This repository includes resources to reproduce training procedures for the paper Fair Multilingual Vandalism Detection System for Wikipedia from data collection to model training.
We publish the dataset that can be directly used for final classification model training. Data includes also raw features, that are not directly used in the final classification model like texts.
The training script that uses mentioned collected datasets:
python modules/train_model_simplified.py --train=data/train_anon_users.csv --test=data/test_anon_user
s.csv --name=anon_model
Data collection logic was done using Wikimedia analytical cluster. How to collect data on the cluster:
for i in ka lv ta ur eo lt sl hy hr sk eu et ms az da bg sr ro el th bn simple no hi ca hu ko fi vi uz sv cs he id tr uk nl pl ar fa it zh ru es ja de fr en
do
python modules/data_collection.py -l $i -m train -f1 0 -f2 0 -n 300000 -uc 1 -p all_users
done
The script above collects the dataset for each of the given languages in the loop. It does not filter anonymous users (-f1) and revision wars (-f2). Also, there is a limit of 300000 records per language.
Data collection of hold-out test:
for i in ka lv ta ur eo lt sl hy hr sk eu et ms az da bg sr ro el th bn simple no hi ca hu ko fi vi uz sv cs he id tr uk nl pl ar fa it zh ru es ja de fr en
do
python modules/data_collection.py -l $i -m test -f1 0 -f2 1 -n 100000 -uc 1 -p full_test
done
The sample for collected data can be found here: .....link...... Full data will be released soon.
Having the data for each language, the next step is preparing it for training. For that purposes, run:
python modules/data_prepareration.py
This script load data for each language in the defined list, do the timestamp-based train-test split, splitting train for MLMs fine-tuning and classifier model, setting the balancing key for further evaluation, filtering revision wars if it is needed.
It returns three aggregated dataframes: train, test, full-test (independent set)
Having collected the training dataset, we proceed with fine-tuning of MLMs.
python modules/feature_trainer.py
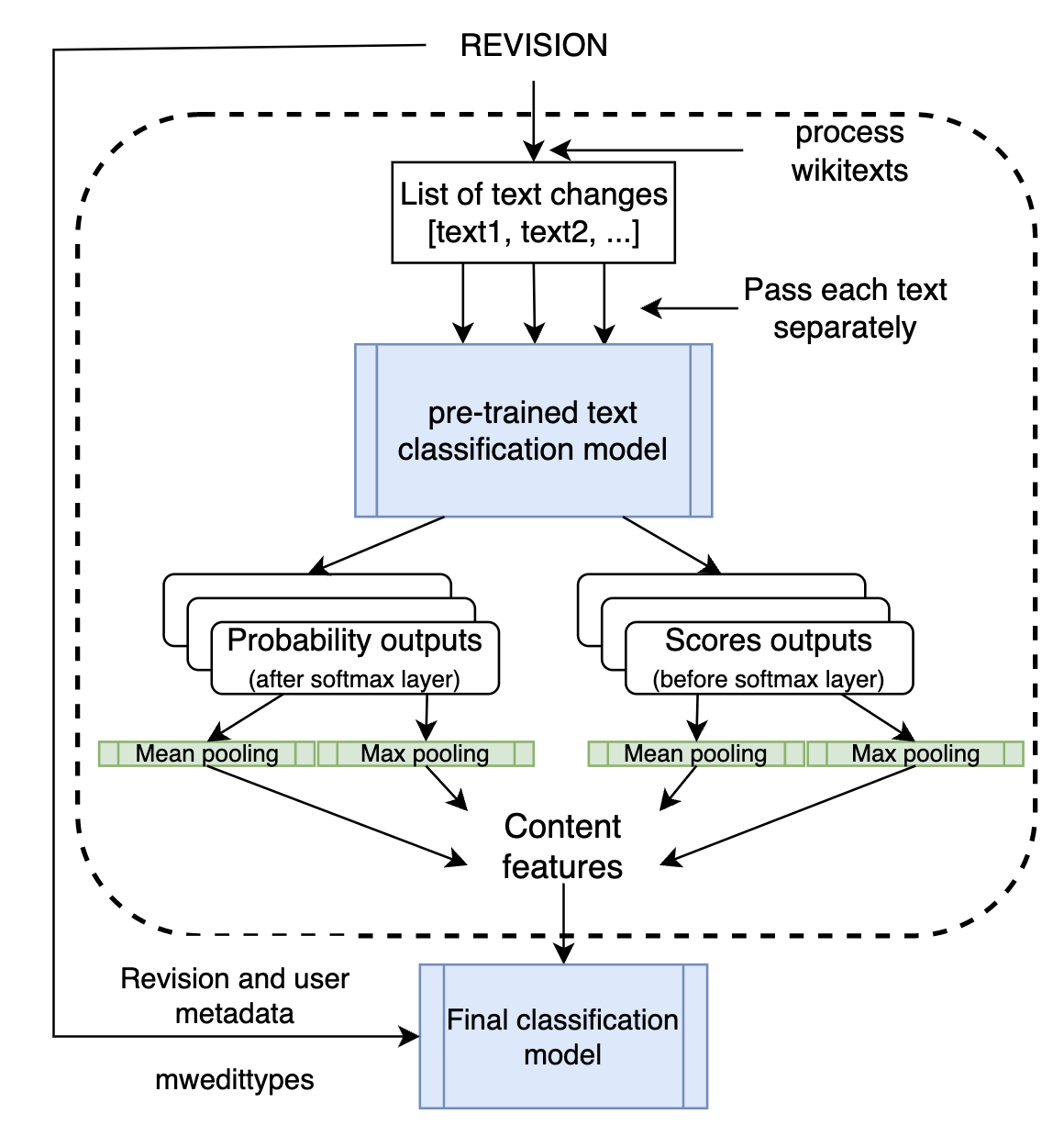
This script prepares the specific dataset for four different MLMs model tuning. Later it uses prepared data and tunes MLM for a pair of text classification (changes), text classification (inserts, removes), and regression (title semantics). And later tune those models and save them to the \models directory. GPU is needed for training. We used AMD Radeon Pro WX 9100 16GB GPU.
Having collected the training dataset and tuned MLMs we proceed with calculation text features for those datasets (training and testing parts)
python modules/feature_builder.py
Before running the script, we should make sure that paths to MLMs and datasets are correct in the script.
Additional user features extraction (is_anonymous, user group):
python modules/users_features_collection.py
The module takes as input the list of files with revisions for which to collect those features. It saves the features to pickle, which can be used if needed.
The training script for the best configuration of the model:
python modules/train_model.py
In this section, we use the prepared data from previous sections. The sample of data used can be found in Prepared data section. Full data will be published after the paper's publication.
Performance metrics: Model analysis based on performance metrics can be found in this notebook: performance evaluation
(Note: This notebook also creates the input for fairness metrics)
Fairness metrics: Model analysis based on fairness metrics can be found in this notebook: fairness evaluation
Also, we are using ORES scores as a reference. The script for their collection is:
python modules/ores_scores_collection.py
Or you can find the file with corresponding scores in the prepared data.
Fair Multilingual Vandalism Detection System for Wikipedia
@inproceedings{10.1145/3580305.3599823,
author = {Trokhymovych, Mykola and Aslam, Muniza and Chou, Ai-Jou and Baeza-Yates, Ricardo and Saez-Trumper, Diego},
title = {Fair Multilingual Vandalism Detection System for Wikipedia},
year = {2023},
isbn = {9798400701030},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3580305.3599823},
doi = {10.1145/3580305.3599823},
abstract = {This paper presents a novel design of the system aimed at supporting the Wikipedia community in addressing vandalism on the platform. To achieve this, we collected a massive dataset of 47 languages, and applied advanced filtering and feature engineering techniques, including multilingual masked language modeling to build the training dataset from human-generated data. The performance of the system was evaluated through comparison with the one used in production in Wikipedia, known as ORES. Our research results in a significant increase in the number of languages covered, making Wikipedia patrolling more efficient to a wider range of communities. Furthermore, our model outperforms ORES, ensuring that the results provided are not only more accurate but also less biased against certain groups of contributors.},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 29th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining},
pages = {4981–4990},
numpages = {10},
location = {Long Beach, CA, USA},
series = {KDD '23}
}