- DENA (Deeplearning Explore Nanopore m6A)
Deep learning model used to detect RNA m6a with read level based on the Nanopore direct RNA data.
E-mail:liangou@ips.ac.cn
Sincere thanks to in-house_scripts developed by Hang Qin (https://github.com/q1134269149).
These instructions will get you a copy of the project up and running on your local machine for development and testing purposes. See deployment for notes on how to deploy the project on a live system.
The links of DENA model files are:
(1) Baidu network disk (百度网盘): https://pan.baidu.com/s/166FmGUziN91kCLknern6Rw?pwd=ocm8;
(2) Google Drive: https://drive.google.com/file/d/10GZaENvetOZ0ClSsHxDhSal0VXHlmK26/view?usp=sharing.
Please clone DENA again, and download the updated DENA model files through the above links, and replace the old model files, and then re-perform RNA m6A modification prediction using the code of step4 (Predict). Thanks!
Utilizing Conda or virtualenv to create a relatively independent & clean work environment may be a wise choice for using DENA
Here are What things you need to install(Please confirm one by one):
- Unix like system(centos,ubuntu,etc)
- Cuda-supported graphics cards(optional)
- Python>=3.7.x and Pytorch
- tombo,minimap2,samtools
Note:
You can get source code of DENA from zenodo with the link: https://zenodoorg/record/5603381 (Discard).
And you can also learn more by reading our research entitled "DENA: training an authentic neural network model using Nanopore sequencing data of Arabidopsis transcripts for detection and quantification of N6-methyladenosine on RNA" .
- a batch of fast5 files containing the raw current signals
- a fastq file which is contain basecalled sequence corresponding fast5 above
- Appropriate reference sequence(Transcriptome is recommended for RNA data)
*Tips: ${variable} : You need to assign it with the your actual value
1.Obtain coordinates matching motif in fasta sequence of reference (Must be transcriptome reference)
python3 LSTM_extract.py get_pos --fasta ${fasta_fn} --motif 'RRACH' --output ./candidate_predict_pos.txtYou will get result(candidate_predict_pos.txt) like this
AT1G01010.1 17 22 + AAACC
*Note:Please confirm that the transcriptome reference is provided instead of the genomic reference before this step.
- We no longer need external C++ tools
- Fixed compatibility bugs in FASTA file of some species
(Optional)If the fast5 files was multi_read_fast5 files, it is necessary to convert folders containing multi_read_fast5 files into single_read_fast5 files using https://github.com/nanoporetech/ont_fast5_api.
multi_to_single_fast5 -t 20 -i ${multi_read_fast5_folder} -s ${single_read_fast5_folder} --recursiveThis step is to obtain the fastq sequences from fast5 files by base-calling using [guppy](Preferred version3.2.4)
${SoftPath}/guppy_basecaller -i ${single_read_fast5_folder} -s ${outfile} --flowcell FLO-MIN106 --kit SQK-RNA001 --cpu_threads_per_caller {thread} --qscore_filtering --fast5_out --records_per_fastq 0 --recursive
cat ${outfile}/pass/*.fastq > basecalls.fq- ${SoftPath}: the path of guppy software
- ${single_read_fast5_folder}: the path of single fast5 files that need to base-call.
- ${outfile}: the path of output folder
*Note: Please check the version offlowcellandkitof the Library Building used in the experiments,and set them correctly.
This step is to obtain a unique mapping between the signal fragment of each base of each reads and the reference sequence For detailed help, please see https://github.com/nanoporetech/tombo
tombo resquiggle --rna --processes {thread} --corrected-group RawGenomeCorrected_001 --basecall-group Basecall_1D_001 --include-event-stdev --overwrite --ignore-read-locks ${params.fast5} ${params.ref}*Note: Please check the basecall-group to be used before re-sqguiggle, and set the corrected-group.
For detailed help, please see minimap2 samtools
minimap2 -ax map-ont -L --secondary=no ${transcriptome} ${basecalls.fq} | samtools view -bh -F 2324 | samtools sort -O bam > basecalls.bam
samtools index basecalls.bam- ${transcriptome}: the fasta of transcriptome reference
- ${basecalls.fq}: the fastq of base-calling from fast5 files in step 2.1
- Support for reading BAM files in BRI mode to reduce memory consumption
Install the C ++ libraries and Python wrappers to enable this functionality https://github.com/nanoporetech/bripy https://github.com/jts/bri
- Flexible window Settings are now supported
- In this step,you need provide two input params for program:fast5_folder(has re-squiggled by tombo) and bam file(sorted & index)
parser.add_argument('--processes',default=24,type=int,
help=("Number of processes allocated"))
parser_a = subparsers.add_parser('get_pos',formatter_class=argparse.RawDescriptionHelpFormatter,help='get candidate position')
parser_a.add_argument('--fasta',required=True, default=None,
help=("reference fasta"))
parser_a.add_argument('--motif', default='RRACH',
help=("specifies a motif pattern"))
parser_a.add_argument('--output', default='./candidate_predict_pos.txt',
help=("output file"))
parser_a.set_defaults(func=get_pos)
parser_b = subparsers.add_parser('predict',formatter_class=argparse.RawDescriptionHelpFormatter,help='predict')
parser_b.add_argument('--fast5',required=True, default=None,
help=("a directory(has been re-squiggled by tombo) that contains the FAST5 files"))
parser_b.add_argument('--corr_grp',default="RawGenomeCorrected_000",
help=("Analysis slot containing the re-squiggle information"))
parser_b.add_argument('--bam',required=True, default=None,
help=("BAM file used to extract base-quality(feature)"))
parser_b.add_argument('--sites',default='./candidate_predict_pos.txt',
help=("candidate position are used to extract features of mapped reads"))
parser_b.add_argument('--label',required=True,
help=("The string used to distinguish the sample"))
parser_b.add_argument('--windows',required=True,nargs=2,metavar='3',type=int,
help=("Window drift away from the center of m6A"))
parser_b.add_argument('--debug',action='store_true',default=False,
help=("Enable debug mode (output more detailed run log)"))
parser_b.add_argument('--bri',action='store_true',default=False,
help=("Enable BRI mode (Reduce RAM consumption of BAM files)")) python3 LSTM_extract.py --processes ${number} predict --fast5 ${fast5_fn} --corr_grp ${RawGenomeCorrected_000} --bam ${bam_fn} --sites ${candidate_predict_pos.txt} --label ${any meaningful string} --windows 2 2-
${RawGenomeCorrected_000}: The path of
corr_grpgenerated in step 2.2. Please confirm to set the samecorr_grpas step 2.2. -
${number}: The Number of threads, default: 25. *Note:
--windows 2 2indicates that a total of 5 bases are extracted, which contains the candidate modified site and 2 bases upstream and downstream of it, e.g. "AAACA". -
You will get result(*.tmp) like this
>AT4G35300.4_2258_GGACT
37b79f1c-c3c2-4c6f-a25c-65e618b7bb6f 28.0,27.0,24.0,31.0,24.0,74.0,6.0,33.0,27.0,63.0,2.6680189601886424,2.4252261046166588,0.16661375589914051,-0.4574264926055352,0.8548283129364287,2.6957830373199303,2.568959475115271,0.08321765590395497,-0.5128530864579424,0.8695237415728408,0.45954324955726,0.7483187244003591,0.23116851931302654,0.21901705697503512,0.23758996696952467
e944b3ff-156c-409f-95f3-996dfa3d3fd3 26.0,30.0,28.0,25.0,31.0,158.0,6.0,47.0,37.0,27.0,2.3582877438291905,2.354059678502405,-0.22480153918158693,-0.5296594244218555,1.084794467401169,2.5690832257777787,2.4814037210635487,-0.24292374684288695,-0.5435391915773902,1.122371397992982,0.7615589741556634,0.6712493289989668,0.19113118923616254,0.20057491958760532,0.21721818493112435
Tips :If the input features NOT changed here is NO need to repeat run step 2
- add "-d" in cmd for output m6a probability for each read at each site.
- Added support for deep learning.
- Caution :Using deep learning model will occupy a lot of computing resources and time costing without GPU
In this step,you need Provide the following parameters:
- ${path_features} :Path contain [0-9]*.tmp (generated by step 2)
- ${path_models} :Path contain *.dat(ensemble learning) or *.pkl (deep learning)
- ${path_output} The output path
- ${prefix_outfile} The prefix of the output file
- conda install pytorch torchvision torchaudio cpuonly -c pytorch
python LSTM_predict.py -i ${path_features} -m ${path_models} -o ${path_output} -p ${prefix_outfile} -d - You will get result ${prefix_outfile}.tsv in ${path_output} like this:
AT1G01010.1 30 AAACA 0 3 0.0
AT1G01010.1 212 AAACA 0 5 0.0
AT1G01010.1 341 AAACA 1 5 0.2
AT1G01020.2 679 AAACA 2 2 1.0
AT1G01030.1 306 AAACA 0 10 0.0
AT1G01030.1 422 AAACA 0 10 0.0
AT1G01030.1 726 AAACA 0 11 0.0
AT1G01030.1 838 AAACA 1 11 0.09090909090909091
AT1G01030.1 876 AAACA 1 11 0.09090909090909091
AT1G01030.1 1233 AAACA 0 11 0.0
-
Note:See the reply for the description of each column: #12
-
if "-d" was added, you will get result ${prefix_outfile}_details.tsv in ${path_output} like this:
AT1G01010.1 30 (# Description: AT1G01010.1 was transcript ID; 30 is the coordinate of candidate "RRACH" site on trancript AT1G01010.1)
b129005a-01e7-49f8-bb50-aadf0d57f079 0.235
85a565d6-08c1-4819-a12a-2beacbf63319 0.447
a5fafedc-1539-4cb8-ad6d-72c8699220cd 0.498
(# Description: The first column was the read ID aligned to AT1G01010.1; Second column was the m6A-modified probability of this read at the candidate coordinate on AT1G01010.1)
- Make sure the rules for gene names are consistent among bam file,fast5 files and fasta file
- python3 ./pca_cluster.py ${some params}
parser.add_argument('--processes',default=24,type=int,
help=("Number of processes allocated"))
parser.add_argument('--input',required=True, default=None,
help=("A directory containing both 'positive_dataset.txt' and 'negative_dataset.txt'"))
parser.add_argument('--output', default='./dimRe_clust_fig',
help=("output directory"))
parser.add_argument('--pos_fast5',required=True, default=None,
help=("a directory(has been re-squiggled by tombo) that contains the FAST5 files of positive_dataset"))
parser.add_argument('--neg_fast5',required=True, default=None,
help=("a directory(has been re-squiggled by tombo) that contains the FAST5 files of negative_dataset"))
parser.add_argument('--corr_grp',default="RawGenomeCorrected_000",
help=("Analysis slot containing the re-squiggle information"))
parser.add_argument('--windows',required=True,nargs=2,metavar='3',type=int,
help=("Window drift away from the center of m6A"))
parser.add_argument('--features',default='norm_mean',nargs=+,choices=['length','norm_mean','norm_med','base_q','norm_stdev']
help=("Input features for dimensionality reduction clustering"))
parser.add_argument('--algorithm_DimRe',default="PCA",choices=['PCA']
help=("Algorithms for dimension reduction"))
parser.add_argument('--algorithm_cluster',default="kmeans",choices=['kmeans']
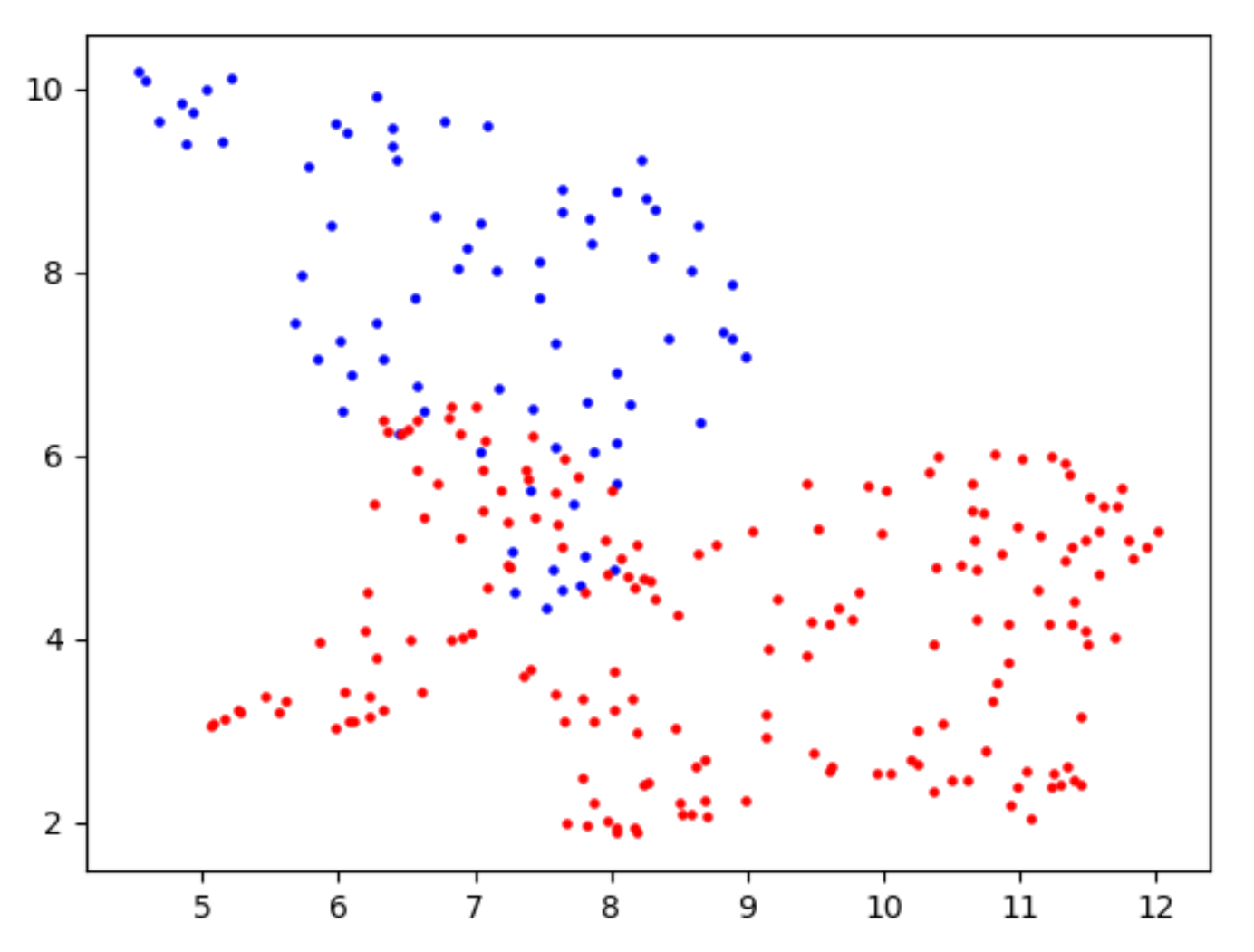
help=("Algorithms for cluster"))- For each candidate site, the corresponding dimensionality reduction result is printed, like this
BLUE:WT sample RED : KO/KD sample
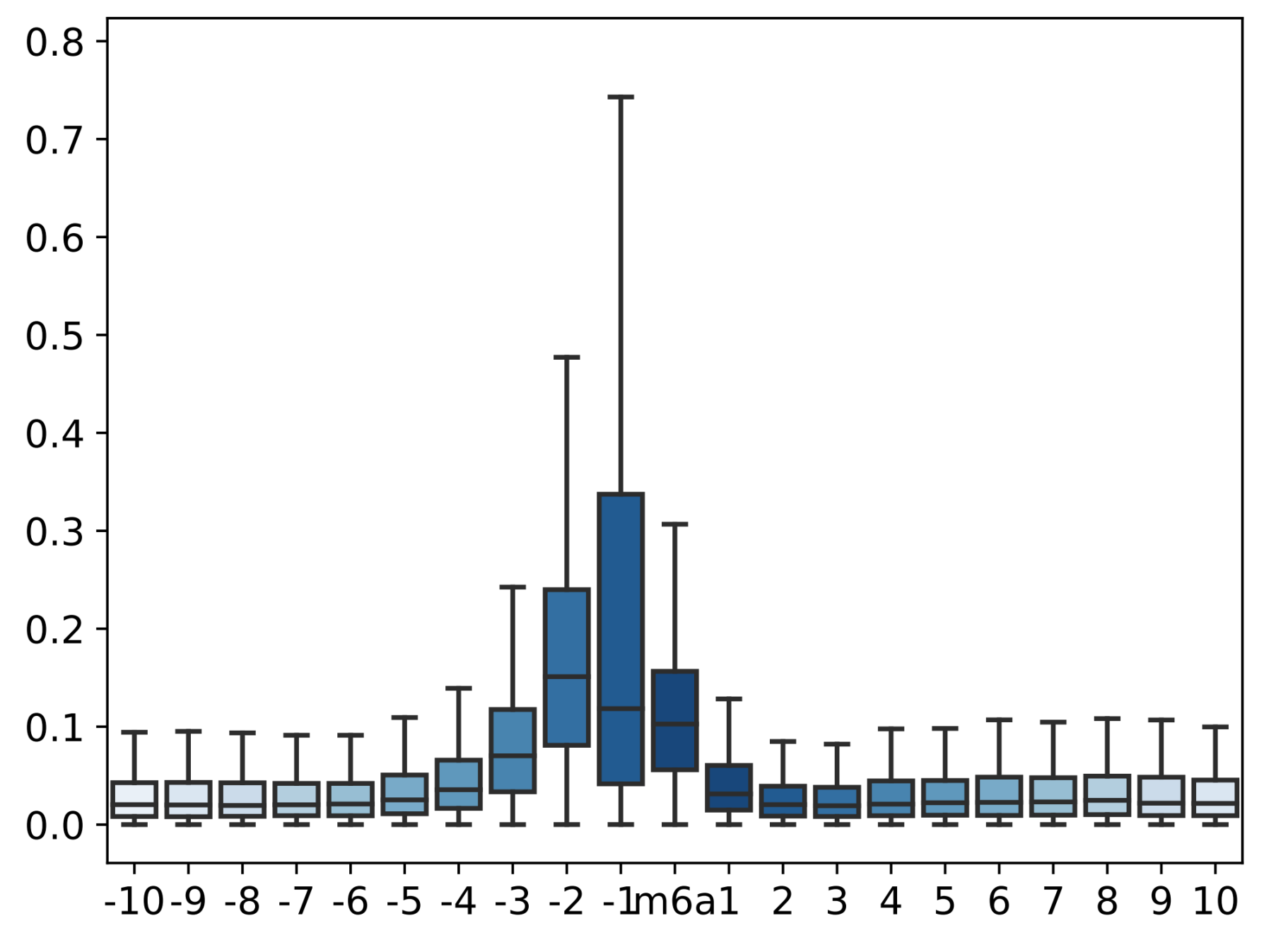
- Calculate and visualize the difference between the current mean values of the two samples covered on the candidate sites
- **python3 ./box_plot.py **
- **Cautions!!!:**Please change the custom variables (below) within the script. This script does not accept CMD parameters
#Defining variables
sites_file="/home/weir/m6a_model/DENA/plotter/final_overlep_sites"
pos_fast5="/home/weir/tair_rawdata/elife_rawdata/VIRc"
neg_fast5="/home/weir/tair_rawdata/elife_rawdata/vir-1"
corrected_group='RawGenomeCorrected_000'
In [4]: !head "/home/weir/m6a_model/DENA/plotter/final_overlep_sites"
AT5G67590.1 787
AT5G67590.1 733
AT5G67560.1 1156
AT5G67560.1 1126
AT5G67510.1 677
AT5G67330.1 2164
AT5G67250.1 2329
AT5G67130.1 1714
AT5G67030.1 2469
AT5G67030.1 2308- result is printed, like this(Data used for drawing is also saved for downstream analysis and visual adjustment)
*All direct RNA-Seq reads of wild-type, fip37-4 and mtb A.thaliana lines generated by this study have been submitted to the ENA under accession PRJEB45935, and National Genomics Data Center, China National Center for Bioinformation (CNCB-NGDC) under project accession PRJCA007105 and GSA accession CRA005317.
If you found this work useful and used our software, please cite our work:
Qin, H., Ou, L., Gao, J., Chen, L., Wang, J. W., Hao, P., & Li, X. (2022). DENA: training an authentic neural network model using Nanopore sequencing data of Arabidopsis transcripts for detection and quantification of N6-methyladenosine on RNA. Genome biology, 23(1), 25. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-021-02598-3
Copyright © 2021 Liang Ou
All suggestions are welcome to liangou@ips.ac.cn