Embedded Typed Readonly In-Memory Document Database for .NET Core and Unity.
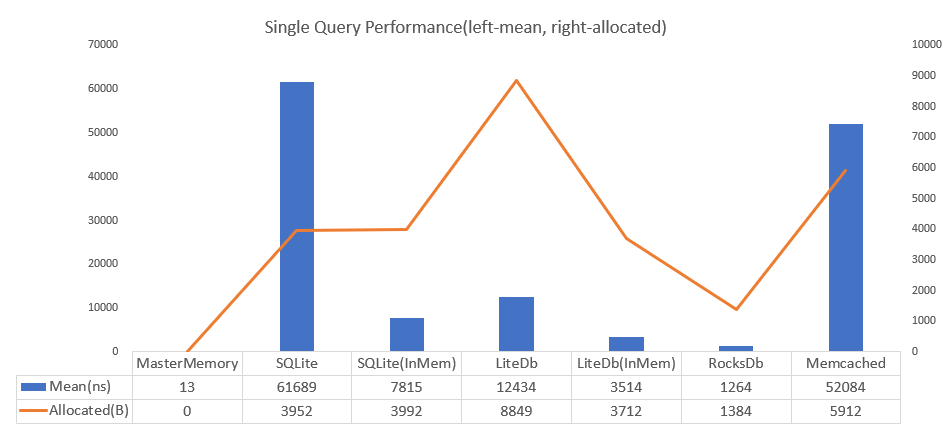
4700 times faster than SQLite and achieves zero allocation per query. Also the DB size is small. When SQLite is 3560kb then MasterMemory is only 222kb.
- Memory Efficient, Only use underlying data memory and do aggressively string interning.
- Performance, Similar as dictionary lookup.
- TypeSafe, 100% Type safe by pre code-generation.
- Fast load speed, MasterMemory save data by MessagePack for C#, a fastest C# serializer so load speed is blazing fast.
- Flexible Search, Supports multiple key, multiple result, range/closest query.
These features are suitable for master data management(write-once, read-heavy) on embedded application such as role-playing game. MasterMemory has better performance than any other database solutions. PalDB developed by LinkedIn has a similar concept(embeddable write-once key-value store), but the implementation and performance characteristics are completely different.
MasterMemory uses C# to C# code-generator. Runtime library API is the same but how to code-generate has different way between .NET Core and Unity. This sample is for .NET Core(for Unity is in below sections).
Install the core library(Runtime and Annotations).
PM> Install-Package MasterMemory
Prepare the example table definition like following.
public enum Gender
{
Male, Female, Unknown
}
// table definition marked by MemoryTableAttribute.
// database-table must be serializable by MessagePack-CSsharp
[MemoryTable("person"), MessagePackObject(true)]
public class Person
{
// index definition by attributes.
[PrimaryKey]
public int PersonId { get; set; }
// secondary index can add multiple(discriminated by index-number).
[SecondaryKey(0), NonUnique]
[SecondaryKey(1, keyOrder: 1), NonUnique]
public int Age { get; set; }
[SecondaryKey(2), NonUnique]
[SecondaryKey(1, keyOrder: 0), NonUnique]
public Gender Gender { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}Edit the .csproj, add MasterMemory.MSBuild.Tasks and add configuration like following.
<ItemGroup>
<PackageReference Include="MasterMemory" Version="1.1.7" />
<!-- Install MSBuild Task(with PrivateAssets="All", it means to use dependency only in build time). -->
<PackageReference Include="MasterMemory.MSBuild.Tasks" Version="1.1.7" PrivateAssets="All" />
</ItemGroup>
<!-- Call code generator before-build. -->
<Target Name="MasterMemoryGen" BeforeTargets="BeforeBuild">
<!-- Configuration of Code-Generator, `UsingNamespace`, `InputDirectory`, `OutputDirectory` and `AddImmutableConstructor`. -->
<MasterMemoryGenerator UsingNamespace="$(ProjectName)" InputDirectory="$(ProjectDir)" OutputDirectory="$(ProjectDir)MasterMemory" />
</Target>After the build, generated files(DatabaseBuilder.cs, ImmutableBuilder.cs, MasterMemoryResolver.cs, MemoryDatabase.cs and Tables/***Table.cs) in OutputDirectory.
Finally, you can regsiter and query by these files.
// to create database, use DatabaseBuilder and Append method.
var builder = new DatabaseBuilder();
builder.Append(new Person[]
{
new Person { PersonId = 0, Age = 13, Gender = Gender.Male, Name = "Dana Terry" },
new Person { PersonId = 1, Age = 17, Gender = Gender.Male, Name = "Kirk Obrien" },
new Person { PersonId = 2, Age = 31, Gender = Gender.Male, Name = "Wm Banks" },
new Person { PersonId = 3, Age = 44, Gender = Gender.Male, Name = "Karl Benson" },
new Person { PersonId = 4, Age = 23, Gender = Gender.Male, Name = "Jared Holland" },
new Person { PersonId = 5, Age = 27, Gender = Gender.Female, Name = "Jeanne Phelps" },
new Person { PersonId = 6, Age = 25, Gender = Gender.Female, Name = "Willie Rose" },
new Person { PersonId = 7, Age = 11, Gender = Gender.Female, Name = "Shari Gutierrez" },
new Person { PersonId = 8, Age = 63, Gender = Gender.Female, Name = "Lori Wilson" },
new Person { PersonId = 9, Age = 34, Gender = Gender.Female, Name = "Lena Ramsey" },
});
// build database binary(you can also use `WriteToStream` for save to file).
byte[] data = builder.Build();
// -----------------------
// for query phase, create MemoryDatabase.
// (MemoryDatabase is recommended to store in singleton container(static field/DI)).
var db = new MemoryDatabase(data);
// .PersonTable.FindByPersonId is fully typed by code-generation.
Person person = db.PersonTable.FindByPersonId(10);
// Multiple key is also typed(***And * **), Return value is multiple if key is marked with `NonUnique`.
RangeView<Person> result = db.PersonTable.FindByGenderAndAge((Gender.Female, 23));
// Get nearest value(choose lower(default) or higher).
RangeView<Person> age1 = db.PersonTable.FindClosestByAge(31);
// Get range(min-max inclusive).
RangeView<Person> age2 = db.PersonTable.FindRangeByAge(20, 29);All table(marked by MemoryTableAttribute) and methods(created by PrimaryKeyAttribute or SecondaryKeyAttribute) are typed.
You can invoke all indexed query by IntelliSense.
Check the releases page, download MasterMemory.Unity.unitypackage(runtime) and MasterMemory.Generator.zip(cli code-generator). MasterMemory also depends on MessagePack-CSharp so you have to download MessagePack.Unity.1.7.3.5.unitypackage and MessagePackUniversalCodeGenerator.zip from MessagePack-CSharp/releases page.
Prepare the example table definition like following.
public enum Gender
{
Male, Female, Unknown
}
// table definition marked by MemoryTableAttribute.
// database-table must be serializable by MessagePack-CSsharp
[MemoryTable("person"), MessagePackObject(true)]
public class Person
{
// index definition by attributes.
[PrimaryKey]
public int PersonId { get; set; }
// secondary index can add multiple(discriminated by index-number).
[SecondaryKey(0), NonUnique]
[SecondaryKey(1, keyOrder: 1), NonUnique]
public int Age { get; set; }
[SecondaryKey(2), NonUnique]
[SecondaryKey(1, keyOrder: 0), NonUnique]
public Gender Gender { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}use the MasterMemory code generator by commandline. Commandline tool support platforms are win-x64, osx-x64 and linux-x64.
argument list:
-i, -inputDirectory: Input file directory(search recursive).
-o, -outputDirectory: Output file directory.
-n, -usingNamespace: Namespace of generated files.
-c, -addImmutableConstructor: [default=False]Add immutable constructor to MemoryTable class.
MasterMemory.Generator.exe -i "C:\UnitySample" -o "C:\UnitySample\Generated" -n "UnitySample"Also you need to generated MessagePack-CSharp code generation.
It is useful to create an editor extension to invoke command-line tool. Here is the sample of MagicOnion - Unified Realtime/API Engine for .NET Core and Unity's code generator extension sample. MagicOnion/.../samples.../Editor/MenuItems.cs. It has a similar option of MasterMemoryGenerator.
Additional steps, Additional steps, you have to set up to use generated resolver.
public static class Initializer
{
[RuntimeInitializeOnLoadMethod(RuntimeInitializeLoadType.BeforeSceneLoad)]
public static void SetupMessagePackResolver()
{
CompositeResolver.RegisterAndSetAsDefault(new[]{
MasterMemoryResolver.Instance, // set MasterMemory generated resolver
GeneratedResolver.Instance, // set MessagePack generated resolver
StandardResolver.Instance // set default MessagePack resolver
});
}
}The rest is the same as .NET Core version.
// to create database, use DatabaseBuilder and Append method.
var builder = new DatabaseBuilder();
builder.Append(new Person[]
{
new Person { PersonId = 0, Age = 13, Gender = Gender.Male, Name = "Dana Terry" },
new Person { PersonId = 1, Age = 17, Gender = Gender.Male, Name = "Kirk Obrien" },
new Person { PersonId = 2, Age = 31, Gender = Gender.Male, Name = "Wm Banks" },
new Person { PersonId = 3, Age = 44, Gender = Gender.Male, Name = "Karl Benson" },
new Person { PersonId = 4, Age = 23, Gender = Gender.Male, Name = "Jared Holland" },
new Person { PersonId = 5, Age = 27, Gender = Gender.Female, Name = "Jeanne Phelps" },
new Person { PersonId = 6, Age = 25, Gender = Gender.Female, Name = "Willie Rose" },
new Person { PersonId = 7, Age = 11, Gender = Gender.Female, Name = "Shari Gutierrez" },
new Person { PersonId = 8, Age = 63, Gender = Gender.Female, Name = "Lori Wilson" },
new Person { PersonId = 9, Age = 34, Gender = Gender.Female, Name = "Lena Ramsey" },
});
// build database binary(you can also use `WriteToStream` for save to file).
byte[] data = builder.Build();
// -----------------------
// for query phase, create MemoryDatabase.
// (MemoryDatabase is recommended to store in singleton container(static field/DI)).
var db = new MemoryDatabase(data);
// .PersonTable.FindByPersonId is fully typed by code-generation.
Person person = db.PersonTable.FindByPersonId(10);
// Multiple key is also typed(***And * **), Return value is multiple if key is marked with `NonUnique`.
RangeView<Person> result = db.PersonTable.FindByGenderAndAge((Gender.Female, 23));
// Get nearest value(choose lower(default) or higher).
RangeView<Person> age1 = db.PersonTable.FindClosestByAge(31);
// Get range(min-max inclusive).
RangeView<Person> age2 = db.PersonTable.FindRangeByAge(20, 29);All table(marked by MemoryTableAttribute) and methods(created by PrimaryKeyAttribute or SecondaryKeyAttribute) are typed.
You can invoke all indexed query by IntelliSense.
Element type of datatable must be marked by [MemoryTable(tableName)], datatable is generated from marked type. string tableName is saved in database binary, you can rename class name if tableName is same.
[PrimaryKey(keyOrder = 0)], [SecondaryKey(indexNo, keyOrder)], [NonUnique] can add to public property, [PrimaryKey] must use in MemoryTable, [SecondaryKey] is option.
Both PrimaryKey and SecondaryKey can add to multiple properties, it will be generated ***And***And***.... keyOrder is order of column names, default is zero(sequential in which they appear).
[MemoryTable("sample")]
public class Sample
{
[ParimaryKey]
public int Foo { get; set; }
[ParimaryKey]
public int Bar { get; set; }
}
db.Sample.FindByFooAndBar((int Foo, int Bar))
// ----
[MemoryTable("sample")]
public class Sample
{
[ParimaryKey(keyOrder: 1)]
public int Foo { get; set; }
[ParimaryKey(keyOrder: 0)]
public int Bar { get; set; }
}
db.Sample.FindByBarAndFoo((int Bar, int Foo))Default of FindBy*** return type is single(if not found, returns null). It means key is unique by default. If mark [NonUnique] in same AttributeList, return type is RangeView<T>(if not found, return empty).
[MemoryTable("sample")]
public class Sample
{
[ParimaryKey, NonUnique]
public int Foo { get; set; }
[ParimaryKey, NonUnique]
public int Bar { get; set; }
}
RangeView<Sample> q = db.Sample.FindByFooAndBar((int Foo, int Bar))[MemoryTable("sample")]
public class Sample
{
[ParimaryKey]
[SecondaryKey(0)]
public int Foo { get; set; }
[SecondaryKey(0)]
[SecondaryKey(1)]
public int Bar { get; set; }
}
db.Sample.FindByFoo(int Foo)
db.Sample.FindByFooAndBar((int Foo, int Bar))
db.Sample.FindByBar(int Bar)In default, MemoryDatabase do all string data automatically interning(see: Wikipedia/String interning). If multiple same string value exists in database(ex: "goblin","goblin", "goblin", "goblin", "goblin"....), standard database creates string value per query or store multiple same values. But MasterMemory stores single string value reference, it can save much memory if data is denormalized.
Use intern or not is selected in constructor. If you want to disable automatically interning, use internString:false.
MemoryDatabase(byte[] databaseBinary, bool internString = true, MessagePack.IFormatterResolver formatterResolver = null).
MemoryDatabase has three query methods.
T|RangeView<T>FindBy***(TKey key)T|RangeView<T>FindClosestBy***(TKey key, bool selectLower = true)RangeView<T>FindRangeBy***(TKey min, TKey max, bool ascendant = true)
By*** is generated by PrimaryKey and SecondaryKey defines.
And has some utility properties.
intCountRangeView<T>AllRangeView<T>AllReverseRangeView<T>SortBy***T[] GetRawDataUnsafe()
struct RangeView<T> : IEnumerable<T> is the view of database elements. It has following property/method.
T[int index]intCountTFirstTLastRangeView<T>ReverseIEnumerator<T>GetEnumerator()
If you want to add/modify data to loaded database, you can use ToImmutableBuilder method.
// Create ImmutableBuilder from original database.
var builder = db.ToImmutableBuilder();
// Add Or Replace compare with PrimaryKey
builder.Diff(addOrReplaceData);
// Remove by PrimaryKey
builder.RemovePerson(new[] { 1, 10, 100 });
// Replace all data
builder.ReplaceAll(newData);
// Finally create new database
MemoryDatabase newDatabase = builder.Build();
// If you want to save new database, you can convert to MemoryDatabase->DatabaseBuilder
var newBuilder = newDatabase.ToDatabaseBuilder();
var newBinary = newBuilder.Build(); // or use WriteToStreamMemoryDatabase's reference can use as snapshot.
// 1 game per 1 instance
public class GameRoom
{
MemoryDatabase database;
// The reference is a snapshot of the timing of game begins.
public GameRoom(MemoryDatabase database)
{
this.database = database;
}
}Element data is shared in the application so ideally should be immutable. But C# only has a constructor to create immutable data, it is too difficult to create many data tables.
Code generator has AddImmutableConstructor(-c, -addImmutableConstructor) option. If enabled it, code generator modify orignal file and add immutable constructor in target type. If you define property as {get; private set;} or {get;}, it will be immutable type.
// For the versioning, MessagePackObject is recommended to use string key.
[MemoryTable("person"), MessagePackObject(true)]
public class Person
{
[PrimaryKey]
public int PersonId { get; }
public int Age { get; }
public Gender Gender { get; }
public string Name { get; }
}
// use AddImmutableConstructor="true" or -c option
<MasterMemoryGenerator UsingNamespace="$(ProjectName)" InputDirectory="$(ProjectDir)" OutputDirectory="$(ProjectDir)MasterMemory" AddImmutableConstructor="true" />
MasterMemory.Generator.exe -i "C:\UnitySample" -o "C:\UnitySample\Generated" -n "UnitySample" -c
// after generated...
[MemoryTable("person"), MessagePackObject(true)]
public class Person
{
[PrimaryKey]
public int PersonId { get; }
public int Age { get; }
public Gender Gender { get; }
public string Name { get; }
public Person(int PersonId, int Age, Gender Gender, string Name)
{
this.PersonId = PersonId;
this.Age = Age;
this.Gender = Gender;
this.Name = Name;
}
}MasterMemory has three kinds of code-generator. MSBuild Task, Standalone Cli Tool, .NET Core Global Tools.
MSBuild Task(MasterMemory.MSBuild.Tasks) is recommended way to use in .NET Core csproj.
<MasterMemoryGenerator
UsingNamespace="string:required"
InputDirectory="string:required"
OutputDirectory="string:required"
AddImmutableConstructor="bool:optional"
/>Standalone Cli Tool(MasterMemory.Generator) is built by .NET Core 3, self-contained single executable binary. It can be used for Unity and other separated use-case.
argument list:
-i, -inputDirectory: Input file directory(search recursive).
-o, -outputDirectory: Output file directory.
-n, -usingNamespace: Namespace of generated files.
-c, -addImmutableConstructor: [default=False]Add immutable constructor to MemoryTable class.
.NET Core Global Tools can install from NuGet, it is same as Standalone Cli Tool.
dotnet tool install --global MasterMemory.Generator
After install, you can call by dotnet mmgen command. This is useful to use in CI. Here is the sample of CircleCI config.
version: 2.1
executors:
dotnet:
docker:
- image: mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/core/sdk:2.2
environment:
DOTNET_SKIP_FIRST_TIME_EXPERIENCE: true
NUGET_XMLDOC_MODE: skip
jobs:
gen-mastermemory:
executor: dotnet
steps:
- checkout
- run: dotnet tool install --global MasterMemory.Generator
- run: dotnet mmgen -i ./ -o ./MasterMemory -m Test
/* git push or store artifacts or etc... */This library is under the MIT License.