Sentiment analysis is becoming a popular area of research and social media analysis, especially around user reviews and tweets. It is a special case of text mining generally focused on identifying opinion polarity (positive, negative, neutral etc)
- We can get the training data which is the sentences mapped to either positive, neutral or negative in a list
- If we have database available in the form of simple sentences, then we can label these sentences as positive, negative or neutral
- We can perform preprocessing to clean our sentences
- For removing the common and unimportant words (we, i, to, is etc)
- We can split the sentence into words
- And then remove the words with length lower than 2
- These cleaned sentences can now be converted to features
- Features are needed so that the model could detected whether the sentence is positive, neg, or neutral
- One simple approach is to break sentences into words
- Then extract features by frequency of their appearance in a tweet
- After getting features from the sentences, we can train a simple model
- One such model is Naive Bayes Classifier
- Available in NLTK (python)
- This approach can have a drawback
- "My house is not great"
- The word ‘great’ weights more on the positive side but the word ‘not’ is part of two negative tweets in our training set so the output from the classifier is ‘negative’
- but 'The movie is not bad' would return ‘negative’ even if it is ‘positive’
- thus even large training data might not help the model in this case
- "Your song is annoying"
- The classifier thinks it is positive. The reason is that we don’t have any information on the feature name ‘annoying’
- Larger the training sample tweets is, the better the classifier will be
-
In this competition, you have to analyze tweets on the first 2016 GOP Presidential Debate
-
Details and data for this competition are available here: First GOP Debate Twitter Sentiment
-
90% of the data is used for training
- While remaining 10% is used for testing
-
The tweets are then separated into positive, negative and neutral sets
-
Tweets contain many unimportant words and things (like mentions, urls etc), so we need to clean them first
- Split the tweet into words
- If the word contains http, then remove it as it is a link
- If a word starts with @, then remove it as it is a mention
- If a word starts with #, then remove it as it is for hashtag
- If a word starts with RT, then remove it as it represents Retweet
-
We can also remove stopwords from the tweets
- These are commonly used words such as the, an, is, this etc
- They donot contain any significant information
- Thus they can be safely ignored
- available in wordcloud.stopwords (python)
-
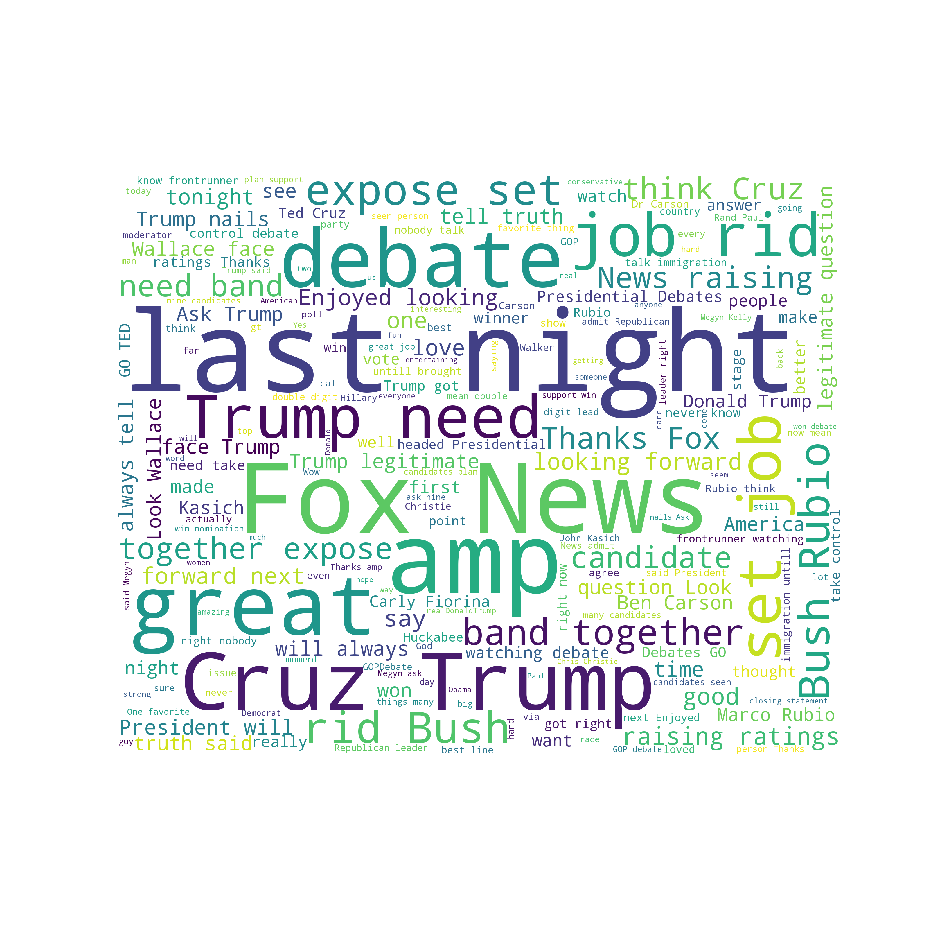
For visualizing the important words in these tweets, we can use Word Cloud library
- Mostly used words in a positive tweet
- Similarly, we can make Word Clouds for negative and neutral tweets (in Visualizations folder)
- Feature words are extracted using bag-of-words model
- The bag-of-words model is commonly used in methods of document classification where the (frequency of) occurrence of each word is used as a feature for training a classifier
- Then we use Naive Bayes Classifier for training the model
- nltk.NaiveBayesClassifier
- Using the same pre-processing and feature techniques, we can use Deep Neural Nets for better performance
- We can use Keras BOW (bag of words) model for this purpose
- Make a Sequential Model (linear stack of layers)
- Add a Dense layer (It is a fully connected layer to perform classification on the features extracted)
- called fully connected because every node in this layer is connected to every other node in the preceding layer
- Add activation function as ReLu (Rectified Linear Unit)
- ReLu is the most popular activation function as of 2018
- It is faster
- Other benefits is Sparsity
- most results are zero
- or positive values
- Add a Dropout layer
- for regularization
- reduces over-fitting
- it drops out the learning of units in the net
- Add final Dense layer (3 units in this case as positive, negative, neutral)
- activation of this layer would be Softmax
- Softmax activation is often used in the final layer of NN based classifiers
- activation of this layer would be Softmax
- Choose appropriate batch size and epoch values
- Also make sure to use validation_split while fitting the model
- it gives the idea about performance of your model on unseen data
- also good for preventing overfitting
- After training the model, make predictions and get the accuracy on unseen data
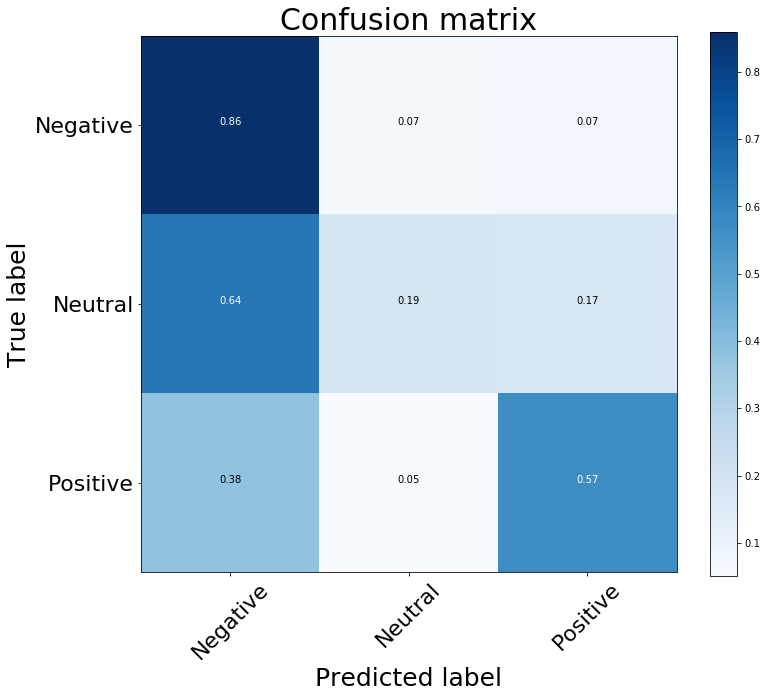
- The confusion matrix is as follows:
- The model works well in detecting negative tweets (86% accurate on unseen data)
- From the confusion matrix, we can see that the model works poorly for neutral and positive tweets
- This is because the training data is unbalanced
- negative tweets: 16986
- positive tweets: 4472
- We should get more data for positive and neutral tweets
- or maybe we could get other dataset and combine them both
- or maybe use some pre-trained model
- One more problem is sarcastic tweets / comments
- tweets which are ironic
- or have difficult context
- Example
- "Muhaha, how sad that the Liberals couldn't destroy Trump. Marching forward"
- the words sad and destroy highly influences the evaluation
- although this tweet should be positive when observing its meaning and context
- Maybe we should look into LSTM network in the future :))
- as it takes trends, context and references into account