This is the code for implementing the GASIL algorithm presented in the paper: Independent Generative Adversarial Self-Imitation Learning In Cooperative Multiagent Systems.
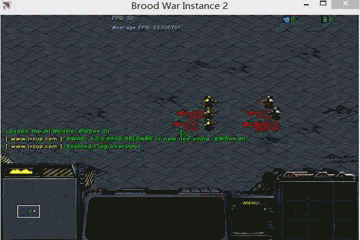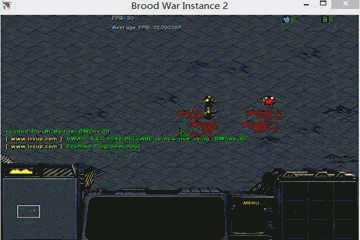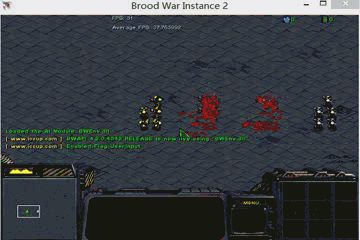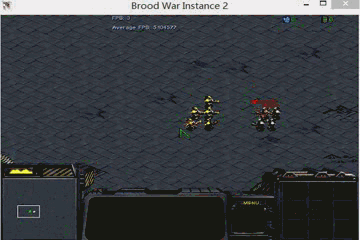
Cooperative predator-prey is a more difficult version of the ’Predator-prey’ task used in MADDPG (Lowe et al. 2017). There are N slower cooperating agents (predators) must cooperatively chase one of the M faster prey in a randomly generated environment. Agents observe the relative positions of all predators and prey and the velocities of the prey only. Actions are accelerations in four directions (up, down, left and right). Each time the cooperative agents collide with a prey simultaneously, the agents will be rewarded by some reward based on the prey they captured. Different prey (e.g., Lion, Wildebeest
and Deer) has different values and different risks in the meantime. This means there are different penalties for miss-coordination on different targets. we assume that the predator can hold a prey for some game steps t before the other partners’ arrival.
In our experiments, we set N to 2, M to 3 and t to 8. In the figure above, 2 predators are in red (translucent red represents the hands of predator) and 3 prey is in blue and purple. Among the three prey, the purple one has the highest value and penalty (if misscoordination). For the other two, the lighter blue one has the lowest value and risk). The controllers of the three prey are pre-trained DDPGs.
global optimal: capture prey in purple.
sub optimal: capture prey in deeper blue.
worst equilibrium: capture prey in ligher blue.
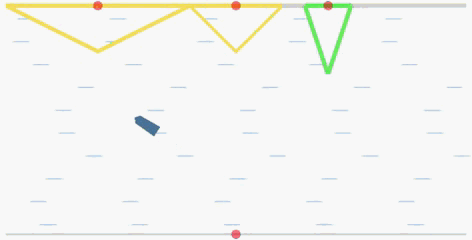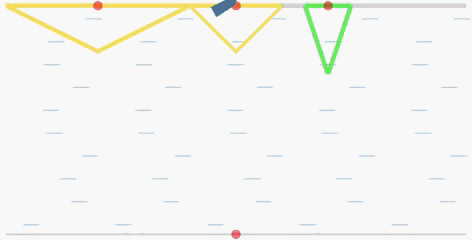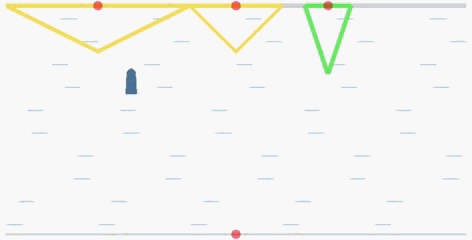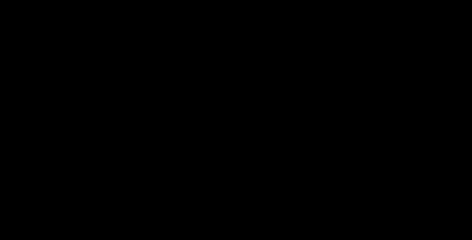
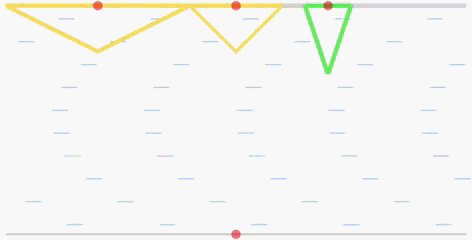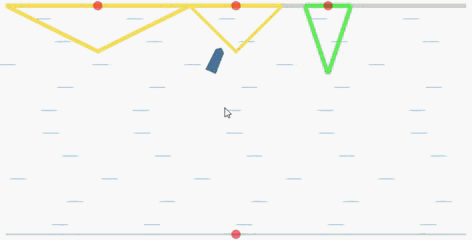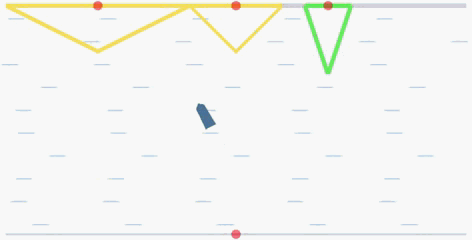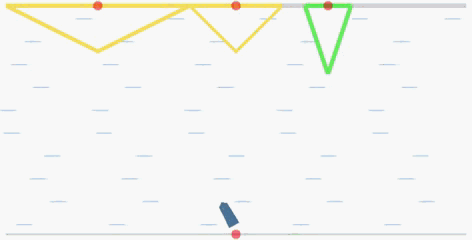
The goal of the cooperative rowing is to drive a boat from the quay center at one side to one of M quay centers at the other side of the river as soon as possible. The boat is driven by two independent controllers, which controls the accelerated speed and the angular accelerated speed respectively. Therefore, they have to learn to coordinate to achieve the goal.
In the flowing figures, the red points represent the centers of the quays. When the ship arrives at one of the three quays, it will recive a positive reward. The triangles (in yellow and green) represent
the reward values R(x) corresponding to the landing locations
x. The closer the distance to the center of each quay, the higher the reward will be (triangle in green is the global optimal with a peak reward
value 15).
global optimal: the quay with a green triangle
python run.py
--env=predator_prey
--seed=1
--max_step_before_punishment=8
--train_discriminator_k=1
--predator_policy=gasil
--prey_policy=ddpg
--reload_prey
--ddpg_plr=0.01
--ddpg_qlr=0.001
--d_lr=0.001