In this project, we focus on the researches applying natural language processing (NLP) technologies in the finance domain. We scrape tweets for forex traders then apply sentiment analysis to generate investment insight.
Sentiment analysis can use natural language processing, artificial intelligence, text analysis and computational linguistics to identify the attitude of several topics. In this project, we focus on the researches applying natural language processing (NLP) technologies in the finance domain. First, we will dig into some people who have huge impact on financial market. Second, we will predict foreign exchange rates by making use of the trending topics from Twitter, using a machine learning based model.
Forex trading is fast, very fast, and Twitter fits like a glove to any forex trader’s hand. There’s lots of quick and useful information coming in the form of tweets and sometimes too much information. We got a list of top forex twitter accounts from here, each one coming with different characteristics, to suit traders interested in different aspects of trading (technical, fundamental, educational,, sentiment, a mix of some or all, etc.). We Crawled 63 forex twitter accounts listed on the website and store it into trader_account list for future use. Here is our notebook.
Twint is an advanced Twitter scraping tool written in Python that allows for scraping Tweets from Twitter profiles without using Twitter's API. We utilise twint to get tweets, and store the results into a pandas dataframe. We created a simple function that you can see in the actual project that integrate Pandas with Twint API for this part. Next, there are many features we have from the query we just did. There’s a lot of different things to do with this data, but for this project we’ll only use some of them, namely date, time, username, tweet, hashtags, likes_count, replies_count, and retweets_count.
We downloaded the forex data from Mecklai Financial. After pre-processing, we get a new column "label", which means the differentiation between two days. Label {0, 1} is the forex movement label telling whether the forex trade price is up or down after a certain time. For this study, we used only GBP/USD price from the Macrotrends website. Macrotrends provides lots of foreign exchange data, such as EUR/USD, USD/JPY, USD/CNY, AUD/USD, EUR/GBP, USD/CHF, EUR/CHF, GBP/JPY and EUR/JPY. Moreover, they also illustrate interactive historical chart showing the daily forex price.
The forex movement prediction task can be defined as assigning movement label for the tweets input. The forex prediction is conducted as a binary classification task (up or down). The evaluation metrics are F1 and Matthews Correlation Coefficient (MCC). MCC is often reported in stock movement forecast (Xu and Cohen, 2018; Ding et al., 2016) because it can overcome the data imbalance issue.
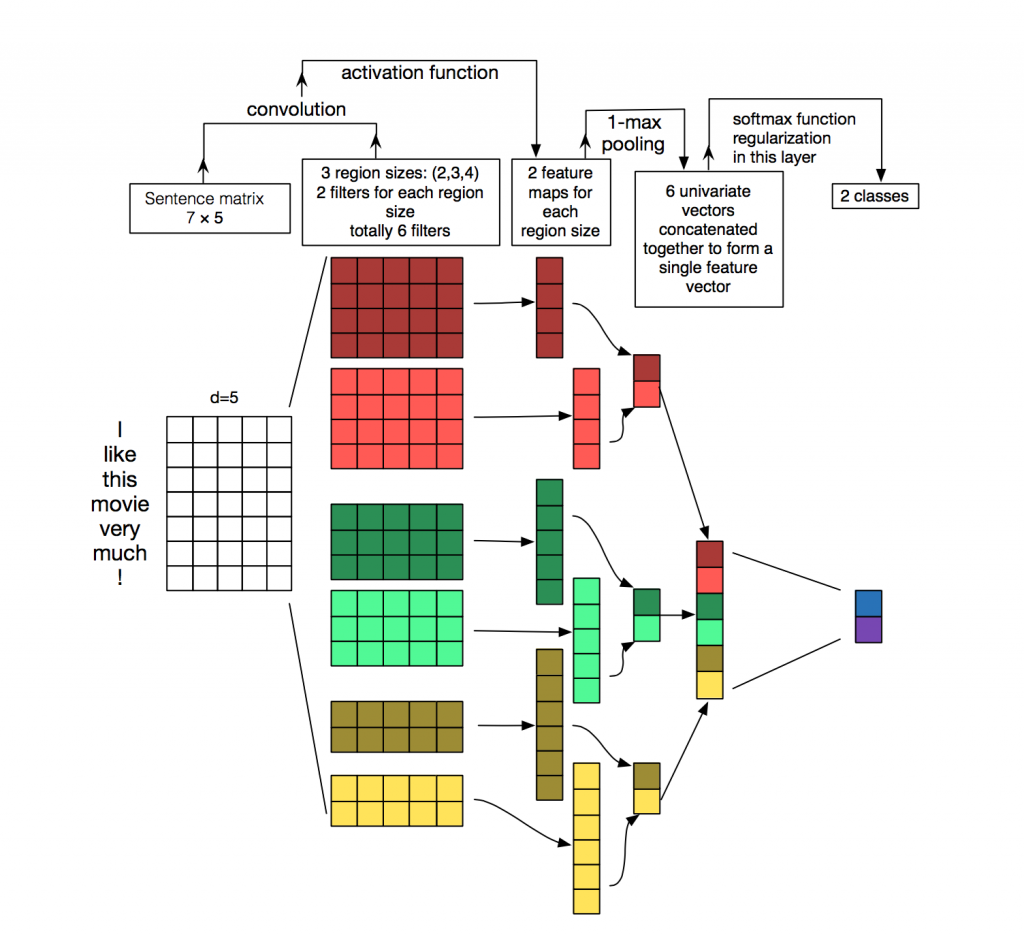
In this work, we combine the strengths of both CNN and LSTM for sentence representation and text classification. CNN-LSTM utilizes CNN to extract a sequence of higher-level phrase representations, and are fed into a LSTM to obtain the sentence representation. CNN-LSTM is able to capture both local features of phrases as well as global and temporal sentence semantics.
Word2vec is a method to efficiently create word embeddings proposed by Google and has been around since 2013. Distributed representations of words in a vector space help learning algorithms to achieve better performance in natural language processing tasks. Jay Alammar articulates Word2Vec in his blog.
Convolutional neural networks (CNN) utilize layers with convolving filters that are applied to local features (LeCun et al., 1998). Originally invented for computer vision, CNN models have subsequently been shown to be effective for NLP and have achieved excellent results in semantic parsing (Yih et al., 2014), search query retrieval (Shen et al., 2014), sentence modeling (Kalchbrenner et al., 2014), and other traditional NLP tasks (Collobert et al., 2011).
Reference:
- Alon Jacovi, Understanding Convolutional Neural Networks for Text Classification: paper
- Yoon Kim, Convolutional Neural Networks for Sentence Classification: paper
Vanilla RNNs (Recurrent Neural Networks) suffer from vanishing and exploding gradient problems. LSTMs (Long Short Term Memory) deal with these problems by introducing new gates, such as input and forget gates, which allow for a better control over the gradient flow and enable better preservation of long-range dependencies. The long range dependency in RNN is resolved by increasing the number of repeating layer in LSTM. GRUs are similar to LSTMs, but use a simplified structure. They also use a set of gates to control the flow of information, but they don't use separate memory cells, and they use fewer gates. Raimi Karim created a animated illustration for RNN, LSTM and GRU in his blog.
The overview of our model is displayed above. The model can be generally devided into three steps:
In step 1, we conduct zero-shot learning on this paragraph to select the most important tweets on a daily basis. Tweets are then ranked by latent embedding approach, which is a common approach to zero shot learning in the computer vision setting. In the text domain, we have the advantage that we can trivially use a single model to embed both the data and the class names into the same space, eliminating the need for the data-hungry alignment step. We therefore decided to run some experiments with Sentence-BERT, a recent technique which fine-tunes the pooled BERT sequence representations for increased semantic richness, as a method for obtaining sequence and label embeddings.
In step 2, we conduct some text pre-processing work. Text classification in general works better if the text is preprocessed well. Do give some extra time to it, it will all be worth it in the end.
In step 3, we combine top k daily tweets in order to aggregate semantic information at the inter-groups level. Finally, pass it into a softmax layer to normalize it into a probability distribution consisting of 2 probabilities (up or down) proportional to the exponentials of the input numbers.
We choose the transformers from HuggingFace as implement and choose the bert-base-uncased version. We truncate the BERT input to 64 tokens and fine-tune the BERT parameters during training. We adopt the Adam optimizer with the initial learning rate of 2e-5. We apply the dropout regularization with the dropout probability of 0.25 to reduce over-fitting. The batch size is 32. The training epoch is 4. The weight of L2 regularization is 0.1. When splitting the dataset, we guarantee that the samples in train set are previous to samples in valid set and test set to avoid the possible information leakage. The forex prediction is conducted as a binary classification task (up or down). The evaluation metrics are F1 and Matthews Correlation Coefficient (MCC). MCC is often reported in stock movement forecast because it can deal with the data imbalance problem.
In this project we investigated sentiment analysis and signal processing features for predicting the forex daily trend. The prediction is posed as a binary classification problem for which the model predicts whether forex is going up or down. Both word2vec and aggregated BERT are used to find best feature subsets for the classification problem. The results show that the proposed model still has a long way to go.