This repository contains my personnal notes and questions, that I have managed to answer, related to the general-purpose programming language JAVA. These notes will cover JAVA Basics, OOP, Inheritance and much more. This repository is intended to be used as a reminder of JAVA concepts.
-
Java Basics
- What is the difference between JDK and JRE?
- What is Java Virtual Machine (JVM)?
- What are the different types of memory areas allocated by JVM?
- What is JIT compiler?
- How Java platform is different from other platforms?
- Why Java is 'write once and run anywhere' language?
- How does ClassLoader work in Java?
- Is ‘main’, used for main method, a keyword in Java?
- Can we write main method as static public void instead of public static void?
- In Java, if we do not specify any value for local variables, then what will be the default value of the local variables?
- What is the difference between byte and char data types in Java?
- What is the difference between static method and instance method in Java?
-
Object-Oriented Programming System (OOPs)
- What are the main principles of Object Oriented Programming?
- What is the difference between Object Oriented Programming language and Object Based Programming language?
- In Java what is the default value of an object reference defined as an instance variable in an Object?
- Why do we need default constructor in Java classes?
- Can we inherit a Constructor?
- Why constructors cannot be final, static, or abstract in Java?
-
Inheritance
- Explain the concept of Inheritance?
- Which class in Java is superclass of every other class?
- Why Java does not support multiple inheritance?
- In OOPS, what is meant by composition?
- How aggregation and composition are different concepts?
- If there are no pointers in Java, then why do we get NullPointerException?
- What is the purpose of ‘super’ keyword in Java?
- What is the meaning of object cloning in Java?
-
Static
- In Java, why do we use static variable?
- Why it is not a good practice to create static variables in Java?
- What is the purpose of static method in Java?
- Why do we mark main method as static in Java?
- In what scenario do we use a static block?
- Is it possible to execute a program without defining a main() method?
- What happens when static modifier is not mentioned in the signature of main method?
- What is the difference between static method and instance method in Java?
-
Method Overloading and Overriding
- What is the other name of Method Overloading?
- How will you implement method overloading in Java?
- Why it is not possible to do method overloading by changing return type of method in java?
- Is it allowed to overload main() method in Java?
- How do we implement method overriding in Java?
- Why Java does not allow overriding a static method?
- Is it allowed to override an overloaded method?
- What is the difference between method overloading and method overriding in Java?
- What is meant by covariant return type in Java?
-
Polymorphism
-
Abstraction
- What is Abstraction in Object Oriented programming?
- How is Abstraction different from Encapsulation?
- What is an abstract class in Java?
- Is it allowed to mark a method abstract as well as final?
- Can we instantiate an abstract class in Java?
- What is an interface in Java?
- Is it allowed to mark an interface method as static?
- Why an Interface cannot be marked as final in Java?
- What is a marker interface?
- What is the difference between abstract class and interface in Java?
- Does Java allow us to use private and protected modifiers for variables in interfaces?
- How can we cast to an object reference to an interface reference?
-
Final
-
Package
-
Serialization
-
Garbage Collection
- The
JREis used to run your Java program. It includes theJVM, a set of libraries that come with Java as well asJava Launcher. - The
JREdoesn't include any development tools.
- The
JDKis the development kit that you need to create Java programs. - The
JDKis basically the tools that will take your Java source code and convert it into a format that theJREand theJVMcan execute. - The
JDKcomes bundled with a Java Runtime Edition as shown in the Image above.
Back to Top ☝️ Table of contents
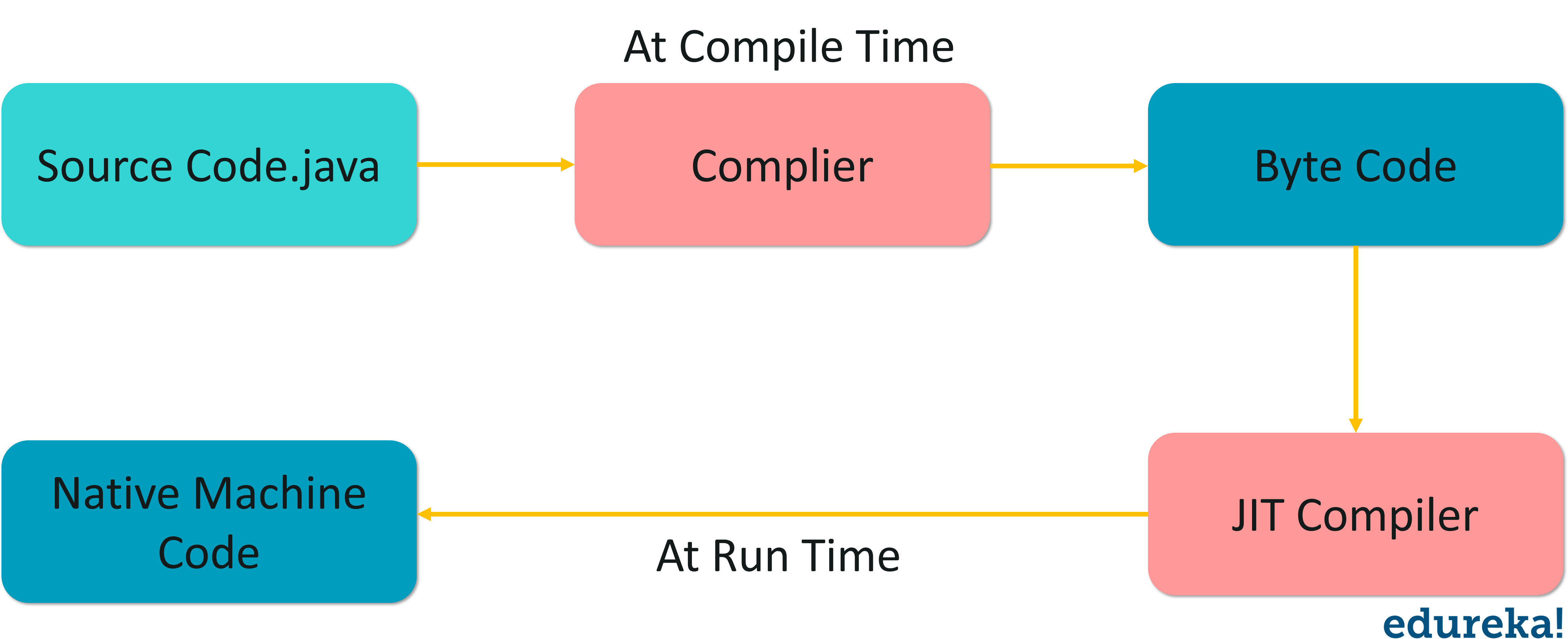
- The
JVM(Java Virtual Machine) is a run-time engine that convertsJava bytecode(generated bythe Compiler), thanks to TheExecution engineinto machine code. - The
JVMis a part of Java Runtime Environment (JRE), which means that it enables a computer to run Java programs as well as programs written in other languages that are also compiled to Java bytecode. - The
JVMis the one that actually calls the main method present in a java code. - The
JVMresides on the RAM.
Back to Top ☝️ Table of contents
All objects created in Java are stored in JVM (Java virtual machine). JVM memory is basically divided into the following parts:
- Method Area.
- Heap Memory.
- Stack Memory.
- Program Counter register.
- Native method Stacks.
- The
Just-In-Time (JIT) compileris a an essential part of the JRE, that improves the performance of Java applications by compiling platform-neutral Java bytecode into native machine code at run time. - Without
the JIT, the JVM has to interpret the bytecodes itself - a process that requires extra CPU and memory.
Back to Top ☝️ Table of contents
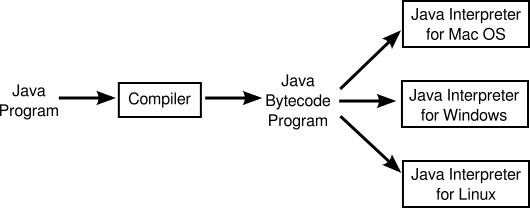
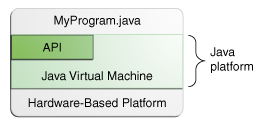
- Most platforms can be described as a combination of the operating system and underlying hardware. The Java platform differs from most other platforms in that it's a software-only platform that runs on top of other hardware-based platforms.
- The Java platform has two components:
- The Java Virtual Machine.
- The Java Application Programming Interface (API).
- Java is platform independent (WORA).
- Java applications are called
WORA (Write Once Run Anywhere). This means Java can be developed on any device, compiled into a standard bytecode and be expected to run on any device equipped with a JVM. - Java is portable, means that you can run Java bytecode on any hardware that has a compliant JVM (Java Virtual Machine).
Back to Top ☝️ Table of contents
ClassLoader in Java is a class that is used to load class files in Java. Java code is compiled into a class file by javac compiler and JVM executes Java program, by executing byte codes written in the class file. ClassLoader is responsible for loading class files from file systems, networks, or any other source.
Java class loaders are used to load classes at runtime. ClassLoader in Java works on three principles: delegation, visibility, and uniqueness.
Delegation principleforward request of class loading to parent class loader and only loads the class if the parent is not able to find or load the class.Visibility principleallows child class loader to see all the classes loaded by parent ClassLoader, but parent class loader can not see classes loaded by a child.Uniqueness principleallows one to load a class exactly once, which is basically achieved by delegation and ensures that child ClassLoader doesn't reload the class already loaded by a parent.
Correct understanding of class loader is a must to resolve issues like NoClassDefFoundError in Java and java.lang.ClassNotFoundException, which are related to class loading.
Back to Top ☝️ Table of contents
- In Java,
mainis the name of Java main method. It is the identifier that the JVM looks for as the starting point of the java program. It’s not a keyword.
- If you write
static public void maininstead ofpublic static void main, then it will make no difference. Program compiles properly and runs. But if you change the sequence of main, then it will give you a compiler error. - In Java, we can declare access modifiers in any order, the method name comes last, the return type comes second to last and then after it's our choice. But it's recommended to put access modifier (public, private and protected) at the forefront as per Java coding standards.
In Java, if we do not specify any value for local variables, then what will be the default value of the local variables?
- There is no default value for local variables, so local variables should be declared and an initial value should be assigned before the first use.
- Using a local variable without initializing would give an error at the time of compilation.
Back to Top ☝️ Table of contents
- The first and foremost difference between byte and char are that byte is a signed data type while char is an unsigned data type.
- From above fact, we can deduce another difference between byte and char. Byte can represent negative values but char values are always positive.
- Another difference between char and byte is that char is a larger data type than a byte. The range of byte is between -128 to 127 but the range of char is from 0 to 65535, because byte is a signed 8-bit data type and char is an unsigned 16-bit data type hence, its maximum value is 2 ^ 16 - 1 which is 65535.
- There are 4 major principles that make a language Object Oriented:
- Encapsulation
- Data Abstraction
- Polymorphism
- Inheritance
What is the difference between Object-Oriented Programming language and Object Based Programming language?
In computer science, the term object-based has two different senses:
- A limited version of object-oriented programming, where one or more of the following restrictions applies:
- There is no implicit inheritance.
- There is no polymorphism.
- Only a very reduced subset of the available values are objects (typically the GUI components).
- Prototype-based systems (that is, those based on "prototype" objects that are not instances of any class).
The core difference between the two is that an object-oriented programming language has the features that an object-oriented paradigm must have in order to be considered an object-oriented programming language. While object based programming languages are Prototype-based where one or more of OOP principles are lacking.
In Java what is the default value of an object reference defined as an instance variable in an Object?
- The object references are all initialized to null in Java. However in order to do anything useful with these references, you must set them to a valid object, else you will get
NullPointerExceptionseverywhere you try to use such default initialized references.
Back to Top ☝️ Table of contents
- The compiler automatically provides a public no-argument constructor for any class without constructors. This is called the default constructor.
- This default constructor initializes the variables of the class with their respective default values (null for objects, 0.0 for float and double, false for boolean, 0 for byte, short, int and, long).
- Constructors are not inherited. They are called implicitly or explicitly by the child constructor.
- A subclass inherits all the members (fields, methods, and nested classes) from its superclass. Constructors are not members, so they are not inherited by subclasses, but the constructor of the superclass can be invoked from the subclass.
- Constructors can't be final because when we say a method is final that means it can't be overriden. Constructors by Java rules can't be overriden anyways so there is no point in making constructors as final.
- Static methods belong to the class. Whereas a Constructor belongs to the object and called when we use the new operator to create an instance. Since a constructor is not class property, it makes sense that it’s not allowed to be static. (Constructors are implicitly final and static, you don’t need to declare it again)
- Constructors can’t be abstract because when you set a method as ‘abstract’, it means method doesn't have any body and you want to implement it at another time in a child class, but the constructor is called implicitly when the new keyword is used so it can’t lack a body.
- Inheritance is a proces in which one class acquires the properties (fields and methods) of an other.
- With inheritance, we can reuse the fields and methods of the existing class. Hence, inheritance facilitates Reusability and is an important concept of OOPs.
- The class which inherits the properties of other is known as subclass (derived class, child class) and the class whose properties are inherited is known as superclass (base class, parent class).
- The Object class, which is stored in the
java.lang package, is the ultimate superclass of all Java classes. Because of this, all Java classes inherit methods fromObject. Half of these methods are final and cannot be overridden.
- Multiple Inheritance is a feature of object oriented concept, where a class can inherit properties of more than one parent class. The problem occurs when there exist methods with same signature in both the super classes and subclass. On calling the method, the compiler cannot determine which class method to be called and even on calling which class method gets the priority.
- Multiple inheritance is not supported by Java using classes , handling the complexity that causes due to multiple inheritance is very complex. It creates problem during various operations like casting, constructor chaining etc and there are very few scenarios on which we actually need multiple inheritance, so better to omit it for keeping the things simple and straightforward.
Back to Top ☝️ Table of contents
- Composition is one of the fundamental concepts in object-oriented programming. It describes a class that references one or more objects of other classes in instance variables. This allows you to model a has-a association between objects.
Both Aggregation and Composition are specific cases of Association. In both aggregation and composition object of one class owns object of another class. But there is a subtle difference :
- Aggregation implies a relationship where the child can exist independently of the parent. Example: Class (parent) and Student (child). Delete the Class and the Student still exist.
- Composition implies a relationship where the child cannot exist independent of the parent. Example: House (parent) and Room (child). Rooms don't exist separate to a House.
Java doesn’t support pointer explicitly, but it uses pointer implicitly :
- Java use pointers for manipulations of references but these pointers are not available for outside use. Any operations implicitly done by the language are actually NOT visible.
- NullPointerException is a RuntimeException. In Java, a special null value can be assigned to an object reference. NullPointerException is thrown when program attempts to use an object reference that has the null value.
- The super keyword refers to superclass (parent) objects.
- The super keyword is used to call superclass methods, and to access the superclass constructor.
- The most common use of the super keyword is to eliminate the confusion between superclasses and subclasses that have methods with the same name.
- Object cloning refers to creation of exact copy of an object. It creates a new instance of the class of current object and initializes all its fields with exactly the contents of the corresponding fields of this object.
- The class whose object’s copy is to be made must have a public clone method in it or in one of its parent class.
Back to Top ☝️ Table of contents
- We use static variables when only one copy of the variable is required. Variables declared static are commonly shared across all instances of a class.
- Static variables reduce the amount of memory used by a program. Static variables are shared among all instances of a class.
Much as it’s often said that “Inheritance breaks encapsulation” statics do this in a far more severe way, by not just exposing internal implementation but also by exposing internal state.
- The problem is when a variable can be altered by any instance of a class then the fundamental principle behind encapsulation/information hiding is lost entirely: An object is no longer in complete control of its state.
- Any instance of the object can alter the static variable which causes ambiguity as individual instances of the object no longer have control over their own state.
- State changes can arbitrarily happen without knowledge of an object which relies on that state which is problematic because the object may not work correctly when this happens.
- We use static method when we want to provide class level access to a method, where the method should be callable without an instance of the class. Static methods don't need to be invoked on the object and that is when you use it.
- Java main() method is always static, so that compiler can call it without the creation of an object or before the creation of an object of the class.
- If the main() is allowed to be non-static, then while calling the main() method JVM has to instantiate its class.
- The main() method in Java must be declared public, static and void. If any of these are missing, the Java program will compile but a runtime error will be thrown.
Back to Top ☝️ Table of contents
- We use a static block when a class that has static members requires initialization.
- The code inside static block is executed only once, the first time the class is loaded into memory.
- Static blocks are executed before constructors.
- Yes, we can execute a JAVA program without a main method by using a static block.
- In the example below, we can execute a JAVA program without a main method (works until Java 1.6 version).
class StaticInitializationBlock{
static{
System.out.println("class without a main method");
System.exit(0);
}
}
- Java 7 and newer versions don’t allow the execution of a JAVA program because JVM checks the presence of the main method before initializing the class.
- Without having declared main method static , our program will successfully compile but won't execute and report error at run time.
- Declaring main method static is necessary since main is called by the Java interpreter before any objects are made.
- Since keyword static allows main to be called without creating an object of the class in which the main method is defined, our main method needs to be declared static.
-
Instance methods are methods which require an object of its class to be created before it can be called.
- To invoke a instance method, we have to create an Object of the class in within which it defined.
- Instance method(s) belong to the Object of the class not to the class. they can be called after creating the Object of the class.
- Every individual Object created from the class has its own copy of the instance method(s) of that class.
- They can be overridden since they are resolved using dynamic binding at run time.
-
Static methods are the methods in Java that can be called without creating an object of class.
- They are referenced by the class name itself or reference to the Object of that class.
- Static method(s) are associated to the class in which they reside. they can be called even without creating an instance of the class.
- They are designed with aim to be shared among all Objects created from the same class.
- They can not be overridden. But can be overloaded since they are resolved using static binding by compiler at compile time.
Back to Top ☝️ Table of contents
- Method Overloading is also known as Compile time Polymorphism or static polymorphism.
- We can implement method overloading in two different ways:
- Implementing two or more methods that have the same name but take different numbers of arguments.
- Implementing two or more methods that have the same name but take arguments of different types.
- Java can distinguish the methods with different method signatures. The methods can have same name but with different parameters list (number of the parameters, order of the parameters, and data types of the parameters) within the same class.
- The compiler does not consider the return type while differentiating the overloaded method. But you cannot declare two methods with the same signature and different return type. It will throw a compile time error.
- If both methods have same parameter types, but different return type, then it is not possible to do method overloading.
- Yes, just like anyother method in java, the main method can be overloaded in a similar manner but JVM only calls the original main method, it will never call our overloaded main method.
- In order for the overloaded main method to be executed , we need to call it from the actual main method.
Back to Top ☝️ Table of contents
- Overriding is a feature that allows a child class to provide a specific implementation of a method that is already provided by one of its parent classes.
- Method Overriding is implemented when a method in a subclass has the same name, same parameters or signature, and same return type(or sub-type) as a method in its super-class, only then the method in the subclass is said to override the method in the super-class.
- Java doesn't allow overriding a static method even though we can declare static methods with same signature in subclass, but it is not considered overriding as there won’t be any run-time polymorphism.
- If a derived class defines a static method with same signature as a static method in base class, the method in the derived class hides the method in the base class.
- A method can be an override for an overloaded method in a superclass. And you can overload a method that you are simultaneously overriding using another method.
- You cannot have one method that is both a new overload and an override.
- For a method to be an override, another method with the same signature must already exist in the superclass, and that means that this method cannot be a new override.
- The most basic difference is that overloading is being done in the same class while for overriding base and child classes are required.
- Overriding is all about giving a specific implementation to the inherited method of parent class while method Overloading is about allowing a class to have more than one method having the same name, if their argument lists are different.
- Covariant return type refers to return type of an overriding method. It allows to narrow down return type of an overridden method without any need to cast the type or check the return type.
- Covariant return type in java means that overriding method can return SubClass.
- Covariant return type works only for non-primitive return types.
Back to Top ☝️ Table of contents
- Run-time Polymorphism, also known as Dynamic Method Dyspatch, is a process in which a call to an overridden method is resolved at runtime rather than compile-time.
- Method invocation is determined by JVM not compiler
- A method is overridden, not the data members, so runtime polymorphism can't be achieved by data members.
If linking between method call and method implementation is resolved at compile time then we call it static binding or if it is resolved at run time then it dynamic binding.
- Static Binding happens at compile time while Dynamic Binding happens at runtime.
- Static binding uses type of the class and fields but Dynamic binding uses object to resolve binding.
- Overloading is an example of static binding while Method overriding is the example of Dynamic binding.
Back to Top ☝️ Table of contents
- Abstraction is one of the key concepts of object-oriented programming languages.
- Its main goal is to handle complexity by hiding unnecessary details from the user. That enables the user to implement more complex logic on top of the provided abstraction without understanding or even thinking about all the hidden complexity.
- Objects in an OOP languages provide an abstraction that hides the internal implementation details, you just need to know which methods of the object are available to call and which input parameters are needed to trigger a specific operation. But you don’t need to understand how this method is implemented and which kinds of actions it has to perform to create the expected result.
- Abstraction hides details at the design level, while Encapsulation hides details at the implementation level.
- Abstraction lets you focus on what the object does instead of how it does it, while Encapsulation means hiding the internal details of how an object works.
- Abstraction is about hiding unwanted details while giving out the most essential details, while Encapsulation means hiding the code and data into a single unit e.g. class or method to protect the inner working of an object from the outside world.
Back to Top ☝️ Table of contents
- Abstract class is a restricted class that cannot be used to create objects (to access it, it must be inherited from another class).
- In Java, we can have an abstract class without any abstract method. This allows us to create classes that cannot be instantiated, but can only be inherited.
- No, you cannot make an abstract method final in Java.
- An abstract method must be overridden to be useful and called but when you make the abstract method final it cannot be overridden in Java, hence there would be no way to use that method.
- Making an abstract method final in Java will result in a compile-time error. In short, the use of keywords abstract and final together is illegal in Java.
- Abstract classes cannot be instantiated, but they can be subclassed.
- An interface is a completely "abstract class" that is used to group related methods with empty bodies.
- Like abstract classes, interfaces cannot be used to create objects.
- Interface methods do not have a body.
- An interface cannot contain a constructor (as it cannot be used to create objects).
Back to Top ☝️ Table of contents
- Prior to java 8, interface in java can only have abstract methods. All the methods of interfaces are public & abstract by default.
- Java 8 allows the interfaces to have default and static methods.
- We can safely add static methods to the existing interfaces without changing the code in the implementation classes. Since these methods are static, we cannot override them in the implementation classes.
- If you make an interface final, you cannot implement its methods which defies the very purpose of the interfaces. Therefore, you cannot make an interface final in Java.
- If you try to make an interface final, a compile time exception is generated saying “illegal combination of modifiers − interface and final”.
- Marker Interface is an empty interface (no field or methods).
- Examples of Marker Interface are:
- Cloneable Interface.
- Serializable Interface.
- Remote Interface.
- Interface can have only abstract methods. Abstract class can have abstract and non-abstract methods. From Java 8, it can have default and static methods also.
- Variables declared in a Java Interface are by default final. An Abstract class may contain non-final variables.
- Abstract class can have final, non-final, static and non-static variables. Interface has only static and final variables.
- Abstract class can provide the implementation of interface. Interface can’t provide the implementation of abstract class.
- An Interface can extend another Java interface only, an Abstract class can extend another Java class and implement multiple Java interfaces.
- Members of a Java Interface are public by default. A Java Abstract class can have class members like private, protected, etc.
Back to Top ☝️ Table of contents
- Java interfaces are meant to specify fields and methods that are publicly available in classes that implement the interfaces. Therefore you cannot use the private and protected access modifiers in interfaces.
- If you implement an interface and provide body to its methods from a class. You can hold object of the that class using the reference variable of the interface that is cast an object reference to an interface reference.
- Using this you can access the methods of the interface only, if you try to access the methods of the class a compile time error is generated.
- You need to cast an object reference to an interface reference. Whenever you need to call the methods of the interface only.
- Final variable in Java cannot be changed. Once if we have assigned the final variable it can not be changed it is fixed. but if you have declare a blank final variable then you can assign value to it only in constructor. also using hiearchical instances can come handy.
- You can declare an entire class final.
- A class that is declared final cannot be subclassed.
- You can declare some or all of a class's methods final.
- You use the final keyword in a method declaration to indicate that the method cannot be overridden by subclasses.
- You can prevent a class from being subclassed by using the final keyword in the class's declaration.
- Similarly, you can prevent a method from being overridden by subclasses by declaring it as a final method.
- A blank final variable in Java is a final variable that is not initialized during declaration.
- Example:
// A simple blank final example
final int i;
i = 30;
- Yes, we can declare the main () method as final in Java. The compiler does not throw any error.
- While it is possible, it is not really meaningful. final methods can not be overriden. But static methods cant anyways.
Back to Top ☝️ Table of contents
- A package in Java is used to group related classes. Think of it as a folder in a file directory.
- We use packages to avoid name conflicts, to control access, to make searching/locating and usage of classes, interfaces, enumerations and annotations easier, and to write a better maintainable code.
- The java.lang package provides classes that are fundamental to the design of the Java programming language.
- The most important class is Object, which is the root of the class hierarchy.
- Every java class is a subclass of Object. It contains the important methods like equals, hashcode, clone, toString, etc.
- It is available from day one of java (JDK 1.0)
- No, java.lang package is a default package in Java therefore, there is no need to import it explicitly.
- Yes, you can import a package or a class multiple times. It doesn't create any issues.
- The JVM will internally load the class and/or package only once no matter how many times you import the same class and/or the package.
Back to Top ☝️ Table of contents
- Static import is a feature introduced in the Java programming language that allows members (fields and methods) which have been scoped within their container class as
public static, to be used in Java code without specifying the class in which the field has been defined. - Example:
We always use sqrt() method of Math class by using Math class i.e. Math.sqrt(), but by using static import we can access sqrt() method directly.
- Serialization is a process used to convert the state of an object into a byte stream, which can be persisted into disk/file or sent over the network to any other running Java Virtual Machine.
- The main purpose of serialization is to save the state of an object in order to be able to recreate it when needed, providing storage of objects as well as data exchange.
- Deserialization is the reverse process of Serialization where the byte stream is used to recreate the actual Java object in memory.
- At the time of serialization, if we don’t want to save the value of a particular variable in a file, then we use transient keyword.
- When JVM comes across transient keyword, it ignores original value of the variable and save default value of that variable data type.
- The Externalizable interface provides control over the serialization process.
- The Externalizable interface supplies two methods, called readExternal() and writeExternal(), where we can write our own set of serialization rules.
- Serializable is a marker interface, it does not contain any method but Externalizable interface contains two methods writeExternal() and readExternal().
- The other difference is performance, you can not do much to improve performance of default serialization process except reducing number of fields to be serialized by using transient and static keyword but with Externalizable interface you have full control over Serialization process.
- When the Serializable interface is implemented, the default constructor is not called during Deserialization, while it is called during the DeSerialization process if Externalizable has been implemented.
Back to Top ☝️ Table of contents
- Java Garbage Collection is the process by which Java programs perform automatic memory management.
- Java provides the Garbage Collector to find the unused objects and deletes them to free up memory so that Java application developers are not burdened with having to explicitly free memory objects that are not being used.