-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 3
Diagnostic Workflow
This diagnostic analysis workflow has been developed to filter for and prioritize pathogenic variation/mutation in patient samples.
- Petrovski, Slavé, et al. "Whole-exome sequencing in the evaluation of fetal structural anomalies: a prospective cohort study." The Lancet (2019).
- Zhu X, et al. "Whole exome sequencing in undiagnosed genetic diseases: Interpreting 119 trios." Genetics in Medicine (2015).
- ATAV CLI and ATAV Database set up on AWS EC2.
conda activate atav-cli
export ATAV_HOME=$(pwd)/atav/
# If you're not running on database server, update the database connection settings.
# For example, replace 127.0.0.1 with your server address (should look like
# ec2-1-1-1-1.compute-1.amazonaws.com) in this file:
# vi $ATAV_HOME/config/atav.dragen.system.config.properties
# Create an output directory; rename to your specific project.
mkdir atav_output
export PROJECT=atav_output
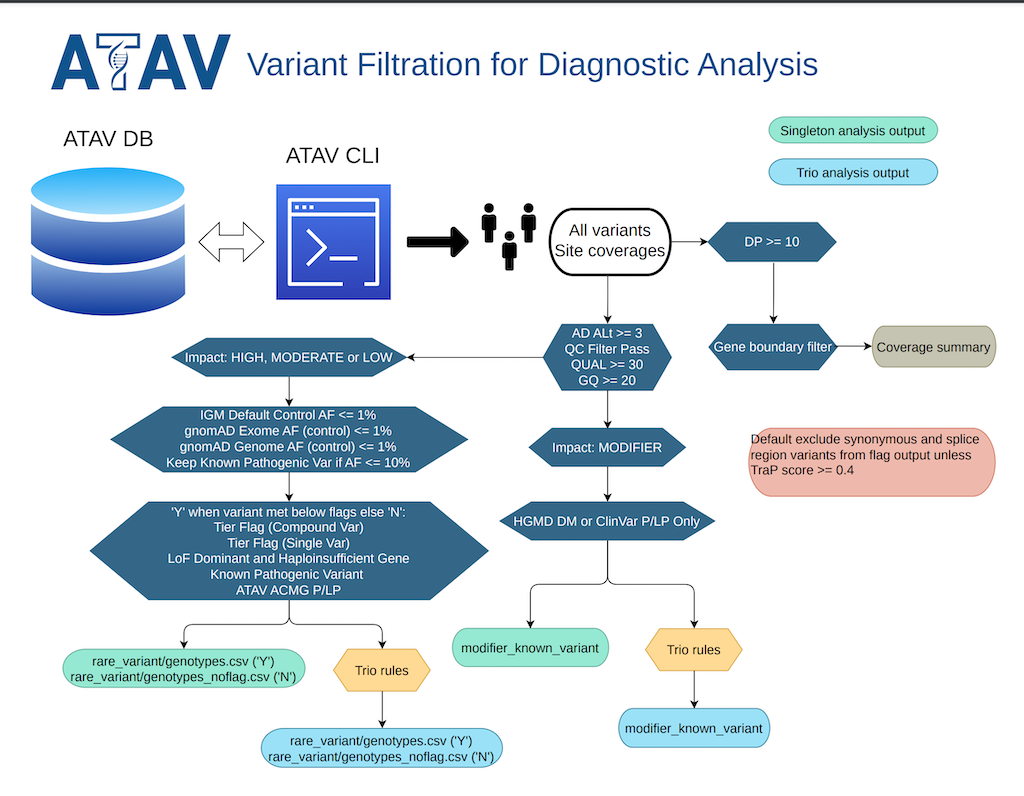
Rare variants:
java -jar $ATAV_HOME/atav_trunk.jar --list-trio --impact HIGH,MODERATE,LOW --min-ad-alt 3 --qual 30 --gq 20 --filter pass,likely,intermediate --max-default-control-af 0.01 --max-gnomad-exome-af 0.01 --max-gnomad-genome-af 0.01 --include-qc-missing --sample $SAMPLE --out $OUTPUT
Modifier known variants:
java -jar $ATAV_HOME/atav_trunk.jar --list-trio --known-var-pathogenic-only --modifier-only --min-ad-alt 3 --qual 30 --gq 20 --filter pass,likely,intermediate --include-qc-missing --sample $SAMPLE --out $OUTPUT
Rare variants:
java -jar $ATAV_HOME/atav_trunk.jar --list-singleton --impact HIGH,MODERATE,LOW --min-ad-alt 3 --qual 30 --gq 20 --filter pass,likely,intermediate --max-default-control-af 0.01 --max-gnomad-exome-af 0.01 --max-gnomad-genome-af 0.01 --include-qc-missing --sample $SAMPLE --out $OUTPUT
Modifier known variants:
java -jar $ATAV_HOME/atav_trunk.jar --list-singleton --known-var-pathogenic-only --modifier-only --min-ad-alt 3 --qual 30 --gq 20 --filter pass,likely,intermediate --include-qc-missing --sample $SAMPLE --out $OUTPUT
Coverage Summary (for trio & singleton):
java -jar $ATAV_HOME/atav_trunk.jar --coverage-summary --gene-boundaries /nfs/goldstein/software/atav_home/data/ccds/addjusted.CCDS.genes.index.r20.hg19.txt --min-coverage 10 --percent-region-covered .9 --sample $SAMPLE --out $OUTPUT
Note: all the external dataset are used in variant prioritization / tier classification will be included by default.
- rare_variant_trio_genotypes.csv: rare variant with Tier1 or Tier2 or LoF Gene or Known Variant
- rare_variant_trio_genotypes_noflag.csv: rare variants do not meet any of the flags above
- modifier_known_variant_trio_genotypes.csv: all non-coding known variants
- rare_variant_singleton_genotypes.csv: rare variant with Tier1 or Tier2 or LoF Gene or Known Variant
- rare_variant_singleton_genotypes_noflag.csv: rare variants do not meet any of the flags above
- modifier_known_variant_singleton_genotypes.csv: all non-coding known variants
- Save CSV file as Excel file
- Create two new columns at the very left of the output. Name the first column “Notes”, and the second column “Clinical Fit”
- Write your notes on Note column
- Document clinical fit in clinical fit column
- Highlight variants you want to present in Green, and rows you need to do more research on in yellow
- Highlight variants that you have analyzed and have ruled out in gray, as they may come up more than once using the filters below
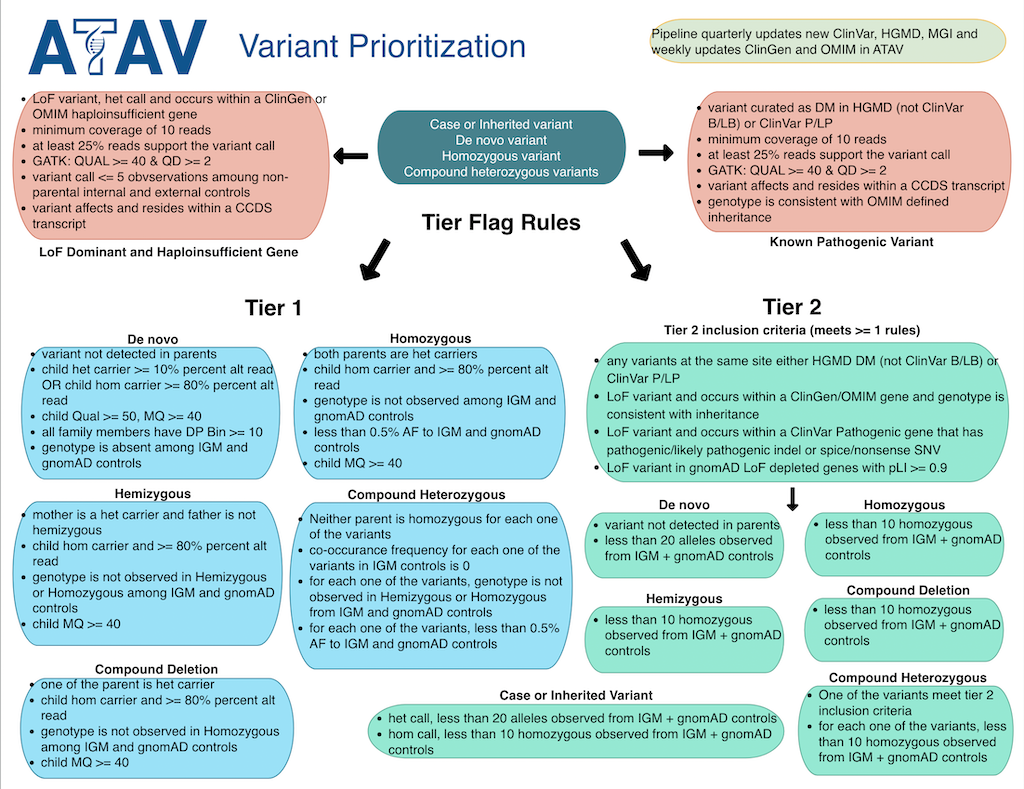
- Apply (Excel) filter to column Single Variant Prioritization to review all single variants:
- 01_TIER1_DNM_HZ: Tier 1 De novo variants in "Hot Zone"
- 02_TIER1_DNM: Tier 1 De novo non-HZ variants
- 03_TIER1_HOMO_HEMI: Tier 1 Homo/Hemi variants
- 04_TIER2_DNM: Tier 2 De novo variants
- 05_TIER2_HOMO_HEMI: Tier 2 Homo/Hemi variants
- 06_LOF_GENE: LoF Dominant and Haploinsufficient Gene
- 07_KNOWN_VAR: Previously reported ClinVar P/LP variants or HGMD DM (as long as it is NOT ClinVar B/LB)
- 08_CLINVAR_SITE: >=1 ClinVar P/LP variant at site. Includes precise indel overlaps.
- 09_CLINVAR_2BP: >= 1 ClinVar P/LP variant within 2bp flanking. Includes precise indel overlaps.
- 10_HGMD_SITE: >=1 HGMD DM variant at site. Includes precise indel overlaps.
- 11_MIS_HOT_SPOT: Missense Dominant and Haploinsufficient Gene + ClinVar PLP 25bpflanks count >= 6
- 12_TIER1_OMIM_MIS_INFRAME: High-quality ultra rare novel missense/inframe indel variants
- 13_ACMG_GENE: ACMG v3 gene associated variants
- Apply (Excel) filter to column Compound Het Variant Prioritization to review all compound het variants:
- 01_TIER1
- 02_TIER2
SOP for Trio Analysis of Rare Coding Variants that meet no Flags (rare_variant_trio_genotypes_noflag.csv)
These are variants that DO NOT meet any of the flags (Tier 1 or 2 or LoF Gene or KV). This output will be helpful for the following: you have a specific gene/gene list in mind, or if you want to look for a second variant, or if the patient has a more common phenotype or if looking for inherited variants from the parents. Note that duos are also included in this Output. In this output review all the variants/genes for clinical overlap.
All variants meet the Known Pathogenic Variant Flag (previously reported P/LP variants on CV or DM (only if it is NOT CV B/LB)). Note that duos are also included in this Output.
- Apply (Excel) filter to column “Tier Flag (Single Var)” for Tier 1 or 2 variants
- Remove Tier filtering then go to column “ACMG Disease” and uncheck NA, review those variants
- Remove ACMG filter, go to “Gene Link” filter for genes that have OMIM genes
- Quickly review phenotypes to see if it is a phenotype fit
- Apply (Excel) filter to column Single Variant Prioritization to review all single variants:
- 01_LOF_GENE: LoF Dominant and Haploinsufficient Gene
- 02_TIER1_HOMO_HEMI: Tier 1 Homo/Hemi variants
- 03_KNOWN_VAR: Previously reported ClinVar P/LP variants or HGMD DM (as long as it is NOT ClinVar B/LB)
- 04_CLINVAR_SITE: >=1 ClinVar P/LP variant at site. Includes precise indel overlaps.
- 05_CLINVAR_2BP: >= 1 ClinVar P/LP variant within 2bp flanking. Includes precise indel overlaps.
- 06_HGMD_SITE: >=1 HGMD DM variant at site. Includes precise indel overlaps.
- 07_MIS_HOT_SPOT: Missense Dominant and Haploinsufficient Gene + ClinVar PLP 25bpflanks count >= 6
- 08_TIER1_OMIM_MIS_INFRAME: High-quality ultra rare novel missense/inframe indel variants
- 09_ACMG_GENE: ACMG v3 gene associated variants
- Apply (Excel) filter to column Compound Het Variant Prioritization to review all compound het variants:
- 01_TIER1
- 02_TIER2
SOP for Singleton Analysis of Rare Coding Variants that meet no Flags (rare_variant_singleton_genotypes_noflag.csv)
These are variants that DO NOT meet any of the flags (Tier 1 or 2 or LoF Gene or KV). This list will have inherited variants, variants in specific gene/gene list in mind, or if you want to look for a second variant, or if the patient has a more common phenotype.. In this output review all the variants/genes for clinical overlap.
SOP for Singleton Analysis of Non-Coding Known Variants (modifier_known_variant_singleton_genotypes.csv)
All variants meet the Known Pathogenic Variant Flag (previously reported P/LP variants on CV or DM (only if it is NOT CV B/LB)).
- Apply (Excel) filter to column “Tier Flag (Single Var)” for Tier 1 or 2 variants
- Remove Tier filtering then go to column “ACMG Disease” and uncheck NA, review those variants
- Remove ACMG filter, go to “Gene Link” filter for genes that have OMIM genes
- Quickly review phenotypes to see if it is a phenotype fit
We suggested to mainly focus on reviewing rare coding variants output (rare_variant_trio_genotypes.csv or rare_variant_singleton_genotypes.csv).
Columns:
1. Family ID: specify a family ID or use the same value as Individual ID to indicate this sample
is being used as a non family sample
2. Individual ID: sample name
3. Paternal ID: either the father's sample ID, or 0 if run as singleton.
4. Maternal ID: either the mother's sample ID, or 0 if run as singleton.
5. Sex: 1 for male, 2 for female.
6. Phenotype: 1 for control, 2 for case.
7. Sample Type: Exome or genome.
8. Capture Kit: The sequencing capture kit.