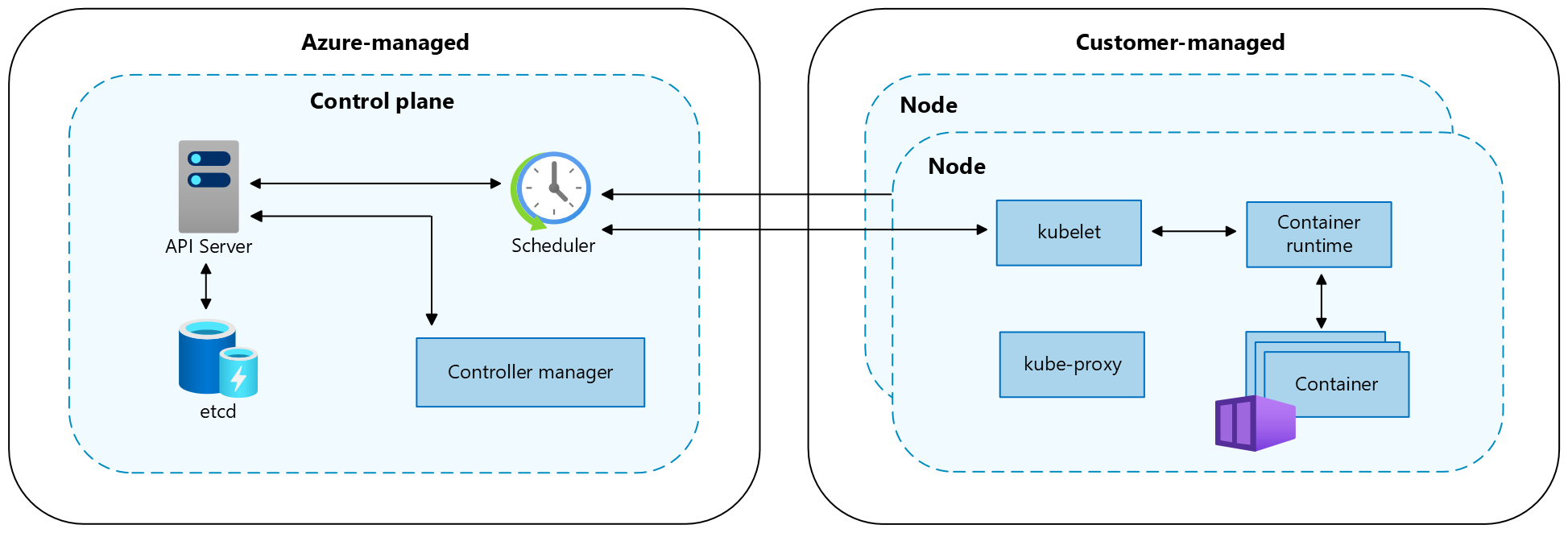
-
Control Plane Components The control plane's components make global decision about the cluster. Examples of the decisions are scheduling new pods and scaling the number of pods in a deployment to satisfy the replicas requirement.
-
❗ CORRECT about AKS control plane In an AKS cluster, we don't have to worry about the control plane components. They are managed by the AKS service. We can't access them directly. However, we can use the kubectl command to interact with them.
-
Kube-scheduler The main responsibility of kube-scheduler is to help newly created Pods to find a suitable node where they can run. There are many factors that kube-scheduler considers when making its decision, following are some examples:
- individual and collective resource requirements (CPU, memory, storage, etc.)
- hardware/software/policy constraints (AMD vs Intel, SSD vs HDD, etc.)
- affinity and anti-affinity specifications
- data locality
- inter-workload interference and deadlines
In Kubernetes, scheduling refers to making sure that Pods are matched to Nodes to taht Kubelet can run them.
Kube-scheduler is the default scheduler for Kubernetes. You can also write your own scheduler. Kube-scheduler will select an optimal node for those not yet scheduled pods. Also, the API allows user to specify a node for a Pod when users create it. Our focus today is figuring out how kube-scheduler achieves the above goals.
- How Kube-scheduler find out the optimal node for a Pod?
- How to specify a node for a Pod when creating it?
The following steps will be taken by kube-scheduler to find out the optimal node for a Pod:
- Filtering At this step, kube-scheduler will filter out those nodes that don't meet the Pod's requirements. For example, if the Pod requires a minimum of 20 cores, then those nodes without enough cores will be filtered out. This is achieved by the PodFitsResources filter.
- Scoring Among those nodes that survived the filtering step, kube-scheduler will score and rank all the nodes. The optimal node will be the one with the highest score.
Finaly, kube-scheduler will bind the Pod to the optimal node. If there are several nodes with the same rank (score), a random node will be selected.
Schedule a pod with super high CPU requirement so that no node can afford it
k run highcpu --image=nginx --dry-run=client -o yaml > HighCPU-Pending.yamlk top nodes- Add the following content
resources: requests: cpu: "4000m"
k apply -f HighCPU-Pending.yamlk get po -wk describe po highcpu
Schedule a pod to a specific node using nodeSelector.
k get nodes --show-labelsk label node aks-nodepool1-15774875-vmss000000 nodecolor=redk label node aks-nodepool1-15774875-vmss000001 nodecolor=greenk get nodes -l nodecolor=redk run rednginx --image=nginx --dry-run=client -o yaml > rednginx.yaml- Add the following content
nodeSelector: nodecolor: red
k apply -f rednginx.yamlk get po -wk get po -o widek get node -l nodecolor=red
Schedule a pod to nodes using node affinity
- Create a new nodepool
az aks nodepool add \ --resource-group k8sLearn \ --cluster-name schedulerLab \ --name silverpool \ --node-count 2 \
k get nodes --show-labelsk run affinitynginx --image=nginx --dry-run=client -o yaml > affinity-nginx.yaml- Add the following content
affinity: nodeAffinity: requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution: nodeSelectorTerms: - matchExpressions: - key: agentpool operator: In values: - silverpool
- Schedule a pod using preferred node affinity
k get po -w- Change
silverpooltogoldpool k apply -f affinity-nginx.yaml- Using
preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution- weight: 1 preference: matchExpressions: - key: agentpool operator: In values: - goldenpool
- About weight: Higher weight means higher priority.
- IgnoreDuringExection: This part means that the scheduling preferences are not reevaluated or considered once the pod is running. This behavior ensures that the pod remains stable and predictable during its execution, even if the node's conditions change.
k apply -f affinity-nginx.yamlk get po -o wide
Node affinity offers the property in pods that makes them more likely to be scheduled onto specific nodes. On the opposite side, taints are applied to nodes and enable a node to reject a set of pods. tolerations are applied to pods.
- Taint the node:
k taint nodes aks-silverpool-68496876-vmss000000 color=blue:NoSchedule k edit node aks-silverpool-68496876-vmss000000- Search for
taints
- Search for
k apply -f affinity-nginx.yaml- Pod will be in pending state
k describe po affinitynginx- Check why the pod is in pending state
- Add the following content to the
affinity-nginx.yamlunderspectolerations: - key: "nodecolor" operator: "Equal" value: "red" effect: "NoSchedule"