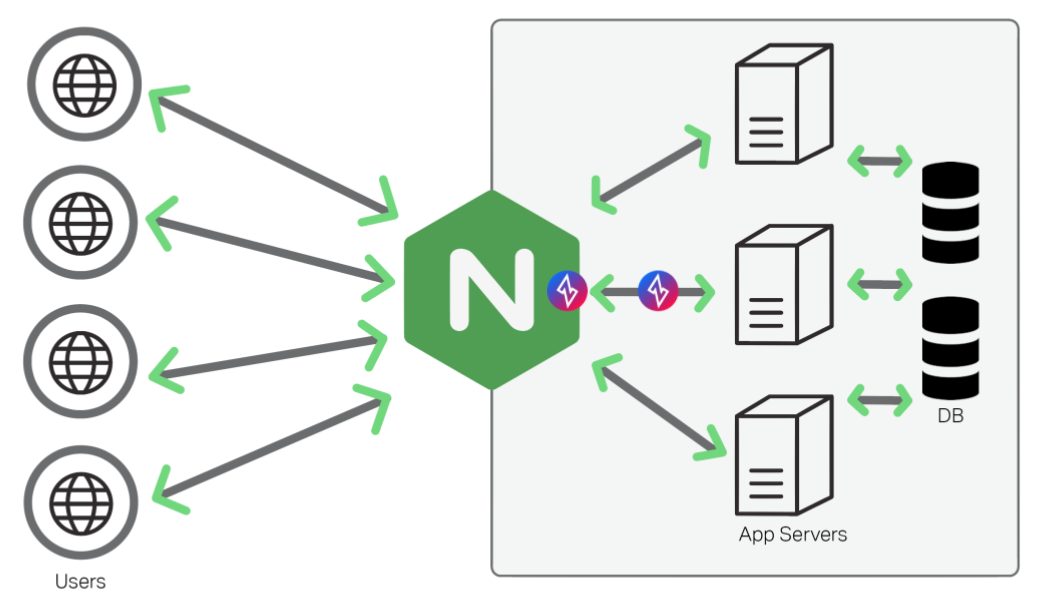
Non-blocking upstream module for Nginx allowing it to securely connect and reverse-proxy to a zero-trust Ziti Network
Learn about Ziti at ziti.dev
This module is not distributed with the Nginx source. See the installation instructions.
- Status
- Version
- Requirements
- Synopsis
- Description
- Directives
- Notes
- Trouble Shooting
- Known Issues
- Installation
- Compatibility
- Report Bugs
- TODO
This module is currently alpha quality, and should not yet be used in production.
This document describes ngx_http_ziti_module v0.1.1.
This module requires:
- Ziti C SDK
- The
--with-threadsoption for./configurefor compilation.
You'll need to update the config file to match your build environment.
This module assumes the existance of a named thread pool, ziti. To get this module to run, you'll need to add a thread_pool directive to your nginx.conf file, e.g.
thread_pool ziti threads=32 max_queue=65536;If you are using this module, adjust the thread count to the needs of your particular application (but the example above should work well).
thread_pool ziti threads=32 max_queue=65536;
load_module modules/ngx_http_ziti_module.so;
http {
...
server {
...
location /dark-service {
ziti_pass my-ziti-service-name;
ziti_identity /path/to/ziti-identity.json;
}
...
}
}This is an nginx upstream module integrating Ziti into Nginx in a non-blocking way.
Essentially it provides an efficient and flexible way for nginx internals to reverse-provy to a web server that is dark on the internet. Here the term dark means that the web server can only be accessed via a zero-trust Ziti connection.
syntax: ziti_buffer_size <size>
default: ziti_buffer_size 4k/8k
context: location, location if
Specify the buffer size for Ziti outputs. Default to the platform page size (4k/8k). The larger the buffer, the less streammy the outputing process will be.
Here's a sample configuration that shows how to adjust the Ziti buffer size:
...
location /some_path {
...
ziti_buffer_size 16384; # Handle up to 16k chunks
...
}
...syntax: ziti_client_pool_size max=<number>;
default: ziti_client_pool_size max=10
context: location
This module supports upstreaming multiple simultaneous HTTP requests to the target Ziti service. Each HTTP request is handled by an internal construct referred to as a client. If more HTTP requests arrive than the pool can simultaneously support, some requests will be queued, and will be handled once previous requests complete and a client is returned to the pool. When this client pool ceiling is hit, you will see a message in the log that resembles the following:
All available clients [10] are now in use; any additional requests will be queued until clients are returned to pool
The above log message is an indication that you may need to increase your client pool size.
This directive allows you to increase the size of the client pool.
Here's a sample configuration that shows how to adjust the client pool size:
...
location /some_path {
...
ziti_client_pool_size max=50; # Handle up to 50 simultaneous requests to Ziti
...
}
...The following options are supported:
max=<num>
Specify the capacity of the client pool for the current location block. The value must be at least 5. The default is 10.
syntax: ziti_identity <path-to-identity.json>
default: no
context: location
This directive specifies the absolute file system path to a Ziti identity file. The identity used must have permissions
to access the servicename specified on the ziti_pass directive that shares the location scope the ziti_identity resides in.
Here's a sample configuration that shows how to specify the Ziti identity:
...
location /some_path {
...
ziti_identity /some/path/to/identity.json;
...
}
...Note that the name identity.json in the above example is arbitrary (name it whatever you like). The actual file is produced during a separate Ziti Enrollment procedure not described here.
syntax: ziti_pass <servicename>
default: no
context: location, location if
phase: content
This directive specifies the name of the Ziti Service to which HTTP requests should be routed when being handled by the given location scope. The <servicename> argument can be the name of any Ziti service defined within the Ziti network for which the ziti_identity has access. The service is typically a web server that responds to HTTP requests.
Here's a sample configuration that shows how to specify the Ziti service name:
...
location /some_path {
...
ziti_pass my-dark-web-server;
...
}
...Note that the name my-dark-web-server in the above example is arbitrary (name it whatever you like). The actual service name is specified during a separate Ziti network administration/setup procedure not described here.
During development of this module, one tricky thing was figuring out how to resume processing of the HTTP request after the background Ziti operation had completed.
The nginx documentation on thread pools doesn't cover that topic. Also, the documentation on HTTP phases erroneously lists ngx_http_core_run_phases() as the function to call to resume processing. Using that doesn't work.
After digging through the nginx sources, it was discovered that the correct function was ngx_http_handler().
-
When you see the following error message in
error.log:ERROR ../library/config.c:41 load_config_file() <some path> - No such file or directorythen you should examine the
pathin yourziti_identitydirective to ensure it properly specifies the path to the Ziti identity file. -
When you see the following error message in
error.log:ERROR ../library/ziti_ctrl.c:164 ctrl_login_cb() INVALID_AUTH(The authentication request failed)then you should examine the
pathin yourziti_identitydirective to ensure that the specified Ziti identity file does indeed have permission to access the Ziti network you intend to connect to.
- Client HTTP requests that contain a
Connection: Closeheader are not processed correctly. A fix is forthcoming.
You will need to download source code from multiple places, and after doing so, you should have a directory structure that looks like the following:
.
+--<TOP-LEVEL-DIR>
|-- nginx-1.19.8 # or whatever version you downloaded
|-- ngx_http_ziti_module
|-- ziti-sdk-c
Users of this module should have an understanding of what a Ziti Network is. To use this module, it is also required to have a functioning Ziti Network available. To learn more about what Ziti is and how to setup a Ziti Network, head over to the official documentation site.
This module depends on the ziti-sdk-c so you must first download and build that.
The ziti-sdk-c build requires Cmake (3.12+),
so make sure cmake is on your path or replace the following cmake commands with the fully qualified path to the binary.
The ziti-sdk-c requires additional dependencies to be retreived. This is accomplished via the git submodule command. Fetch
the third party libs with git recursively. The following commands can be used:
$ cd <where you cloned the ziti-sdk-c>
$ git submodule update --init --recursiveThe ziti-sdk-c should be built to use the openssl libraries. The following command can be used to install them:
$ sudo apt install libssl-devBuilding the ziti-sdk-c on Linux can then be accomplished with:
$ cd <where you cloned the sdk>
$ mkdir build
$ cd build
$ cmake -DUSE_OPENSSL=ON .. && makeBuilding the ziti-sdk-c on Mac can be accomplished with:
$ cd <where you cloned the sdk>
$ mkdir build
$ cd build
$ cmake -G Ninja -DUSE_OPENSSL=on -DCMAKE_POSITION_INDEPENDENT_CODE=ON -DCMAKE_C_COMPILER=clang -DCMAKE_CXX_COMPILER=clang++ -DOPENSSL_ROOT_DIR=/usr/local/opt/openssl -DOPENSSL_LIBRARIES=/usr/local/opt/openssl/lib ..After the ziti-sdk-c is built, now download the source code for Nginx itself. You can find it here.
Now that all source code has been downloaded, you should now have a directory structure that looks like the following:
.
+--<TOP-LEVEL-DIR>
|-- nginx-1.19.8 # or whatever version you downloaded
|-- ngx_http_ziti_module
|-- ziti-sdk-c
- Building the
ngx_http_ziti_moduleon Linux can then be accomplished with:
$ cd <nginx src code dir>
$ ./configure \
--with-compat \
--with-debug \
--with-threads \
--without-http_rewrite_module \
--without-http_gzip_module \
--add-dynamic-module=../ngx_http_ziti_module \
--with-ld-opt=" \
../ziti-sdk-c/build/library/libziti.a \
../ziti-sdk-c/build/_deps/libsodium-build/lib/libsodium.a \
../ziti-sdk-c/build/_deps/uv-mbed-build/libuv_mbed.a \
../ziti-sdk-c/build/_deps/libuv-build/libuv_a.a \
-lssl \
-lcrypto \
-lm" \
--with-cc-opt=" \
-Wno-unused-variable \
-Wno-unused-but-set-variable \
-Wno-unused-value \
-Wno-cast-function-type \
-g -O0 \
-fno-strict-aliasing \
-Wno-unused-function \
-I/usr/local/include \
-I../ziti-sdk-c/includes \
-I../ziti-sdk-c/build/_deps/uv-mbed-src/include \
-I../ziti-sdk-c/build/_deps/libuv-src/include \
-I../ziti-sdk-c/build/_deps/http_parser-src \
-I../ziti-sdk-c/build/_deps/uv_link-src/include"
$ make- Building the
ngx_http_ziti_moduleon Mac can then be accomplished with:
$ cd <nginx src code dir>
$./configure \
--with-compat \
--with-debug \
--with-threads \
--add-dynamic-module=../ngx_http_ziti_module \
--with-ld-opt=" \
../ziti-sdk-c/build/library/libziti.a \
../ziti-sdk-c/build/_deps/libuv-build/libuv_a.a \
../ziti-sdk-c/build/_deps/libsodium-build/lib/libsodium.a \
../ziti-sdk-c/build/_deps/uv-mbed-build/libuv_mbed.a \
/usr/local/Cellar/openssl@1.1/1.1.1j/lib/libssl.a \
/usr/local/Cellar/openssl@1.1/1.1.1j/lib/libcrypto.a" \
--with-cc-opt=" \
-g -O0 \
-fno-strict-aliasing \
-fno-pie \
-Wno-unused-function \
-I/usr/local/include \
-I../ziti-sdk-c/includes \
-I../ziti-sdk-c/build/_deps/uv-mbed-src/include \
-I../ziti-sdk-c/deps/uv-mbed/deps/libuv/include \
-I../ziti-sdk-c/build/_deps/http_parser-src \
-I../ziti-sdk-c/build/_deps/uv_link-src/include \
-I../ziti-sdk-c/build/_deps/libuv-src/include"
$ makeYou should now have a ./objs/ngx_http_ziti_module.so that you can copy into your Nginx's modules directory. This is typically accomplished with:
$ sudo make installYou should then update your nginx.conf file with suitable Directives.
This module has been tested on Linux and Mac OS X. Reports of successful use on other POSIX-compliant systems will be highly appreciated.
The following versions of Nginx should work with this module:
- 1.18.x
- 1.19.x
Earlier versions of Nginx may not work. We haven't tested.
Please submit bug reports, wishlists, or patches by
- creating a ticket on the issue tracking interface provided by GitHub,
- things.