and ceases their attempts to gain access.
- The cybersecurity professionals use the information gathered from the honeypot to identify and track down the hacker, potentially leading to their arrest and prosecution.
My Reflection on Honeypot: Honeypots are security resources that are specifically designed to attract and trap cybercriminals. These resources can be used to monitor and track the actions of attackers, gather intelligence on their tactics and techniques, and potentially divert them away from more valuable assets within an organization's network. One of the main benefits of using honeypots is that they can help organizations to better understand the threats that they face. By studying the behavior of attackers who are interacting with a honeypot, security teams can learn more about the tactics, techniques, and procedures that are being used by attackers and use this information to improve their defenses. However, there are also some potential drawbacks to using honeypots. One of the main concerns is that they can be resource-intensive to set up and maintain. Additionally, honeypots can potentially attract a lot of unwanted attention from attackers, which can put additional strain on an organization's security team. Overall, honeypot attacks can be a useful tool in an organization's security arsenal, but they should be used carefully and with a clear understanding of the potential risks and benefits.
What is Dos Attack?
A Denial of Service (DoS) attack is a type of cyber-attack in which a perpetrator seeks to make a particular computer or network resource unavailable to its intended users by overwhelming it with traffic or requests for data. This can be done in a variety of ways, such as sending a flood of messages to a server or website, or by exploiting vulnerabilities in a network to cause it to crash or become otherwise unavailable.
My Reflection on DOS/DDOS: DDOS attacks can have a significant impact on individuals, as well as on organizations. If you are a victim of a DDOS attack, you may find that you are unable to access certain websites or online services, which can be frustrating and inconvenient. In some cases, you may also be at risk of losing access to important personal data or sensitive information. It is important for individuals to be aware of the risks associated with DDOS attacks and to take steps to protect themselves. This can include using strong and unique passwords, avoiding clicking on links or downloading attachments from unknown sources, and keeping your devices and software up to date with the latest security patches. Additionally, it is a good idea to be cautious when accessing sensitive or personal information online, and to use trusted websites and services whenever possible. By taking these precautions, you can help to reduce your risk of being caught up in a DDOS attack or other cyber security incident.
Implementing Port Security
Port security is a method of protecting network devices from unauthorized access or activity. It involves the use of various measures to prevent unauthorized devices from connecting to a network through physical port connections, such as Ethernet ports or USB ports.
This week we are asked to review the Man In the Middle Attack by watching videos. We have to write our reflection based on the video and discuss the operation of the attack in the context of enterprise networks.
My Reflection on Man In The Middle Attack: In the first video,it shows the details and basically steps of the attack and implements it using a third-party application. A man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack is a type of cyber-attack where an attacker intercepts communication between two parties and can manipulate or view the data being transmitted. It is important to note that MITM attacks can be difficult to detect, as communication between the two parties may appear normal and no errors may be reported. Therefore, it is important to take steps to protect against these types of attacks, such as using encryption and secure protocols.
In the second video,the scenario was simpler and more usual than the first one. It gave real world examples such as a hacker who brings his laptop to café and creates a bait Wi-Fi to let other customers connect to internet via himself. When customers hit their credentials on any website using hacker’s Wi-Fi, hackers can see their credentials because of Network sniffing tool.
In the context of an enterprise network, an MITM attack could be carried out by an employee who has access to the network, or by an outsider who has gained access to the network through, for example, a phishing attack or by exploiting a vulnerability in the network. Once the attacker has positioned themselves in the middle of the communication, they can potentially read, alter, or block the communication as they see fit. For example, an attacker could intercept and alter an email being sent from one employee to another, or they could intercept and read sensitive information being transmitted between systems on the network. To protect against MITM attacks, it is important for organizations to use secure communication protocols, such as SSL/TLS, and to use strong authentication methods to verify the identity of parties involved in a communication. It is also important to regularly update and patch systems and to educate employees on how to recognize and avoid phishing attacks.
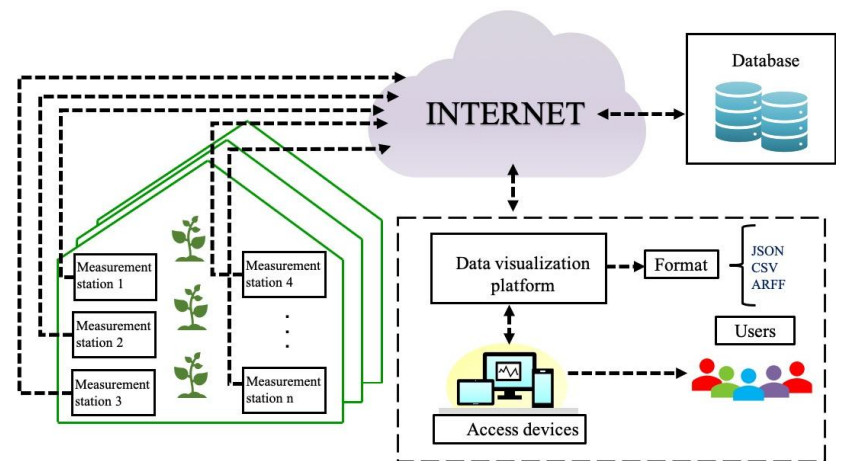
This week we started to study on IOT topic. As a class topic we had to fill a table about infsastructures of greenhouses in the context of IOT. You can check the table under the Week 8-9 folder by downloading the document.
My Reflection on IOT - Greenhouse Infrastructure: A typical Internet of Things (IoT) infrastructure for a greenhouse might include sensors to monitor temperature, humidity, light intensity, soil moisture, and other relevant environmental variables. These sensors would be connected to a local gateway, which would transmit the sensor data to a cloud-based server for storage and analysis. The server would run software that processes and analyzes the sensor data to provide insights and trigger alerts, or automated responses as needed. For example, the software might send a notification to a farmer if the temperature in the greenhouse exceeds a certain threshold, or it might automatically adjust the irrigation system to provide more water to a particular section of the greenhouse based on soil moisture levels. The farmer might also be able to access the sensor data and control the various systems in the greenhouse using a mobile app or web-based dashboard. This would allow them to remotely monitor and manage the greenhouse environment from anywhere with an internet connection. It's also worth considering incorporating security measures into the IoT infrastructure to protect against unauthorized access or tampering. This might include things like secure communication protocols, authentication, and data encryption.
In the last week of December 2022, we had a seminar about IoT by Babak Reihani who has been professional in this field for so long. His company provides smart home solutions. He brought some products to the seminar to show us how they work and what they do. At the end of the presentation, we are asked to create a brief report about the seminar. This report simply includes the important points of the seminar we attended.