VGG Face is a dataset of 2.6 million face images of 2,622 people that is used for the development facial recognition technology. The development of VGG Face dataset was supported by United States Office of the Director of National Intelligence (ODNI) and Intelligence Advanced Research Projects Activity (IARPA).
In these expreiments I built a Convolutional Neural Network with 16 Convolutional Layers, One CNN Layer is followed by a Zero Padding Layer and then the next CNN layer is followed by a Max Pooling Layer.
The number of filters in CNN layers started from 64 in the first layer to 4096 filters in the last layer.
The model was then loaded with pretrained weights found here.
When applied to a preprocessed image, the model generates an array of another array which contains 2622 values. These values are nothing but numerical representation of what our model learnt from that image, or the extracted features of our image.
To check the similarity between two images, we have to run the model on both images seperately, it gives us two arrays of 2622 values each. Now to compare the values or the extracted features we usually use two different metrices, namely cosine similarity and Euclidean distance. I will try to give a basic intution into both these metrices but I highly recommend reading this article by Chris Emmery who is a Researcher/Lecturer at the Department of Cognitive Science & Artificial Intelligence at Tilburg University in Netherlands.
I used only Cosine Similarity in the first notebook and then used both cosine similarity and Euclidean distance in the second notebook.
Cosine Similarity:
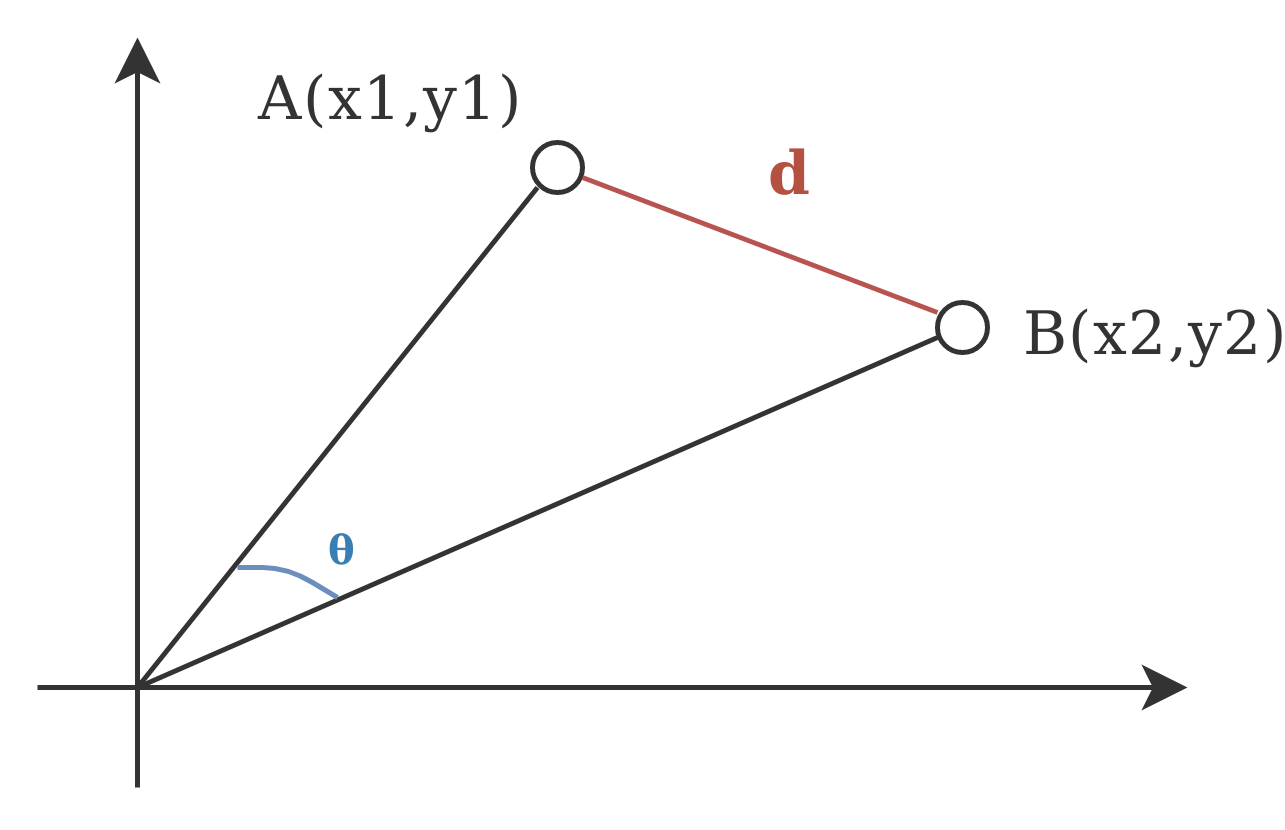
Consider you have two vectors plotted in a 2 dimensional space, consine similarity is nothing but the cosine of the angle between these two vectors as measured from the point of origin.
In the image below, the angle θ is the value of cosine of the angle between two vectors. Subtracting the value from 1 gives us the cosine similarity.
Euclidean Distance:
Euclidean distance is the physical distance between these two vectors, named after the ancient Greek mathematician Euclid. The distance 'd' in the above image is the Euclidean distance.
The choice of the metric depends on the use case and problem domain, for facial recognition/verification, Cosine similarity generally works fine but sometimes its better to use Euclidean distance. Thats why I used both in this repository. Cosine similarity value ranges from 0 to 1 and I have set 0.40 as the epsilon.