backend is known for snapshot of terraform state.
It also helps in other ways such as In many cases there are multiple users who are working on the same project and they all might need to make changes in the files at the same file; here the backend helps to work in synchronized way as it locks the staging file for one user's change and then releases the lock for others to make modifications.
Prerequisites:
-
To create IAM user and attach policy click here [also attach AmazonDynamoDBFullAccess]
-
To install and configure AWS CLI click here
Here I have created a terraform module for an instance. If you need you can add resources as per your needs. Refer below code.
variables.tf file
# Server Module Variables
variable "my_env" {
description = "Define which environment you are working on"
type = string
}
variable "aws_region" {
description = "Define region"
type = string
default = "us-east-1"
}
variable "instance_count" {
description = "Number of instances to create"
type = number
default = 1
}
variable "ami" {
description = "EC2 AMI"
type = string
}
variable "instance_name" {
description = "Name of the instance"
}
variable "instance_type" {
description = "EC2 Instance Type"
type = string
}
variable "key_name" {
description = "EC2 Key Pair Name"
type = string
}
my_servers.tf
> Here I only created and configured aws instance.
resource "aws_instance" "my_app_server" {
count = var.instance_count
ami = var.ami
instance_type = var.instance_type
key_name = var.key_name
tags = {
Name = "${var.my_env}-${var.instance_name}"
}
}
I created a new folder where I will call the module.
terraform.tf
terraform {
required_providers {
aws = {
source = "hashicorp/aws"
version = "~> 4.16"
}
}
required_version = ">= 1.2.0"
}
provider.tf file
provider "aws" {
region = "us-east-1"
}
main.tf file to call module
# dev env
module "dev-app" {
source = "../tf-module"
my_env = "dev"
instance_count = 1
ami = "ami-0c7217cdde317cfec"
instance_name = "my-app-server"
instance_type = "t2.micro"
key_name = "my-linux-key"
}
In the module block source is the destination folder of the module. And entered the values of the variables.
If you need you can create multiple instances with module block such as:
You can skip this.
# prod env
module "prod-app" {
source = "../tf-module"
my_env = "prod"
instance_count = 1
ami = "ami-0c7217cdde317cfec"
instance_name = "my-app-server"
instance_type = "t2.medium"
key_name = "my-linux-key"
}
# staging env
module "stg-app" {
source = "../tf-module"
my_env = "stg"
instance_count = 1
ami = "ami-0c7217cdde317cfec"
instance_name = "my-app-server"
instance_type = "t3.medium"
key_name = "my-linux-key"
}
# This will create 3 instances with different names and instance types.
Next, for the backend, there are a few things which are required:
-
AWS S3 Bucket
-
AWS DynamoDB table
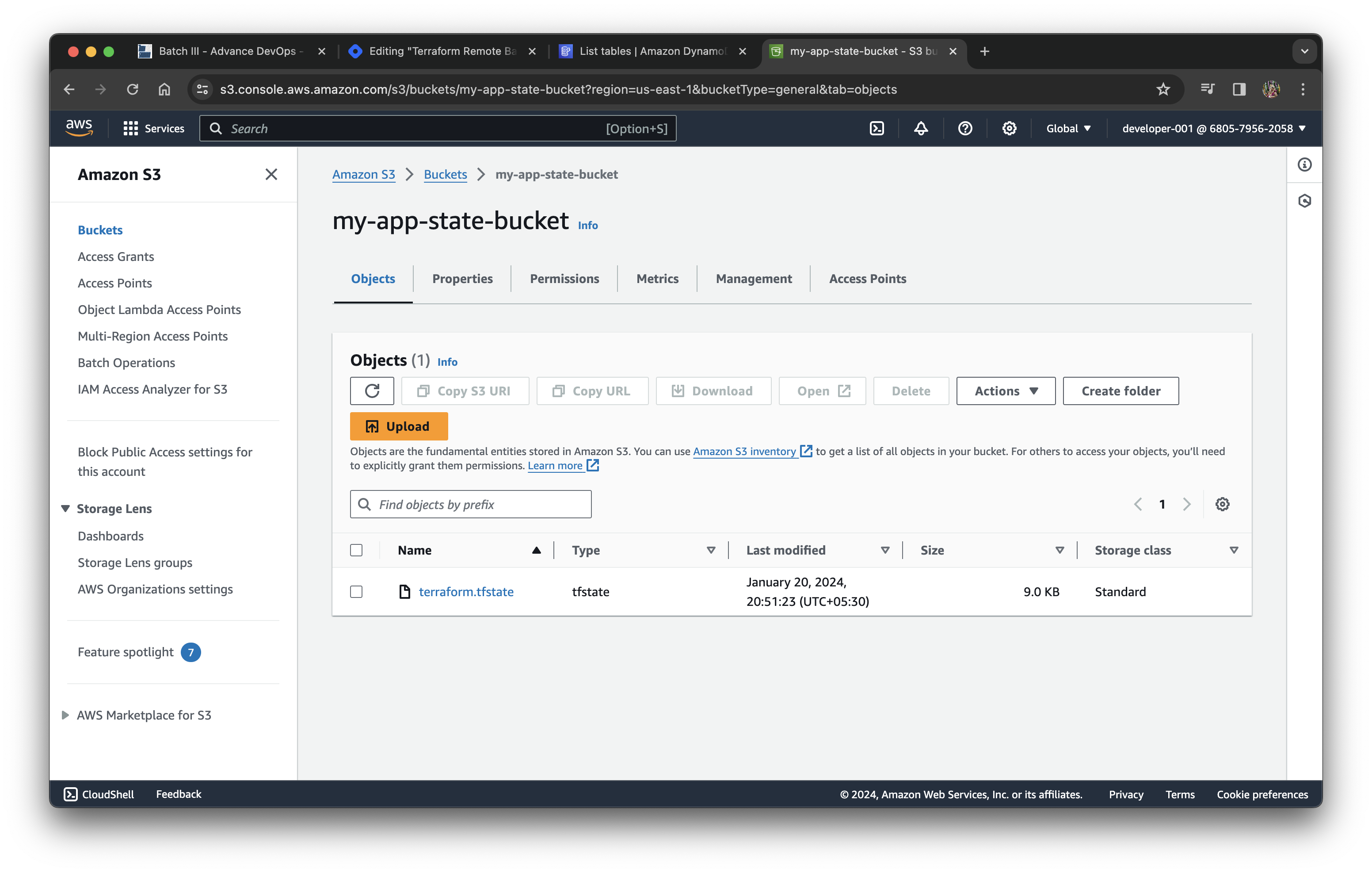
Bucket will store the terraform.tfstate file and DynamoDB table will keep the status of the lock for the file.
Create a new file for creating bucket and table.
backend_infra.tf
resource "aws_s3_bucket" "my_app_bucket" {
bucket = "my-app-state-bucket"
tags = {
Name = "my-app-state-bucket"
}
}
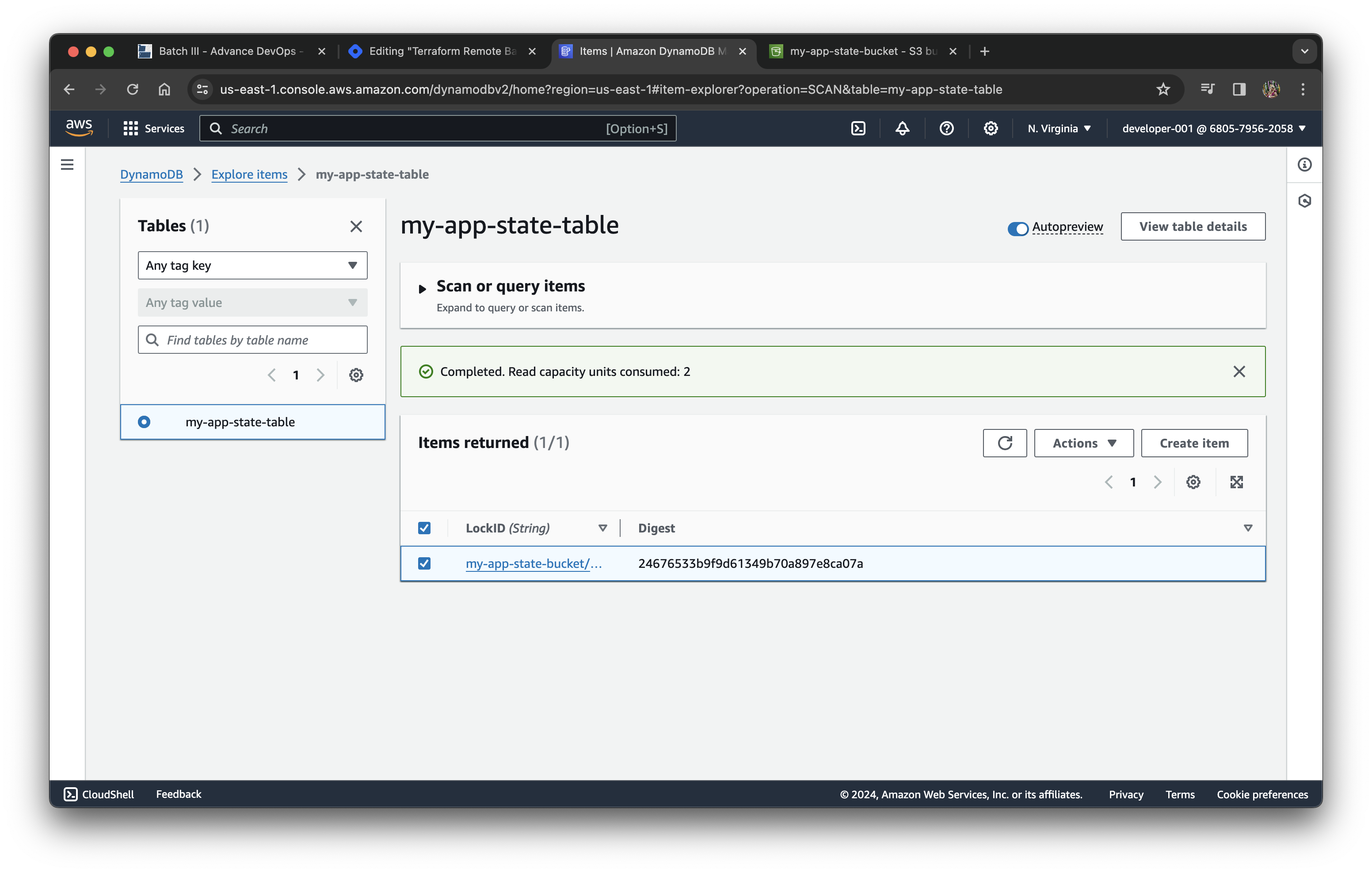
resource "aws_dynamodb_table" "my_app_state_table" {
name = "my-app-state-table"
billing_mode = "PAY_PER_REQUEST"
hash_key = "LockID"
attribute {
name = "LockID"
type = "S"
}
tags = {
Name = "my-app-state-table"
}
}
Now, give command terrform init and terraform apply
Make sure bucket and table are created.
After creating these, add backend block in the terraform block:
terraform {
required_providers {
aws = {
source = "hashicorp/aws"
version = "~> 4.16"
}
}
required_version = ">= 1.2.0"
backend "s3" {
bucket = "my-app-state-bucket"
key = "terraform.tfstate"
region = "us-east-1"
dynamodb_table = "my-app-state-table"
}
}
NOTE: bucket and table needs to be created before adding backend block.
backend "s3" will access the bucket with the given name, update the status in the table and key is the file name which will be used to remote backend.
Now, again give command terrform init because there is a change in the terraform block as we added the backend and then terraform apply
That’s it. You have successfully stored the terraform state file at remote backend. Now whenever you will apply the changes it will acquire the stage file from S3 and make changes as required.
Thank you for reading! If you like the blog, make sure you like and share it.