- Main repository & issues: gitlab.cern.ch/mrieger/CMSSW-DNN
- Code mirror: github.com/riga/CMSSW-DNN
This interface provides simple and fast access to TensorFlow in CMSSW and lets you evaluate trained models right within your C++ modules. It does not depend on a converter library or custom NN implementation. In fact, it is a thin layer on top of TensorFlow's C++ API (available via exernals in /cvmfs) and handles session and graph loading, custom exceptions, and thread management within CMSSW. As a result, you can load and evaluate every model that was previously trained and saved in Python (or C++).
To learn more about TensorFlow 2, see this tutorial.
The interace is part of the official CMSSW release, located at PhysicsTools/TensorFlow. Therefore, this development repository should be set up in a CMSSW environment via
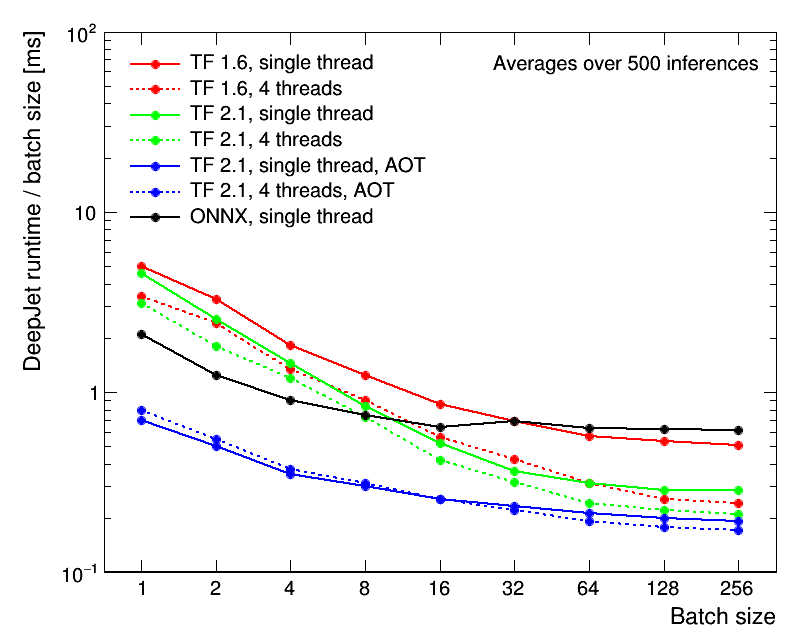
git clone https://gitlab.cern.ch/mrieger/CMSSW-DNN.git PhysicsToolsThe following comparison shows the performance of the interface, evaluated using the DeepJet model within CMSSW for different TensorFlow versions and threading strategies (CPU only).
The CMS software environment evolved since the first working interface version in 8_0_X. Hence, there are multiple versions, depending on the deployed TensorFlow API. However, since 9_4_X, the interface API is essentially frozen and handles all changes made within TensorFlow internally. The following table summarizes all available versions:
| CMSSW version | TF API & version (externals) | Interface branch |
|---|---|---|
| 11_1_X | C++, 2.1.0 | tf_cc_2.1 |
| 10_6_X | backport coming soon | |
| 10_2_X | C++, 1.6.0 | tf_cc_1.6 |
| 10_1_X | C++, 1.5.0 | tf_cc_1.5 |
| 9_4_X | C++, 1.3.0 | tf_cc_1.3 |
| 9_3_X | C, 1.1.0 | tf_c |
| 8_0_X | CPython, 1.1.0 | tf_py_cpython |
Please note that TensorFlow versions above 1.6.0 were not integrated into CMSSW due to issues related version incompatibilities of Protobuf and/or Eigen.
You can find examples that show how to use the interface at mrieger/CMSSW-TensorFlowExamples.
TensorFlow provides multiple ways to save a computational graph. Depending on which method is used, the API calls to load a graph in CMSSW vary.
After defining and training a neural network in Python, you typically don't want to continue training within CMSSW. If this is the case, you want to save a constant graph. Otherwise, jump to the SavedModel format.
A constant graph is saved in a single protobuf file. During the saving process, variables are converted to constant tensors, and ops and tensors that are no longer required (cost function, optimizer, etc.) are removed. The memory consumption during evaluation in CMSSW - especially in multi-threaded mode - can greatly benefit from this conversion.
import tensorflow as tf
# for tf v2, fgo into v1 compatibility mode
if tf.__version__.startswith("2."):
tf = tf.compat.v1
tf.disable_eager_execution()
# define your model here
x_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10], name="input")
W = tf.Variable(tf.ones([10, 1]))
b = tf.Variable(tf.ones([1]))
y = tf.add(tf.matmul(x_, W), b, name="output")
# create a session and initialize everything
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
# training
...
# convert and save it
outputs = ["output"] # names of output operations you want to use later
constant_graph = tf.graph_util.convert_variables_to_constants(
sess, sess.graph.as_graph_def(), outputs)
tf.train.write_graph(constant_graph, "/path/to", "constantgraph.pb", as_text=False)#include "PhysicsTools/TensorFlow/interface/TensorFlow.h"
//
// setup
//
// load the graph definition, i.e. an object that contains the computational graph
tensorflow::GraphDef* graphDef = tensorflow::loadGraphDef("/path/to/constantgraph.pb");
// create a session
tensorflow::Session* session = tensorflow::createSession(graphDef);
// create an input tensor
tensorflow::Tensor input(tensorflow::DT_FLOAT, { 1, 10 }); // single batch of dimension 10
// example: fill a single batch of the input tensor with consecutive numbers
// -> [[0, 1, 2, ...]]
for (size_t i = 0; i < 10; i++) input.matrix<float>()(0, i) = float(i);
//
// evaluation
//
std::vector<tensorflow::Tensor> outputs;
tensorflow::run(session, { { "input", input } }, { "output" }, &outputs);
//
// process outputs
//
// print the output
// -> [[float]]
std::cout << outputs[0].matrix<float>()(0, 0) << std::endl;
// -> 46.
// cleanup
tensorflow::closeSession(session);
delete graphDef;For more examples, see TensorFlow/test/testGraphLoading.cc.
TensorFlow's SavedModel serialization format is a more generic
import tensorflow as tf
# for tf v2, fgo into v1 compatibility mode
if tf.__version__.startswith("2."):
tf = tf.compat.v1
tf.disable_eager_execution()
# define your model here
x_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10], name="input")
W = tf.Variable(tf.ones([10, 1]))
b = tf.Variable(tf.ones([1]))
y = tf.add(tf.matmul(x_, W), b, name="output")
# create a session and initialize everything
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
# training
...
# save it
builder = tf.saved_model.builder.SavedModelBuilder("/path/to/simplegraph")
builder.add_meta_graph_and_variables(sess, [tf.saved_model.tag_constants.SERVING])
builder.save()The tag passed to add_meta_graph_and_variables serves as an identifier for your graph in the saved file which potentially can contain multiple graphs. tf.saved_model.tag_constants.SERVING ("serve") is a commonly used tag, but you are free to use any value here.
#include "PhysicsTools/TensorFlow/interface/TensorFlow.h"
//
// setup
//
// load the meta graph, i.e. an object that contains the computational graph
// as well as some meta information
tensorflow::MetaGraphDef* metaGraph = tensorflow::loadMetaGraph("/path/to/simplegraph");
// create a session
// we need to pass the export directory again so that the session can
// properly initialize all variables
tensorflow::Session* session = tensorflow::createSession(metaGraph, "/path/to/simplegraph");
// create an input tensor
tensorflow::Tensor input(tensorflow::DT_FLOAT, { 1, 10 }); // single batch of dimension 10
// example: fill a single batch of the input tensor with consecutive numbers
// -> [[0, 1, 2, ...]]
for (size_t i = 0; i < 10; i++) input.matrix<float>()(0, i) = float(i);
//
// evaluation
//
std::vector<tensorflow::Tensor> outputs;
tensorflow::run(session, { { "input", input } }, { "output" }, &outputs);
//
// process outputs
//
// print the output
// -> [[float]]
std::cout << outputs[0].matrix<float>()(0, 0) << std::endl;
// -> 46.
// cleanup
tensorflow::closeSession(session);
delete graphDef;For more examples, see test/testMetaGraphLoading.cc.
As Keras can be backed by TensorFlow, the model saving process is identical:
import tensorflow as tf
# for tf v2, fgo into v1 compatibility mode
if tf.__version__.startswith("2."):
tf = tf.compat.v1
tf.disable_eager_execution()
sess = tf.Session()
from keras import backend as K
K.set_session(sess)
# define and train your keras model here
...
# save at as a constant graph
outputs = [...]
constant_graph = tf.graph_util.convert_variables_to_constants(
sess, sess.graph.as_graph_def(), outputs)
tf.train.write_graph(constant_graph, "/path/to", "constantgraph.pb", as_text=False)If you are aiming to use the TensorFlow interface in your personal CMSSW plugin (!), make sure to include the following lines in your plugins/BuildFile.xml:
<use name="PhysicsTools/TensorFlow" />If you are using the interface in a file in the src/ or interface/ directory of your module, make sure to create a (global) BuildFile.xml containing (at least):
<use name="PhysicsTools/TensorFlow" />
<export>
<lib name="1" />
</export>Please make sure you do not import the TensorFlow python module in a CMSSW Python configuration files. TensorFlow will crash when it is loaded again within the same process via C++. Currently, there is no way to shutdown the TensorFlow environment within Python.
You can set the number of threads when loading a GraphDef, MetaGraphDef, and Session. By default, only one thread is used but it's easy to use more.
When loading a constant graph:
// load the graph
tensorflow::GraphDef* graphDef = tensorflow::loadGraphDef("/path/to/constantgraph.pb");
// create a session and use 4 threads
tensorflow::Session* session = tensorflow::createSession(graphDef, 4);
// set inputs as shown above
...
// evaluation
std::vector<tensorflow::Tensor> outputs;
std::string threadPool = "tensorflow"; // use "tbb" to enable scheduling by TBB
tensorflow::run(session, { { "input", input } }, { "output" }, &outputs, threadPool);When loading a saved model:
// load the meta graph
tensorflow::MetaGraphDef* metaGraph = tensorflow::loadMetaGraph("/path/to/simplegraph", 4);
// create a session and use 4 threads
tensorflow::Session* session = tensorflow::createSession(metaGraph, "/path/to/simplegraph", 4);
// set inputs as shown above
...
// evaluation
std::vector<tensorflow::Tensor> outputs;
std::string threadPool = "tensorflow"; // use "tbb" to enable scheduling by TBB
tensorflow::run(session, { { "input", input } }, { "output" }, &outputs, threadPool);By default, TensorFlow logging is quite verbose. This can be changed via setting the TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL environment varibale before calling (e.g.) cmsRun, or via calling tensorflow::setLogging(level) in your code. Log levels:
TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL value |
Verbosity level |
|---|---|
| "0" | debug |
| "1" (default) | info |
| "2" | warning |
| "3" | error |
| "4" | none |
Forwarding to the MessageLogger service is not possible yet.