Kafka Consumer Side Offset Store is a Java library to assist storing the consumer group offsets on the consumer application side instead of __consumer_groups on the Kafka cluster. This allows the Kafka consumer applications to more easily achieve exactly-once message processing by atomically updating both the offsets and the consumption result using a transaction.
Kafka Consumer Side Offset Store provides several templates to implement the required functions for storing the consumer group offsets on the consumer application side while achieving high quality and ease. Several solutions are provided:
- Based on ConsumerSideOffsetStoreHandler template, which is the most core template available for all types of application.
- [TBD] Based on relational database offset store template, which is a more JDBC specific template.
- [TBD] Based on Kafka offset store template, which is a more Kafka specific template.
Caution: This project is in incubation, and is published for personal interest, so this library doesn't have sufficient quality yet.
- Java 8+
- Kafka Java Client 2.6.0+,
- KafkaConsumer with 'enable.auto.commit=false'
- Provides several templates to implement the required functions
- Check status and timeout for zombie fencing
<dependency>
<groupId>org.tyamashi</groupId>
<artifactId>kafka-consumer-side-offset-store-core</artifactId>
<version>VERSION</version>
</dependency>Available versions can be found here: https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.tyamashi/kafka-consumer-side-offset-store-core.
// configure KafkaConsumer
Map<String, Object> consumerProps = new HashMap<>();
consumerProps.put(ConsumerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, kafkaContainer.getBootstrapServers());
consumerProps.put(ConsumerConfig.ENABLE_AUTO_COMMIT_CONFIG, "false"); // auto commit should be disabled
consumerProps.put(ConsumerConfig.AUTO_OFFSET_RESET_CONFIG, "earliest"):
consumerProps.put(ConsumerConfig.GROUP_ID_CONFIG, GROUP_IP);
consumerProps.put(ConsumerConfig.KEY_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, IntegerDeserializer.class.getName());
consumerProps.put(ConsumerConfig.VALUE_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, IntegerDeserializer.class.getName());
// configure consumer side offset store
Map<String, Object> offsetStoreProps = new HashMap<>();
offsetStoreProps.put(OffsetStoreConfig.OFFSET_NOT_FOUND_ON_CONSUMER_SIDE_STRATEGY, OffsetNotFoundOnConsumerSideStrategy.USE_KAFKA_OFFSETS);
offsetStoreProps.put(OffsetStoreConfig.ENABLE_KAFKA_SIDE_OFFSET_COMMIT, true);
offsetStoreProps.put(OffsetStoreConfig.KAFKA_SIDE_OFFSET_COMMIT_STRATEGY, KafkaSideOffsetCommitStrategy.COMMIT_ASYNC_WITH_UPDATING_CONSUMER_SIDE_OFFSETS);
// define ConsumerSideOffsetStoreHandler
ConsumerSideOffsetStoreHandler<Connection> consumerSideOffsetStoreHandler = new ConsumerSideOffsetStoreHandler<Connection>() {
@Override
public void initializeOffsetStore(String groupId) throws Exception {
// initialize consumer side offset store, optionally
// for example, create a database table to store offsets if not exists
}
@Override
public Map<TopicPartition, OffsetAndMetadata> loadOffsets(ConsumerGroupMetadata groupMetadata, Collection<TopicPartition> partitions) throws Exception {
// load consumer side offsets
// for example, query the database table that has offsets
}
@Override
public void saveOffsets(ConsumerGroupMetadata groupMetadata, Map<TopicPartition, OffsetAndMetadata> offsets, Connection transactionalObject) throws Exception {
// save offsets on consumer side store
// for example, upsert offsets in the database table
}
};
// consume messages
try (KafkaConsumer<Integer, Integer> kafkaConsumer = new KafkaConsumer<>(consumerProps)) {
// call OffsetStoreContext.subscribe() with offsetStoreHandler, instead of kafkaConsumer.subscribe()
OffsetStoreContext<Connection> offsetStoreContext = OffsetStoreContext.subscribe(offsetStoreProps, kafkaConsumer, Collections.singleton(TOPIC), consumerSideOffsetStoreHandler);
while(true) {
ConsumerRecords<Integer, Integer> records = kafkaConsumer.poll(Duration.ofSeconds(10));
for (ConsumerRecord<Integer, Integer> record : records) {
// use transactional object
// for example, create a JDBC connection and a transaction.
try (Connection connection = getConnection()) {
// do some business updates using your JDBC connection participating in the transaction
doSomething(record, connection);
// update consumer side offsets in the transaction before JDBC connection commit(), and optionally commit kafka side offsets
// this will call ConsumerSideOffsetStoreHandler.saveOffsets() with your JDBC connection participating in the transaction
offsetStoreContext.updateConsumerSideOffsets(record, connection);
// transaction commit
connection.commit();
}
}
}- ConsumerSideOffsetStoreHandler with JDBC connection
- This example project use ConsumerSideOffsetStoreHandler template with JDBC connection
Handler responsible for implementing the input/output adapter for the consumer side offset store.
| Method name | Description | Parameters | Return value |
|---|---|---|---|
| initializeOffsetStore(...) | Implement Initializing the consumer side offset store in this method. This method will be called when OffsetStoreContext is created using OffsetStoreContext.subscribe(...). |
|
- |
| loadOffsets(...) | Implement loading the consumer side offsets in this method. This method will be called when partitions are assigned to the KafkaConsumer and ConsumerRebalanceListener.onPartitionsAssigned(...) is called. |
|
A map of loaded offsets by the topic partition. |
| saveOffsets(...) | Implement saving the consumer side offsets in this method. This method will be called when the application call OffsetStoreContext.updateConsumerSideOffsets(...). |
|
- |
Configuration for Kafka Consumer Side Offset Store.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| offsetnotfound.on.consumerside.strategy | Whether to user __consumer_offsets on the Kafka cluster when the offsets cannot be found from the consumer side offset store.
|
| enable.kafkasideoffset.commit | Indicates whether kafka side offset commit is enabled. "true" if kafka side offset commit is enabled, or "false" otherwise. Default is "true". |
| kafkaside.offset.commit.strategy | If kafka side offset commit is enabled (enable.kafkasideoffset.commit=true), strategy to update Kafka side offset.
|
| enable.kafka.consumer.timeout.check | Indicates whether kafka consumer timeout check is enabled. This is one of the zombie fencing features. "true" if kafka consumer timeout check is enabled, or "false" otherwise. Default is "true". |
OffsetStoreContext is the main APIs for Kafka Consumer Side Offset Store. Here only the main methods are introduced:
| Method name | Description | Parameters | Return value |
|---|---|---|---|
| subscribe(...) : static method | Create OffsetStoreContext with offsetStoreHandler, then call ConsumerSideOffsetStoreHandler.initializeOffsetStore(...) and KafkaConsumser.subscribe(pattern). |
|
- |
| updateConsumerSideOffsets(...) | Update the consumer side offsets, this will call ConsumerSideOffsetStoreHandler.saveOffsets(...). This method should be called just before commit() if possible. |
|
- |
| checkConsumerTimeoutMs(...) | Check KafkaConsumser's session timeout and poll timeout. If any of these expire, OffsetStoreValidationException occurs. | - | The remaining timeout value in milliseconds. The smaller remaining timeout value of KafkaConsumser's session timeout or poll timeout. |
- This library doesn't support static consumer feature.
Kafka Consumer Side Offset Store is designed to be simple and stateless. The core source code is quite small. This library class doesn't contain much information, but rather obtains it from KafkaConsumer and method parameters. A transaction would complete commit or rollback outside of this library, so this is necessary to avoid inconsistency.
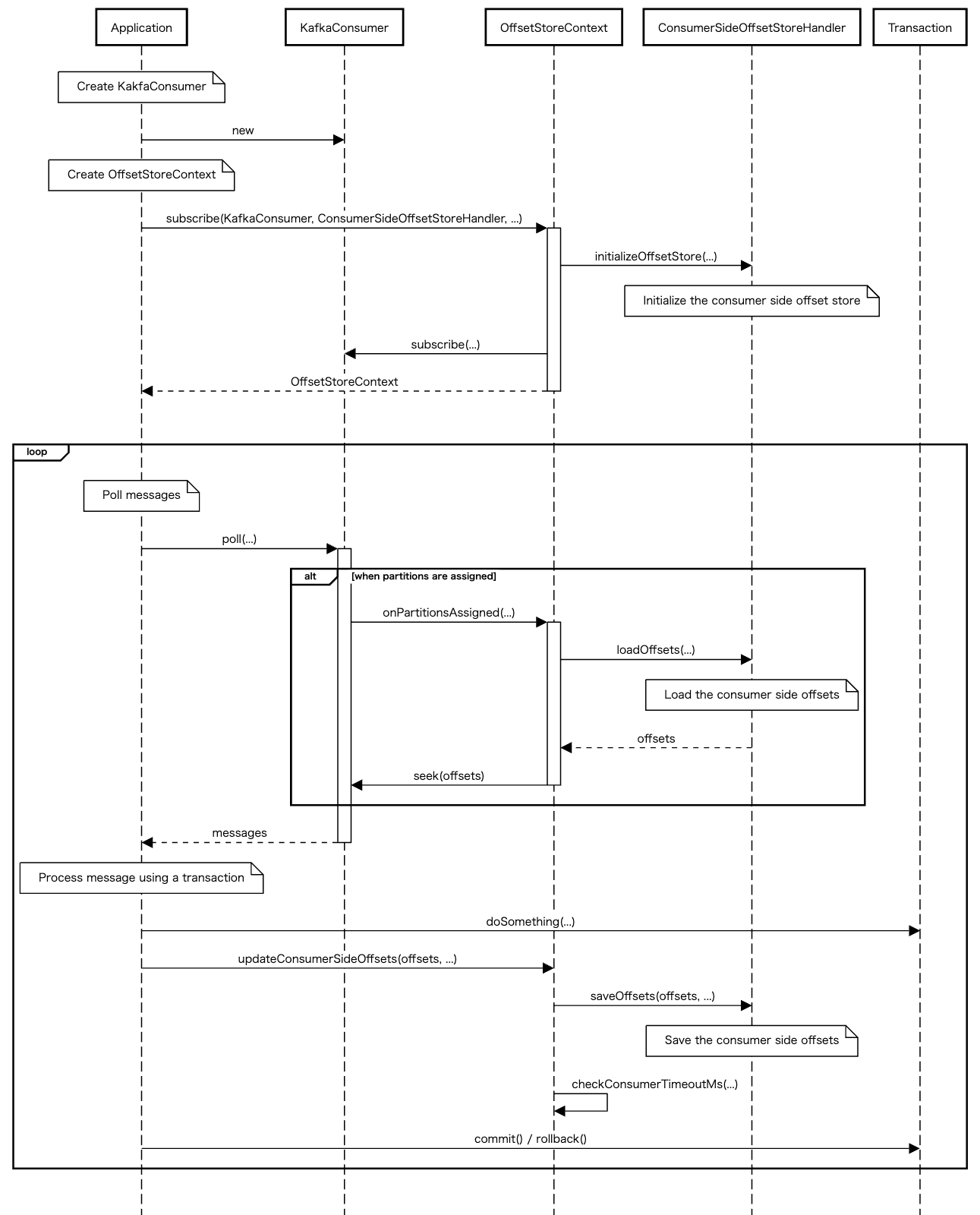
Kafka Consumer Side Offset Store listens the consumer re-balance events using ConsumerRebalanceListener internally.
The following sequence diagram indicates main flow, and it excludes exception flow such as leaving the ConsumerGroup due to timeout or other reasons:
Unfortunately, Kafka Consumer Side Offset Store accesses to the following private fields in KafkaConsumer internally, to get status and times for zombie fencing feature.
- KafkaConsumer
- coordinator: AbstractCoordinator
- heartbeat: Heartbeat
- sessionTimer: Timer
- pollTimer: Timer
For your information, externalize the offsets like Kafka Consumer Side Offset Store does is also pointed out in Javadoc for KafkaConsumer. It is described as follows:
The consumer application need not use Kafka's built-in offset storage, it can store offsets in a store of its own choosing. The primary use case for this is allowing the application to store both the offset and the results of the consumption in the same system in a way that both the results and offsets are stored atomically. This is not always possible, but when it is it will make the consumption fully atomic and give "exactly once" semantics that are stronger than the default "at-least once" semantics you get with Kafka's offset commit functionality.
"Javadoc for KafkaConsumer, https://kafka.apache.org/"
Although Kafka support exactly-once transaction, it is only available for specific case, such as within the same Kafka cluster. Basically, Kafka support at-least-once message processing, so it can be duplicate message processing. Kafka Consumer Side Offset Store allows the Kafka consumer applications to more easily achieve exactly-once message processing by atomically updating both the offsets and the consumption result using a transaction. However, this doesn't mean to guarantee exactly-once message processing.
To achieve exactly-once, it is import for Kafka consumer group that only one KafkaConsumer is assigned for each partition. However, your consumer application can be a zombie because of the heartbeat timeout(session.timeout.ms) or the poll timeout(max.poll.interval.ms). So that Kafka consumer will be conflict in a Kafka consumer group, and duplicate message processing.
Kafka Consumer Side Offset Store has zombie fencing feature to check whether KafkaConsumer itself might have become a zombie and throw an exception. And it also provides the feature to retrieve the remaining time until timeout.
This check will useful before commit to determine rollback. And you can use it when you call offsetStoreContext.updateConsumerSideOffsets(...), and then ConsumerSideOffsetStoreHandler.saveOffsets(...) is called. This can avoid many cases that message duplicate processing can be happened.
However, when you call commit of transactional object the Kafka consumer application can also be a zombie. For example, if your Kafka consumer application delays during commit, and it can become a zombie, and another Kafka consumer application is able to consumer messages, the zombie is consuming. This may be a rare case. However, it is your application's responsibility to avoid duplicate message processing during commit, if you need.
If you cannot accept duplicate message processing during commit, your application have to avoid it yourself. The implementation of additional zombie fencing depends on the transactional capabilities of your consumer side offset store, such as a relational database and another Kafka cluster.
Here are some helpful examples:
When to save offsets, verify the offsets are increased one by one. Each message must be processed in a transaction to be fully effective, but may affect performance.
When to load offsets, load them with relational database shared lock. This means that if a zombie is in the middle of a transaction involving offset updates, the offsets loading with shared lock will be waited until that transaction is finished. And the zombie consumer is assumed to be stopped and back to normal state within the processing of the next new transaction by the zombie fencing feature on Kafka Consumer Side Offset Store. As the result, duplicate message processing can be avoided. However, the consumers will be delayed due to loading offsets.
When to consume messages, they guarantied at-least-once and include sequential offsets. You can store offsets into records as a part of the consumption result, and verify that the offsets are increased when the records are update to achieve exactly-once. However, its implementation will not be easy, and if it can, it would also mean that exactly-once can be achieved without Kafka Consumer Side Offset Store.
Kafka producer has transactional.id function. transactional.id is used to identify the same producer instance across application, and old producers are considered zombies and are fenced out. However, as a reality, it may be difficult to determine transactional.id.