-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 2
Home
Intel‘s 12th Gen Core processor lineup (aka Alder Lake) does not officially support the AVX-512 instruction set, however it may be possible to enable it as the P-cores are functionally capable of doing so.
The feature was initially rumoured to be present until Intel declared otherwise. Despite that, actual released chips had the feature, which Intel tried to rectify via microcode updates, only to be defied by motherboard manufacturers. Finally, Intel decided to settle the matter by fusing off the functionality themselves (assuming their claim really is accurate).
This means that if you‘re one of the few people hoping to have an Alder Lake setup with AVX-512, there are a few things to look out for, and information regarding the matter is scattered around the place, so this page aims to collate all that around to hopefully make the process easier. If you have any new info available, please feel free to update this page.
You will need three things for AVX-512 functionality on Alder Lake:
- Older Alder Lake CPU without AVX-512 functionality fused off
- Check the CPU’s batch# starts with V149 or X149, or a lower number. Those starting with V150/X150 to V201/X201 may support it, whilst V202/X202 or a higher number likely don’t.
- Compatible BIOS with compatible CPU microcode
- Asrock is likely good, whilst ASUS/Gigabyte/MSI may require staying on an older BIOS version. Unknown for other vendors.
- Disabling E-cores (if present) and enabling AVX-512 in BIOS
It has been suggested that the Intel logo on the IHS (where 'halo' = AVX-512 support, squares = no support) can be used as a guide, however this advice is contested - see below.
The rest of the article contains more detailed info of the above.
Reports of Intel fusing off AVX-512 on Alder Lake were first published at the beginning of March 2022. Despite it claiming non-K chips were affected at the time, I can confirm that -K chips are also affected. This means that you‘ll need a CPU manufactured before the change was made.
A rough guess on whether AVX-512 is available can be obtained by looking at the batch number. This number is printed on the CPU box in the bottom-right corner of the info panel, or on the last line printed on the chip’s IHS.


(Pictured: Core i5 12600K CPU from batch X202J832, box and IHS shown; this CPU does not have AVX-512 enabled)
This number should start with a V or X, followed by three digits. The first digit signifies the year (1 = 2021, 2 = 2022), whilst the next two indicate the week number.
CPUs produced during 2022 week 2 (i.e. batch# starting with X202 or V202) appear to have AVX-512 functionality fused off. There is a report of a batch 201 12900K chip with AVX-512, whilst here’s a report of a last week 2021 (batch 152?) 12400F lacking support, whilst a batch 201 12700 has it. It seems like chips prior to batch 150 seem to be guaranteed to support AVX-512, whilst some SKUs between 150 and 201 might as well.
However, this overclocker shows a batch 202 G7400 not supporting AVX-512, whilst a batch 211 G7400 does. He suggests that the logo above the text on the IHS might signify AVX-512 availability, with the halo meaning it's available, whilst the rectangle meaning it isn't. However, this advice goes against the 12600K pictured above, which has a halo, but no AVX-512. I'm not sure how to interpret this exactly, but perhaps later batches of CPUs have AVX-512 enabled again?
The first Alder Lake products were 12600K/KF, 12700K/KF and 12900K/KF desktop SKUs, so you‘re most likely going to find chips from older batches there. Whilst non-K desktop SKUs supporting AVX-512 exist, it‘s unlikely any 12900KS or later chip supports AVX-512. Mobile Alder Lake is unknown, but I‘d expect it to not be present there either. Intel’s upcoming 13th gen core (Raptor Lake) is rumoured to still use Gracemont for E-cores, so one would expect AVX-512 to be fused off there.
In addition to the CPU, the motherboard’s BIOS also needs to support the feature. This includes the BIOS, as well as the CPU microcode supplied by the BIOS. Z690 was the first Alder Lake compatible chipset released, so has the highest likelihood of supporting the feature, though there’s been reports of B660 chipset motherboards having the feature.
Across motherboard manufacturers:
- Asrock: can’t find much info, but this post suggests support on Z690 Phantom Gaming with the right BIOS. This post also suggests support on Asrock boards in general, whilst this H610M-HDV manual lists it as an option, further confirming the likelihood. This post does recommend against Asrock for AVX-512, so there may be conditions on getting it working.
-
ASUS: there seems to be many reports of ASUS Z690 motherboards supporting AVX-512. Microcode may need to be patched on newer BIOS. Suggestions of support on B660 exist, but may be removed from 1009 BIOS.
AVX-512 reportedly works on the ROG Strix Z690-A Gaming Wifi D4 with BIOS 1404, so support may vary across all Z690 boards. - Biostar: status unknown
- EVGA: this screenshot shows the option for an EVGA BIOS; considering the limited EVGA LGA1700 lineup, my guess is it's available all on EVGA motherboards with the right BIOS version
- Gigabyte: various reports suggesting it’s unavailable, however this poster claims support on B660 Aorus Master if BIOS is older than F7, whilst this post has it on B660M DS3H using BIOS F4. Unknown if this is just a microcode issue, or BIOS lacking the option. This thread suggests that the BIOS may need modding, even if an earlier microcode is supplied. Also note that the original AnandTech article claims support; my guess is that it worked better on older BIOSes.
- Maxsun: B660m Challenger has AVX-512 support starting from BIOS version B2.2G. official support page in Chinese
- MSI: AVX-512 is supported on BIOS v1.1 and v1.2 Z690 boards. BIOS v1.2 includes an option to toggle the CPU microcode for AVX-512, however, this feature is missing in v1.3 (even though the other AVX-512 options are listed, which means that AVX-512 can be enabled if you mod the BIOS with older microcode). This video shows a B660M Mortar with the option available, and this post mentions it on Pro B660M-A, so it’s likely available across the B660 line.
- Soyo: status unknown
AVX-512 support is present in microcode 0x16 and earlier, absent in 0x18 and later (0x17 is unknown). You‘ll need to make sure your BIOS is paired with the older microcode for the feature, or mod newer BIOSes with older microcode (unless it provides the option to switch it).
BIOSes may display which microcode is being used. You can also check it from the OS:
-
Linux: use the command
grep microcode /proc/cpuinfo -
Windows: tools like HWiNFO can show the microcode

If you have a compatible CPU and BIOS, all that‘s left to do is configure the BIOS correctly. Generally the following needs to be set:
-
Disable all E-cores (if present on your SKU)
-
Enable AVX-512 (if not done automatically)
If your CPU has E-cores (12600K/KF SKU or higher), these will need to be disabled to enable AVX-512, as the E-cores do not support the instruction set. All BIOSes should provide functionality to do this.

(Pictured: MSI BIOS, advanced mode, under OC > Advanced > Per E-Core Control)
After disabling E-cores, you may need to explicitly enable AVX-512 (if the ‘auto’ option doesn’t do it).

(Pictured: MSI BIOS v1.1, advanced mode, under OC section)
If you are using a motherboard with a selectable CPU microcode (like some MSI boards on BIOS v1.2), you may also need to select the AVX-512 compatible microcode (again, if ‘auto’ doesn’t do it).

(Pictured: MSI BIOS v1.2, advanced mode, under OC > Microcode Selection)
Under Linux, use the command grep avx512 /proc/cpuinfo - if you see a bunch of lines starting with flags, then it‘s enabled, whilst no output means it‘s disabled.
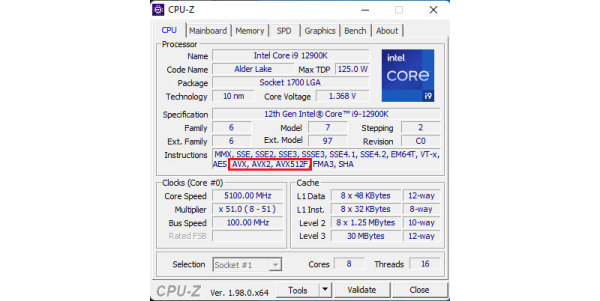
Under Windows, tools like HWiNFO, CPU-Z and AIDA64 can show the presence of the functionality.
As AVX-512 isn‘t officially supported, it‘s possible that Alder Lake may have unexpected issues with AVX-512. However I haven‘t seen any such reports so far, and I‘m doubtful that they‘ll ever arise.
Hence, the only downsides I can think of with enabling AVX-512 are largely what‘s noted above:
- Cannot have both AVX-512 and E-cores enabled at the same time
- Cannot update motherboard BIOS without modding it with older microcode (not an issue if your BIOS supports microcode selection)
- If modding a BIOS, be sure that the motherboard supports dual BIOS or has BIOS flashback functionality, to be able to recover from a broken BIOS
- CPU microcode cannot be updated past 0x16, so if CPU bugs are found and patched in a later microcode, you won‘t get access to them
- This post seems to suggest that AVX-512 may limit overclocking potential
There have been power usage/heat concerns with AVX-512 on earlier Intel processors, but there are also reports that this is no longer an issue on Alder Lake (unsure if this somehow differs with the overclocking scenario).