Using LightGBM to predict bank customers' credit risk, based on their financial history.
- There are two types of credit: good credit and bad credit.
- The main task is to predict if a customer will be going to pay his credit according to the available data.
Note: the dataset used for this task is really small (the
customer_dataset has 1125 rows, and thepayment_datahas 8250 rows), so that will definitely impact in the accuracy of the final model.
- max_depth: Set this parameter to prevent trees from growing too deep. Shallow trees have less likelihood to overfit. Setting this parameter is particularly important if the dataset is small.
- num_leaves: Controls the complexity of the tree model. The value should be less than 2^(max_depth) to prevent overfitting. Setting
num_leavesto a large value can increase accuracy at the risk of a higher chance of overfitting. - min_data_in_leaf: Setting this parameter to a large value can prevent trees from growing too deep. This is another parameter you can set to help control overfitting. Setting the value too large can cause underfitting.
- max_bin: LightGBM groups the values of continuous features into discrete bukcets using histograms. Set
max_binto specify the number of bins that the values will be grouped in. A small value can help control overfitting and improve training speed, while a larger value improves accuracy. - feature_fraction: This parameter enables feature subsampling. This parameter specifies the fractions of features that will be randomly selected in each iteration. For instance, setting
feature_fractionto 0.75 will randomly select 75 % of the features in each iteration. Setting this parameter can increase training speed and help prevent overfitting. - bagging_fraction: Specifies the fraction of data that will be selected in each iteration. For instance, setting
bagging_fractionto 0.75 will randomly select 75 % of the data in each iteration. Setting this parameter can increase training speed and help prevent overfitting. - num_iteration: Sets the number of boosting iterations. The default is 100. For multiclass classification, LightGBM builds
num_class*num_iterationtrees. Setting this parameter influences training speed. - objective: Like XGBoost, LightGBM supports multiple objectives. The default objective is set to regression. Set this parameter to specify the type of tasj that your model is trying to perform. For regression tasks, the options are
regression_l2,regression_l1,poisson,quantile,mape,gamma,huber,fair, ortweedie. For classification tasks, the options arebinary,multiclass, ormulticlassova. It is important to set the objective correctly to aovid unpredictable results or poor accuracy.
I performed a grid search to find the best value for the learning_rate, n_estimators, and for num_leaves.
The final results were:
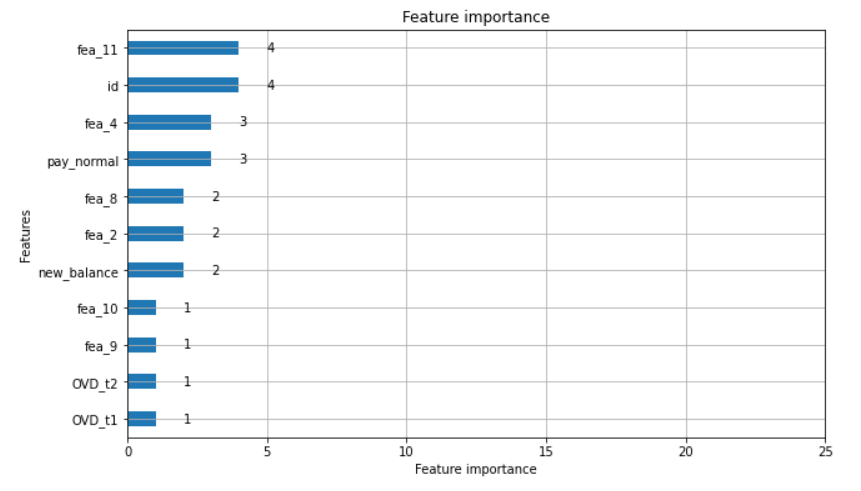
- The accuracy of prediction is: 0.8017751479289941
- The roc_auc_score of prediction is: 0.5953703703703704
- The null accuracy is: 0.7988165680473372
The final accuracy of the model is 0.802. It is not the most accurate model but is enough for the small dataset that I used for the train stage.
The next time, I could use a bigger dataset so we can be able to see the real capabilities of this algorithm.