A.I. first coined in 1956 in the Dramouth Summer Research Project by John Mc Carthy
at that time the strongest computor could provide 200000 operations/s
today (2019) 130 quadrillon operations/s (1s->20611years)
A.I. revolution these last 20years when people started to be connected, an data started to build
The Hebbian Learning Rule is a learning rule that specifies how much the weight of the connection between two units should be increased or decreased in proportion to the product of their activation. The rule builds on Hebbs's 1949 learning rule which states that the connections between two neurons might be strengthened if the neurons fire simultaneously. The Hebbian Rule works well as long as all the input patterns are orthogonal or uncorrelated. The requirement of orthogonality places serious limitations on the Hebbian Learning Rule. A more powerful learning rule is the delta rule, which utilizes the discrepancy between the desired and actual output of each output unit to change the weights feeding into it.
In real neurons, time-domain signal pulses travel along the dendrites, and then arrive at the neuronal body independently, and are integrated in time and space inside it (some excite, some inhibit). When the neuronal body is triggered, it produces a time-dependent set of pulses down its axon, that split up as it branches and take time to travel out to the synapses, which themselves exhibit a non-linear, delayed, time-dependent integration as the chemical neurotransmitter signal passes across the synapse to eventually trigger a signal in the post-synaptic dendrite. There is a strengthening of the synapse, or learning, in the process, if the neurons on both sides of it fire together within a certain interval, called Hebbian learning. (https://www.quora.com/What-is-the-simplest-example-for-a-Hebbian-learning-algorithm-in-terms-of-AI)
Machine Learning is divided in many fields, mainly we will study:
- Reinforcement Learning (like a baby learns)
- Supervised Learning (included training, needs a supervisor!)
- Unsupervised Learning (usually grouping, clustering - helps to find patterns)
First neuron programmed in 1958, to recognized a circle from triangle.
Perceptron models are contained within the set of neural net models. A (single layer) perceptron is a single layer neural network that works as a linear binary classifier. If you're talking about a multilayer perceptron (MLP), however, then the term is the same as a feed-forward neural network. MLPs are useful in research for their ability to solve problems stochastically, which often allows approximate solutions for extremely complex problems like fitness approximation. In artificial intelligence, stochastic programs work by using probabilistic methods to solve problems.
Summary of the code operation:
Set up the arrays and assign random weights.
Start a loop which runs through each item of training data.
Randomise the order in which the training data is run through each iteration to ensure that convergence on local minimums does not occur.
Feed the data through the network calculating the activation of the hidden layer’s nodes, output layer’s nodes and the errors.
Back propagate the errors to the hidden layer.
Update the associated weights.
Compare the error to the threshold and decide whether to run another cycle or if the training is complete.
Send a sample of the training data to the Serial monitor every thousand cycles.
Mathematically, we can describe Hebbian learning as:
w#ij [ n + 1 ] = w#ij [ n ] + ε x x#i [ n ] x x#j [ n ]
Δw#ij=ε·pre#i·post#j
Here, ε is a learning rate coefficient, and x are the outputs of the ith and jth elements.
It was proposed by Rumelhart and Zipser (1985) and is referred to as the competitive learning rule:
Δw#ij=ε·pre#i·post#j−ε·post#j·w#ij
Δw#ij=ε·post#j·(pre#i−w#ij)
Oja Rule:
Δw#ij=ε·post#j·(pre#i−post#j.w#ij)
Δw#ij=ε·(post#j·pre#i−post#j^2.w#ij)
(1, 2, 3) • (8, 10, 12) = 1×8 + 2×10 + 3×12 = 64
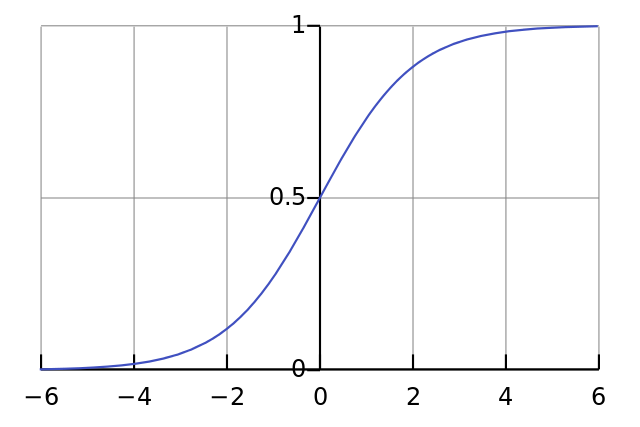
This is our "nonlinearity". While it can be several kinds of functions, this nonlinearity maps a function called a "sigmoid". A sigmoid function maps any value to a value between 0 and 1.
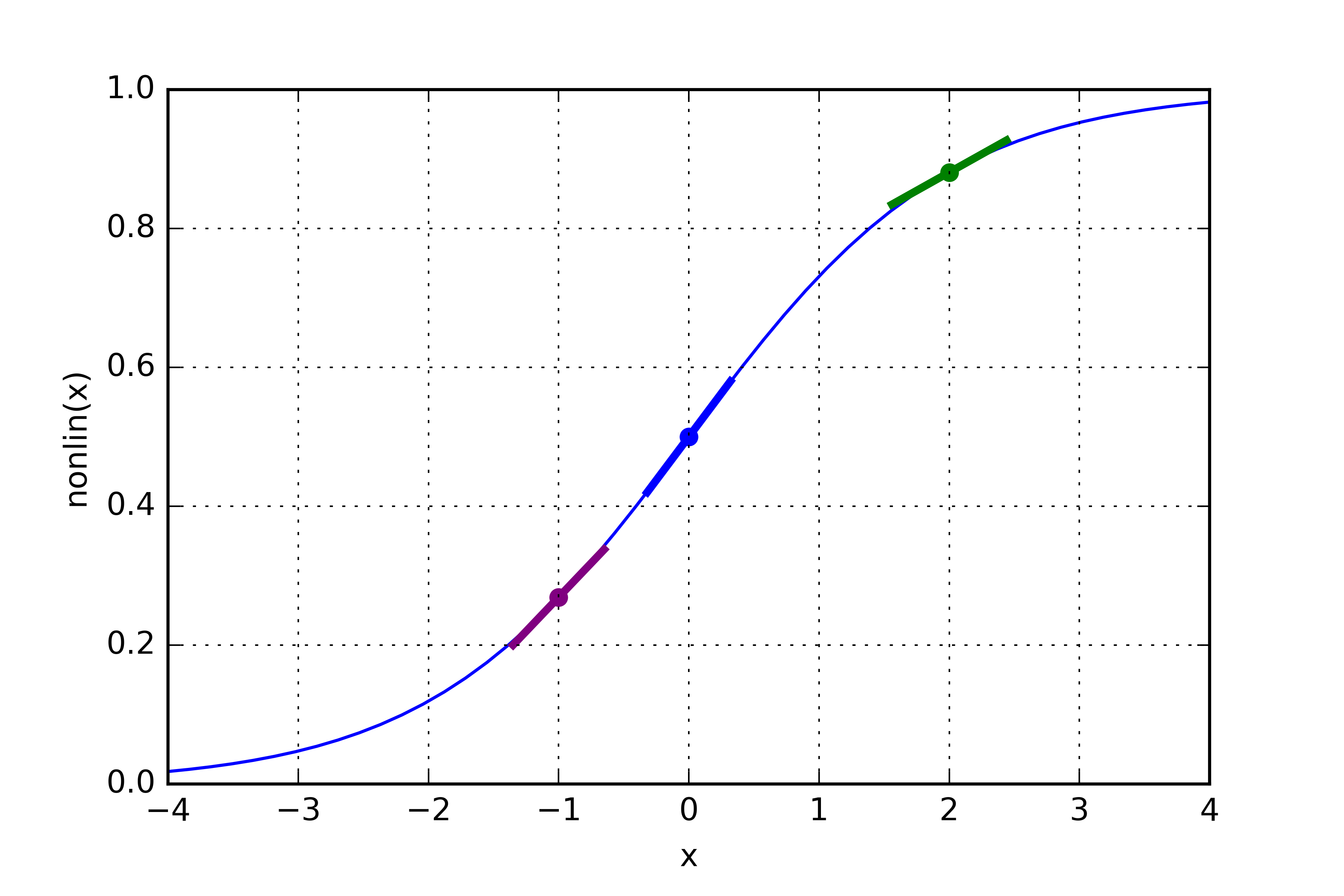
The derivative of the sigmoid for error backward correction:
used for: l1_delta = l1_error * nonlin(l1,True)
When we multiply the "slopes" by the error, we are reducing the error of high confidence predictions. Look at the sigmoid picture again! If the slope was really shallow (close to 0), then the network either had a very high value, or a very low value. This means that the network was quite confident one way or the other. However, if the network guessed something close to (x=0, y=0.5) then it isn't very confident. We update these "wishy-washy" predictions most heavily, and we tend to leave the confident ones alone by multiplying them by a number close to 0.
ADDITIONAL LINKS: An easy-to-follow scikit-learn tutorial that will help you get started with Python machine learning https://pythonprogramming.net/flat-clustering-machine-learning-python-scikit-learn/
How to create a poet / writer using Deep Learning (Text Generation using Python)? https://www.analyticsvidhya.com/blog/2018/03/text-generation-using-python-nlp/
Unsupervised learning only trains using inputs, and the network has to figure out how they relate to each other. This method is used to solve Clustering problems, estimation problems.
Learnind without teacher, without knowing the correct answer 2 types Data Visualisation PCA Principal Component Analysis for Data preprocessing and Data visualization Clustering for Data classification, segmenting into a collection of objects "clusters"
Our first algorithm to cover is the K-Means algorithm. The idea of K-Means is to attempt to cluster a given dataset into K clusters. https://pythonprogramming.net/machine-learning-clustering-introduction-machine-learning-tutorial/ See Unsupervise-KMeans.py
Reinforcement learning (RL) is an area of machine learning concerned with how software agents ought to take actions in an environment so as to maximize some notion of cumulative reward. Reinforcement learning is one of three basic machine learning paradigms, alongside supervised learning and unsupervised learning.
Backpropagation theory and formulas: https://mattmazur.com/2015/03/17/a-step-by-step-backpropagation-example/
KMeans from scratch: https://pythonprogramming.net/k-means-from-scratch-machine-learning-tutorial/
Python code for regression types/ linear models: https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/linear_model.html
https://www.udemy.com/cluster-analysis-unsupervised-machine-learning-python/
Unsupervised Machine Learning: Flat Clustering K-Means clusternig example with Python and Scikit-learn: https://pythonprogramming.net/flat-clustering-machine-learning-python-scikit-learn/
Complete Robot Make Tutorial https://www.reddit.com/r/learnmachinelearning/comments/ckoy0k/want_to_build_your_own_machine_learning_robot/
Reddit serach: https://www.reddit.com/search/?q=neural%20network%20arduino
Example character recognition: http://neuralnetworksanddeeplearning.com/chap1.html