Benchmark and analyze functions' time execution and results over the course of development.
- No boilerplate code
- Saves history and additional info
- Saves function output and parameters to benchmark data science tasks
- Easy to analyze results
- Disables garbage collector during benchmarking
- I need to benchmark execution time of my function
- I don't want to memorize and write boilerplate code
- I want to compare results with previous runs before some changes were introduced
- I don't want to manually write down results somewhere
- I want to know exact commits of my previous runs months ago
- I want to benchmark accuracy, precision, recall of my models and keep track of hyperparameters
pip install benchmarkit
Put @benchmark decorator over function with piece of code that should be timed
from benchmarkit import benchmark, benchmark_run
N = 10000
seq_list = list(range(N))
seq_set = set(range(N))
SAVE_PATH = '/tmp/benchmark_time.jsonl'
@benchmark(num_iters=100, save_params=True, save_output=False)
def search_in_list(num_items=N):
return num_items - 1 in seq_list
@benchmark(num_iters=100, save_params=True, save_output=False)
def search_in_set(num_items=N):
return num_items - 1 in seq_set- num_iters - how many times to repeat benchmarked function. Default 1
- save_params - save parameters passed to the benchmarked function in the file with benchmark results. In the example above
num_itemswill be saved. Default False - save_output - save benchmarked function output. Should return dict
{'name': value}. Default False. See example how to benchmark model results.
Run benchmark:
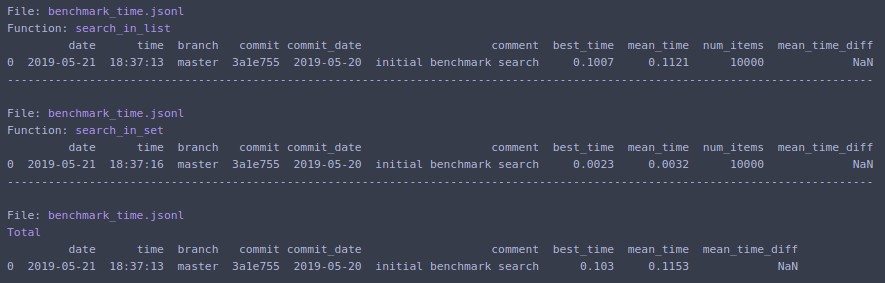
benchmark_results = benchmark_run(
[search_in_list, search_in_set],
SAVE_PATH,
comment='initial benchmark search',
rows_limit=10,
extra_fields=['num_items'],
metric='mean_time',
bigger_is_better=False,
) - functions - function or list of functions with
benchmarkdecorator - save_file - path to file where to save results
- comment - comment to save alongside the results
- rows_limit - limit table rows in console output. Default 10
- extra_fields - extra fields to include in console output
- metric - metric which is used for comparison. Default
mean_time - bigger_is_better - whether bigger value of metric indicates that result is better. For time benchmarks should be
False, for model accuracy should beTrue. Default False
Prints to terminal and returns list of dictionaries with data for the last run.
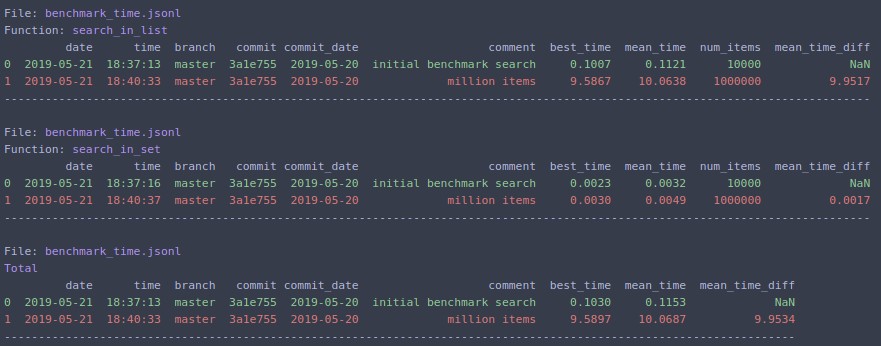
Change N=1000000 and rerun
The same can be run from command line:
benchmark_run test_data/time/benchmark_functions.py --save_dir /tmp/ --comment "million items" --extra_fields num_items
from benchmarkit import benchmark, benchmark_run
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
MODEL_BENCHMARK_SAVE_FILE = '/tmp/benchmark_model.jsonl'
x, y = load_iris(return_X_y=True)
@benchmark(save_params=True, save_output=True)
def log_regression(C=1.0, fit_intercept=True):
clf = LogisticRegression(
random_state=0,
solver='lbfgs',
multi_class='multinomial',
C=C,
fit_intercept=fit_intercept,
)
clf.fit(x, y)
score = clf.score(x, y)
return {'score': score}
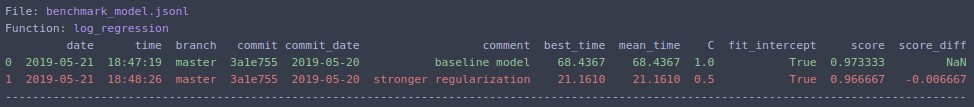
model_benchmark_results = benchmark_run(
log_regression,
MODEL_BENCHMARK_SAVE_FILE,
comment='baseline model',
extra_fields=['C', 'fit_intercept'],
metric='score',
bigger_is_better=True,
)Change hyperparameter C=0.5 and rerun. Output:
The same can be run from command line:
benchmark_run file_with_benchmark.py --save_dir /tmp/ --comment "stronger regularization" --extra_fields C fit_intercept --metric score --bigger_is_better
from benchmarkit import benchmark_analyze
SAVE_PATH = '/tmp/benchmark_time.jsonl'
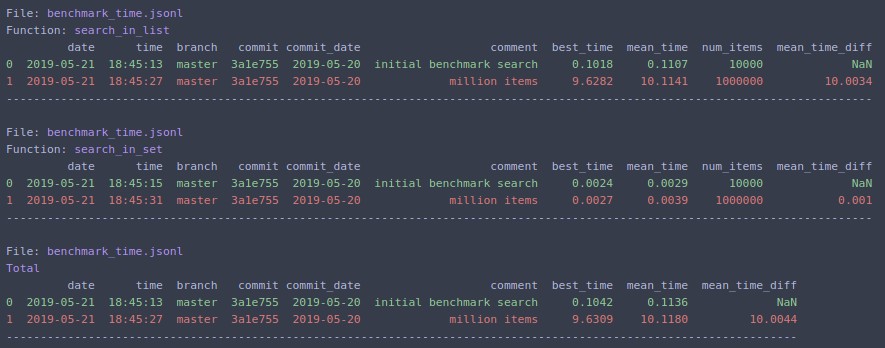
benchmark_df = benchmark_analyze(
SAVE_PATH,
func_name=None,
rows_limit=10,
metric='mean_time',
bigger_is_better=False,
extra_fields=['num_items'],
)- input_path - path to
.jsonlfile or directory with.jsonlfiles with benchmark results - func_name - display statistics for particular function. If
Nonethen all functions, stored in file, are displayed. Default None - rows_limit - limit table rows in console output. Default 10
- metric - metric which is used for comparison. Default
mean_time - bigger_is_better - whether bigger value of metric indicates that result is better. For time benchmarks should be
False, for model accuracy should beTrue. Default False - extra_fields - extra fields to include in console output
Prints to terminal and returns pandas DataFrame.
The same can be run from command line:
benchmark_analyze /tmp/benchmark_time.jsonl --extra_fields num_items