This is my attempt to learn ruby on rails. I will be making sample apps by following tutorials.
rvm list # List down the ruby versions
rvm use [version ] # Switch the ruby version
rails -v # Current rails version
rails _5.3.4_ new [project_name] # Generate new project
rails s -p [port] # Run rails by specifying a port
rais s --binding=0.0.0.0 -p [port] # Start with with host name and port
rails c # Open the console
ruby [filename]
rails routes # List down all available routes.
It's a dynamic, OO, Open source programming language developed by Martz. Ruby is considered to follow the principle of POLA (principle of least astonishment). It means that the language behaves in such a way to minimize the confusion for experienced users. It has been for 20+ years. With rails, the popularity of Ruby increased.
- Pure OO Language
- No multiple inheritance
- Modules and Classes
- Modules contain only methods
- Supports mixings - Define methods inside modules and use as required them in classes
- Loosely typed
- When a method is called on an object, Ruby only looks up at the name irrespective of the type of object
- Mutating constants wont stop the execution of the program
- Naming:
- Constants start with capital letter
- Globals with $
- Instance var @
- Class var @@
- Method names usually follow snake case
- Case sensitive
However, JRuby and Rubinius, which are popular implementations of ruby are compiled
- Rubinius -COMPILES(Rubinius compiler)-> BYTECODE -COMPILES(Rubinius JIT Compiler (C++)) @ Runtime-> MACHINE CODE
rbx compile simple.rb -o simple.bytecode - JRuby - -COMPILES(JRuby compiler(Java)-> BYTECODE -COMPILES(Execute bytecode using JVM (JAVA JIT Compiler (C))) @ Runtime-> MACHINE CODE
rvm jruby-head
ruby simple.rb
jrubyc simple.rb
ls # simple.class simple.rb
javap -c simple.class > simple.bytecode
rails --tasks # view all possible tasks
rails [class_name]:[function_name] # run a task
-
Ruby Variables local global class instance
-
Strings
-
string.class - Type of String
-
string.methods - All methods
-
.to_s .nil? .empty? .exists? .length .reverse
-
ctrl + lwill clear up irb -
Strings are pass by value
-
#{ } - Acts as a template string for interpolation
-
Single quotes doesn't work with interpinolation
-
Escape characters also doesn't work with single quotes
-
Empty spaces are counted as characters
" ".nil?# false
- Conversions
.to_s .to_i .to_f .odd? .even? .round
- Methods and branching
- Return is implicit
- Comments
- Hash for single line comment
- Multi line comments
=begin
=end
- Model Name: Singular, First letter upper case.
- Table Name: Plural, lower case model name
- Model File: Snake case
- Controller file: Snake Case
- Classes: Pascal case More @ git
Rails framework follows the MVC architecture.
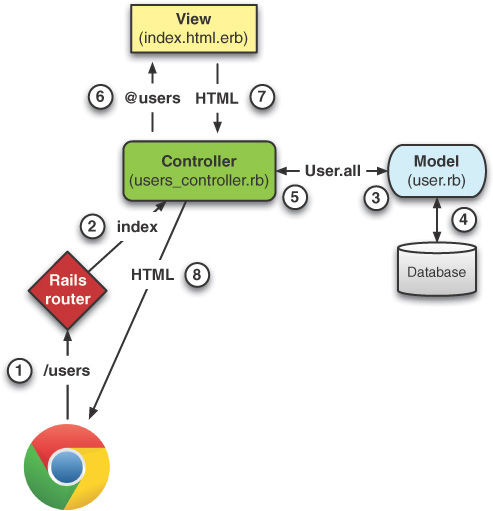
The data flow will be as follows
- Call the route
- Controller
- Model Optional
- Database Optional
- View
Common errors in Ruby are;
NameError: uninitialized constant []
NameError: uninitialized constant Object::Something
- Ruby is case sensitive.
- Extends from NameError exception class
- Thrown when the code refers to an unknown variable (The code can't resolve)
- Classes start with upper case letters, instance variables or class variables start with lower case, Therefore it can be a side effect of misusing.
Rails Router has the following types
- Collection routes (Index action) - Used to show a collection of items /articles
- Member routes (show action) - Used to show a specific item /articles/:id
You can setup the root route to goto any route.
root articles#index