This repository is created to track my progress in solving LeetCode problems. Each problem that I solve will be listed here, along with the solution and any relevant explanations or insights. This will serve as a record of my problem-solving journey and a resource for others who are interested in learning from my solutions. Description
| Solution | Problem | Problem Link |
|---|---|---|
| #1 | Roman to Integer | Link |
| #2 | Check If Two String Arrays are Equivalent | Link |
| #3 | Design Parking System | Link |
| #4 | Shuffle the Array | Link |
| #5 | Defanging an IP Address | Link |
| #6 | Power of Two | Link |
| #7 | Number of Days Between Two Dates | Link |
| #8 | Maximum Product Difference Between Two Pairs | Link |
| #9 | Merge Strings Alternately | Link |
| #10 | Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array | Link |
| #11 | Rotate Image | Link |
| #12 | Partitioning Into Minimum Number Of Deci-Binary Numbers | Link |
| #13 | Valid Palindrome | Link |
| #14 | Two Sum | Link |
-
Problem Description: Given a roman numeral, convert it to an integer. The input is guaranteed to be within the range from 1 to 3999.
-
Example:
Input: "XIV"
Output: 14
Explanation: The roman numeral "XIV" represents the number 14.
- Solution:
const romanValues = new Map([
["I", 1],
["V", 5],
["X", 10],
["L", 50],
["C", 100],
["D", 500],
["M", 1000],
]);
function romanToInt(str) {
let total = 0;
let prevValue = 0;
let reverseStr = str.split("").reverse();
reverseStr.forEach((item) => {
const currentValue = romanValues.get(item);
if (currentValue >= prevValue) {
total += currentValue;
} else {
total -= currentValue;
}
prevValue = currentValue;
});
return total;
}- Explanation:
I have implemented a function
romanToIntin JavaScript that converts a given roman numeral string to its corresponding integer value. I use an objectromanNumeralsto store the values of each roman numeral. Starting from the end of the input string, I iterate through each character and check its corresponding value. If the current value is greater than or equal to the previous value, I add it to the result. Otherwise, I subtract it from the result. Finally, I return the result.
- Problem Description:
Given two string arrays
word1andword2, return `true
if the two arrays represent the same string, andfalse` otherwise. A string is represented by an array if the array elements concatenated in order forms the string.
- Example:
Input: word1 = ["ab", "c"], word2 = ["a", "bc"]
Output: true
Explanation: Concatenating the elements of word1 in order gives "ab" + "c" = "abc", which is the same as word2.
- Solution:
var arrayStringsAreEqual = function(word1, word2) {
const str1 = word1.join("");
const str2 = word2.join("");
return str1 === str2;
};- Explanation:
The
arrayStringsAreEqualfunction takes two string arraysword1andword2. It joins the elements of each array into two separate stringsstr1andstr2using thejoin("")method. It then comparesstr1andstr2using the strict equality operator===to determine if they are equal. The function returnstrueif they are equal andfalseotherwise.
-
Problem Description: Design a parking system for a parking lot. The parking lot has three kinds of parking spaces: big, medium, and small, with a fixed number of slots for each size. Implement the
ParkingSystemclass:ParkingSystem(int big, int medium, int small)Initializes an object of theParkingSystemclass. The number of slots for each parking space are given asbig,medium, andsmallrespectively.bool addCar(int carType)Checks whether there is a parking space ofcarTypefor the car that wants to get into the parking lot.carTypecan be of three kinds: big, medium, or small, which are represented by integers1,2, and3respectively. A car can only park in a parking space of itscarType. If there is no space available, returnfalse, else park the car in that size space and returntrue.
-
Example:
Input
["ParkingSystem", "addCar", "addCar", "addCar", "addCar"]
[[1, 1, 0], [1], [2], [3], [1]]
Output
[null, true, true, false, false]
Explanation
ParkingSystem parkingSystem = new ParkingSystem(1, 1, 0);
parkingSystem.addCar(1); // return true because there is 1 available slot for a big car
parkingSystem.addCar(2); // return true because there is 1 available slot for a medium car
parkingSystem.addCar(3); // return false because there is no available slot for a small car
parkingSystem.addCar(1); // return false because there is no available slot for a big car (no available slots for big or medium cars left)
- Solution:
/**
* @param {number} big
* @param {number} medium
* @param {number} small
*/
var ParkingSystem = function(big, medium, small) {
this.spots = [null, big, medium, small];
};
/**
* @param {number} carType
* @return {boolean}
*/
ParkingSystem.prototype.addCar = function(carType) {
return this.spots[carType] && this.spots[carType]-- > 0;
};
/**
* Your ParkingSystem object will be instantiated and called as such:
* var obj = new ParkingSystem(big, medium, small)
* var param_1 = obj.addCar(carType)
*/- Explanation:
The
ParkingSystemclass is implemented with a constructor that takes the number of available slots for each car type (big,medium, andsmall). TheaddCarmethod checks if there is an available slot for the givencarType. If there are available slots, it decreases the count for that car type and returnstrue. Otherwise, it returnsfalseindicating that there is no available slot for the car type.
-
Problem Description: Given the array
numsconsisting of2nelements in the form[x1,x2,...,xn,y1,y2,...,yn]. Return the array in the form[x1,y1,x2,y2,...,xn,yn].Note:
nis a positive integer. -
Example:
Input: nums = [2,5,1,3,4,7], n = 3
Output: [2,3,5,4,1,7]
Explanation: Since n is 3, we split the array into [2,5,1] and [3,4,7] and shuffle them together to obtain [2,3,5,4,1,7].
- Solution:
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @param {number} n
* @return {number[]}
*/
var shuffle = function(nums, n) {
const x = nums.slice(0, n);
const y = nums.slice(n);
let newArr = [];
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
newArr.push(x[i], y[i]);
}
return newArr;
};- Explanation:
The
shufflefunction takes an arraynumsand a positive integernas input. It creates two new arraysxandyby slicingnumsinto two parts. It then iteratesntimes and pushes thei-th element fromxandyinto a new arraynewArr. Finally, it returnsnewArrwhich contains the shuffled elements.
-
Problem Description: Given a valid IP address
address, return a defanged version of that IP address.A defanged IP address replaces every period
"."with"[.]". -
Example:
Input: address = "1.1.1.1"
Output: "1[.]1[.]1[.]1"
- Solution:
/**
* @param {string} address
* @return {string}
*/
var defangIPaddr = function(address) {
return address.replaceAll('.','[.]')
};- Explanation:
The
defangIPaddrfunction takes a stringaddressas input. It uses thereplaceAllmethod to replace all occurrences of a period (.) in the address with"[.]". Finally, it returns the defanged IP address.
-
Problem Description: Given an integer
n, returntrueif it is a power of two. Otherwise, returnfalse.An integer
nis a power of two, if there exists an integerxsuch thatn == 2^x. -
Example:
Input: n = 16
Output: true
Explanation: 2^4 = 16.
- Solution:
/**
* @param {number} n
* @return {boolean}
*/
var isPowerOfTwo = function(n) {
return Number.isInteger(Math.log2(n));
};- Explanation:
The
isPowerOfTwofunction takes an integernas input. It checks if the logarithm base 2 ofnis an integer usingNumber.isInteger(Math.log2(n)). If the logarithm is an integer, it means thatnis a power of two. The function returnstruein that case, andfalseotherwise.
-
Problem Description: Write a function
getDaysBetweenDatesto calculate the number of days between two dates. The input dates are given as strings in the format"YYYY-MM-DD". -
Example:
Input: date1 = "2022-01-01", date2 = "2023-01-01"
Output: 365
- Solution:
/**
* @param {string} date1
* @param {string} date2
* @return {number}
*/
var daysBetweenDates = function(date1, date2) {
date1 = new Date(date1)
date2 = new Date(date2)
let oneDay = 1000 * 3600 * 24
return Math.abs(Math.round((date1 - date2) / oneDay))
};- Explanation:
The
daysBetweenDatesfunction takes two date stringsdate1anddate2as input. It converts the date strings intoDateobjects and calculates the difference in milliseconds between the two dates. This difference is then divided by the number of milliseconds in a day to obtain the number of days. The function returns the absolute value of the rounded number of days.
-
Problem Description: The maximum difference between two elements in an array is defined as the absolute difference between two elements, where the first element is larger than the second element. For example, the maximum difference between
[4, 2, 5, 9]is9 - 2 = 7.You are given an integer array
numsof lengthn. You want to maximize the difference between the product of any two integers innums. Return the maximum difference. -
Example:
Input: nums = [5,6,2,7,4]
Output: 34
Explanation: We can choose indices 1 and 3 for the first pair (6, 7) and indices 2 and 4 for the second pair (2, 4). The product difference is (6 * 7) - (2 * 4) = 34.
- Solution:
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {number}
*/
var maxProductDifference = function(nums) {
nums.sort((a, b) => a - b);
let n = nums.length;
let max1 = nums[n - 1];
let max2 = nums[n - 2];
let min1 = nums[0];
let min2 = nums[1];
return (max1 * max2) - (min1 * min2);
};
/**
we need 2 max number and 2 min number
i think we can make maxnumerArr and minNumberArr
in nums arr we get the max number split then get max agin .
then min number split then min number
then implement the equation
*/- Explanation:
The
maxProductDifferencefunction takes an integer arraynumsas
input. It first sorts the array in ascending order using the sort method with a comparison function (a, b) => a - b. After sorting, the maximum difference between the product of two integers can be obtained by subtracting the product of the first two elements from the product of the last two elements. The function returns the calculated difference.
-
Problem Description: You are given two strings,
word1andword2. Merge the strings by adding letters in alternating order, starting withword1. If one of the strings is longer than the other, append the remaining letters of the longer string at the end of the merged string.Return the merged string.
-
Example:
Input: word1 = "abc", word2 = "def"
Output: "adbecf"
Explanation: The merged string will be "a" + "d" + "b" + "e" + "c" + "f".
Input: word1 = "ab", word2 = "xyz"
Output: "axbyz"
Explanation: The merged string will be "a" + "x" + "b" + "y" + "z".
- Solution:
/**
* @param {string} word1
* @param {string} word2
* @return {string}
*/
var mergeAlternately = function(word1, word2) {
var merged = "";
var i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < word1.length && j < word2.length) {
merged += word1[i] + word2[j];
i++;
j++;
}
merged += word1.slice(i) + word2.slice(j);
return merged;
};-
Explanation: The
mergeAlternatelyfunction takes two strings,word1andword2, as input and merges them alternately. It initializes an empty stringmergedto store the merged result. Then, it uses two pointersiandjto iterate overword1andword2respectively.Inside the while loop, it appends the characters at the current positions of
iandjto themergedstring. Then, it increments bothiandjby 1.After the while loop, it checks if there are any remaining characters in
word1orword2. If there are, it appends the remaining characters to themergedstring usingsliceto extract the substrings starting from the current positions ofiandj.Finally, it returns the merged string.
-
Problem Description: Given a sorted array
nums, remove the duplicates in-place such that each element appears only once and returns the new length. Do not allocate extra space for another array; you must do this by modifying the input array in-place with O(1) extra memory. -
Example:
Input: nums = [1,1,2]
Output: 2
Explanation: The function should modify the array to return the new length and remove the duplicates. The modified array will be [1, 2], and the length is 2.
Input: nums = [0,0,1,1,1,2,2,3,3,4]
Output: 5
Explanation: The function should modify the array to return the new length and remove the duplicates. The modified array will be [0, 1, 2, 3, 4], and the length is 5.
- Solution:
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {number}
*/
var removeDuplicates = function(nums) {
if (nums.length === 0) {
return 0;
}
var i = 0;
for (var j = 1; j < nums.length; j++) {
if (nums[j] !== nums[i]) {
i++;
nums[i] = nums[j];
}
}
return i + 1;
};-
Explanation: The
removeDuplicatesfunction takes an input arraynumsand removes the duplicates in-place. It uses two pointers,iandj, whereirepresents the position to store the next non-duplicate element, andjiterates over the array.Initially, it checks if the length of
numsis 0. If it is, it means there are no elements, and the function returns 0.Inside the for loop, it compares
nums[j]withnums[i]to check for duplicates. Ifnums[j]is different fromnums[i], it means a new non-duplicate element is found. In that case, it incrementsi, updatesnums[i]with the new element, and proceeds to the next iteration.The loop continues until all elements are processed. Finally, the function returns
i + 1, which represents the length of the modified array without duplicates.
This solution effectively removes duplicates from the sorted array in-place by keeping track of two pointers and updating the array elements accordingly.
-
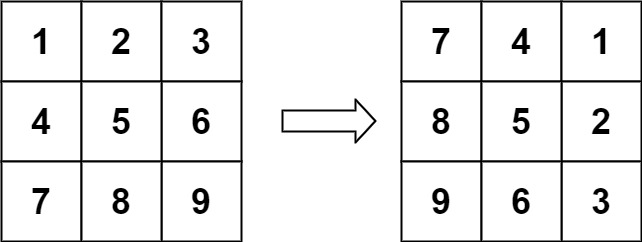
Problem Description: You are given an
n x n2D matrix representing an image, rotate the image by 90 degrees (clockwise).You have to rotate the image in-place, which means you have to modify the input 2D matrix directly. DO NOT allocate another 2D matrix and do the rotation.
-
Example:
Input: matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]] Output: [[7,4,1],[8,5,2],[9,6,3]] -
Solution:
var rotate = function(matrix) {
for(let i=0;i<matrix.length;i++){
for(let j = i+1;j<matrix.length;j++){
[matrix[i][j],matrix[j][i]] = [matrix[j][i],matrix[i][j]]
}
matrix[i].reverse()
}
};- Explanation:
The
rotatefunction takes a 2D matrix as input and rotates the image by 90 degrees clockwise. To achieve this, we first transpose the matrix by swapping elements along the diagonal. Then, we reverse each row of the transposed matrix. This in-place operation modifies the input matrix directly.
-
Problem Description: A decimal number is called deci-binary if each of its digits is either '0' or '1' without any leading zeros. For example, 101 and 1100 are deci-binary, while 112 and 3001 are not.
Given a string
nthat represents a positive integer, return the minimum number of positive deci-binary numbers needed so that they sum up ton. -
Example:
Input: n = "32" Output: 3 Explanation: 32 can be represented as "11111" + "11" + "10". -
Solution:
var minPartitions = function(n) {
const arr = n.split("")
return Math.max(...arr)
};- Explanation:
The
minPartitionsfunction takes a stringnas input and returns the minimum number of positive deci-binary numbers needed to sum up ton. Since each deci-binary digit can only be '0' or '1', the largest digit inndetermines the number of deci-binary numbers needed. We convertnto an integer and return the maximum digit using themaxfunction.
-
Problem Description: Given a string
s, determine if it is a palindrome, considering only alphanumeric characters and ignoring cases. -
Example:
Input: s = "A man, a plan, a canal: Panama"
Output: true
Explanation: "amanaplanacanalpanama" is a palindrome.
- Solution:
function isPalindrome(s) {
const alphanumeric = s.toLowerCase().match(/[a-z0-9]/g);
if (alphanumeric === null) {
return true;
}
const reversedArr = alphanumeric.slice().reverse();
return alphanumeric.join("") === reversedArr.join("");
}- Explanation:
The function
isPalindromechecks if the given stringsis a valid palindrome. It converts the string to lowercase and uses a regular expression to match alphanumeric characters. If there are no alphanumeric characters in the string, it returnstrueas it is considered a palindrome. Otherwise, it creates a reversed copy of the alphanumeric characters and compares it with the original to determine if it is a palindrome. The function returnstrueif it is a palindrome andfalseotherwise.
-
Problem Description: Given an array of integers
numsand an integertarget, return indices of the two numbers such that they add up totarget. You may assume that each input would have exactly one solution, and you may not use the same element twice. You can return the answer in any order. -
Example:
Input: nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9 Output: [0,1] Explanation: The sum of 2 and 7 is 9. Therefore, the indices of the two numbers are 0 and 1. Input: nums = [3,2,4], target = 6 Output: [1,2] Input: nums = [3,3], target = 6 Output: [0,1] -
Solution:
/** * @param {number[]} nums * @param {number} target * @return {number[]} */ var twoSum = function(nums, target) { const map = new Map(); for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { const complement = target - nums[i]; if (map.has(complement)) { return [map.get(complement), i]; } map.set(nums[i], i); } return []; };
-
Explanation: The
twoSumfunction takes an array of integersnumsand an integertargetas input. It uses a hash map to store the complement of each number encountered during the iteration. For each numbernuminnums, it calculates the complement ascomplement = target - num. If the complement exists in the hash map, it means that the pair of numbers that sum up to the target has been found. The function returns the indices of the two numbers as[map.get(complement), i]. If no such pair is found, an empty array[]is returned.
If you have any suggestions, improvements, or alternative solutions for the listed problems, feel free to contribute by submitting a pull request. Your contributions are highly appreciated.
Note: The table above will be updated as I solve more problems.
This project is licensed under the MIT License.