This packages provides a ros-wrapper for mohou, which enables collect data (via kinesthetic teaching or HTC vive controller), data conversion to mohou's format, train, and execute on the real robot.
install this package as pip
pip3 install -e .
If you are scared, please use virtualenv or whatever. Future direction would be using catkin virtual env.
If you get stuck at installing opencv-python because of skbuild, please refere to https://stackoverflow.com/questions/63448467/installing-opencv-fails-because-it-cannot-find-skbuild
Currently, there is no ros pacakge dependency which must be installed from source. So, no need to create new workspace and you can install this package by
We need to build a workspace, because pr2eus is not released yet in noetic.
sudo apt-get install python3-wstool python3-catkin-tools
source /opt/ros/noetic/setup.bash
mkdir -p ~/mohou_ws/src
cd ~/mohou_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/HiroIshida/mohou_ros.git
wstool init
wstool merge mohou_ros/rosinstall.noetic
wstool update
rosdep install --from-paths . --ignore-src -y -r
cd ~/mohou_ws
catkin init
catkin buildIf you are using melodic, you need to build some packages from source with the following configuration to use python3.
sudo apt-get install python3-catkin-pkg-modules python3-rospkg-modules python3-venv python3-empy
sudo apt-get install python-catkin-tools python-wstool ros-melodic-rostest
source /opt/ros/melodic/setup.bash
mkdir -p ~/mohou_ws/src
cd ~/mohou_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/HiroIshida/mohou_ros.git
wstool init
wstool merge mohou_ros/rosinstall.melodic
wstool update
rosdep install --from-paths . --ignore-src -y -r
cd ~/mohou_ws
catkin init
catkin config -DPYTHON_EXECUTABLE=/usr/bin/python3 -DPYTHON_INCLUDE_DIR=/usr/include/python3.6m -DPYTHON_LIBRARY=/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libpython3.6m.so
catkin buildMost of the command below end with -pn {your_project_name} option. However this can be omitted by setting the global configuration of the project.
The global configuration can be set by adding and editting ~/.mohou/setting.yaml file, and by setting primary_project_name, you can omit -pn {your_project_name} option.
To do that, please hit the following command (replace your_project_name by your projcet name)
echo "primary_project_name: your_project_name" >> ~/.mohou/setting.yamlmohou and mohuo_ros manage each project by a corresponding project directory under ~/.mohou. For example, if your project is named pr2_kitchen, all the config, rosbags must be put under ~/mohou/pr2_kitchen directory. Also, any training results such as trained autoencoder and trained lstm is put under the project directory.
So, the first step is creating a project directory by
mkdir ~/.mohou/{your_project_name}Then, create a ~/.mohou/{your_project_name}/main_config.yaml file and edit this file while referencing an example. main_config.yaml basically configure which ros topic (e.g. CompressedImage and JointStates) is converted to which mohou primitive type (e.g. AngleVector and RGBImage).
Each conversion rule can be found in mohou_ros_utils/conversion.py. Let us explain how to add a new custom rule. Say, you bought a new robot named Pikachu and add a new rule from PikachuDualArmGripperStates(I just made up) to GripperState. In that case please add the following class to mohou_ros_utils/conversion.py
@dataclass
class PikachuGripperStateConverter(MessageConverter[PikachuDualArmGripperStates, GripperState]):
@classmethod
def out_element_type(cls) -> Type[GripperState]:
return GripperState
def apply(self, msg: PikachuDualArmGripperStates) -> GripperState: # type: ignore[override]
# please write the main conversion rule that convert the message to a single vector
values = []
values.append(msg.right_arm_gripper.finger1.command)
values.append(msg.right_arm_gripper.finger2.command)
values.append(msg.left_arm_gripper.finger1.command)
values.append(msg.left_arm_gripper.finger2.command)
vec = np.array(values)
return GripperState(vec)
@classmethod
def from_config(cls, config: Config): # in many case you don't have to edit this
assert cls.is_compatible(config)
return cls.from_config_topic_name_only(config)
@classmethod
def input_message_type(cls) -> Type[PikachuDualArmGripperStates]:
return PikachuDualArmGripperStateswhere the anything is ok for the class name. After adding the class, the high-level converter, seeing the ~/.mohou/{your_project_name}/main_config.yaml, automatically select the compatible converter according to the input and output type (In this case PikachuDualArmGripperStates to GripperState).
home position is the initial robot joint configuration. By saving and applying this, you cam keep the data-collection phase and test phase condition consistent.
rosrun mohou_ros save_home_position.py -pn {your_project_name}
Please save your rosbag files under ~/.mohou/{project_name}/rosbag. Each rosbag file name must be ended with .bag extension.
You can use whatever your favorite way to collect rosbag. To make is easier, this package provides
save_rosbag.py
rosrun mohou_ros save_rosbag.py -pn {your_project_name} # with `--gif` option, gif files of rgb image will be dumped for debugging(pr2 only) Also you can use vive controller to teach pr2-robot and save:
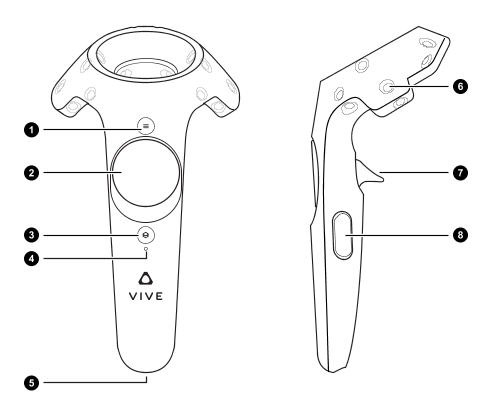
rosrun mohou_ros vive_controller_pr2.py -pn {your_project_name}the button to usage map of vive controllers is follows. Note that right and left arm controllers have a little bit different usage. The following image is took from https://github.com/knorth55/eus_vive
Right arm controller
| Button | Usage |
|---|---|
| 1 | start / stop saving rosbag |
| 2 | start / stop tracking |
| 7 | grasp / open |
| 8 | return to home position |
Left arm controller
| Button | Usage |
|---|---|
| 1 | delete the latest rosbag |
| 2 | start / stop tracking |
| 7 | grasp / open |
| 8 | return to home position |
NOTE: when you delete that latest rosbag after stop saving rosbag, please wait few seconds.
Interactively create image config, which include crop and gaussian blur and hsv filter.
# press Ctrl-C to quit and save the configuration as `image_config.yaml` under the project folder.
rosrun mohou_ros tune_image_filter.py -pn {your_project_name}GaussianBlurFilter:kernel_width = 5 is recommended. Altering HSV value is not recommended.
ResolutionChangeResizer:resol change the image resolution. This must be 112 or 224 due to the implementation of mohou side.
Bundle here means the binary dataset that will be used in the training deep network. We must create this bundle by converting the rosbag data. This section explains how to do this.
For better training of autoencoder, much image is required. So we want to create a bundle with high hz. (20 hz or higher is recommended)
rosrun mohou_ros bags2chunk.py -hz 20 -remove_policy donothing -postfix autoencoder -untouch 5 --compress --gif -pn {your_project_name}Here, untouch means number of episodes which will be kept untouch (will not used in the training). This is helpful when
you want to use it only for visualization or debugging.
Other command line options for this script is
| option | meaning |
|---|---|
--compress |
compress RGBImage sequence using mp4 when dumping EpisodeBundle. This reduce the bundle size by a factor of more than 10. |
--gif |
dump gif image corresponding with each episode |
On the other hand, lstm training require lower frequency data (5hz ~ 8hz) is recommended.
rosrun mohou_ros bags2chunk.py -hz 5 -remove_policy remove -untouch 5 --compress --gif -pn {your_project_name}Sometimes, in the initial phase of the episode, data is static, which is usually bad for learning lstm because the policy becomes long-time-dependent. remove_policy may fix such data.
-
remove_policy = remove, the such too long static initial sequence will be removed and the removeed sequence will be added to bundle. (recommended if your many of your episode needs to be ammended) -
remove_policy = skip, too long static initial sequence will be skipped and will not be added to the bundle. -
remove_policy = donothing, regardless of the initial static phase, any episode will be added to the bundle. (recommended for autoencoder training)
Currently theses remover handles only initial state.
rosrun mohou_ros train.py -pn {your_project_name} -n_vae 1500 -n_lstm 20000
rosrun mohou_ros reset_to_home.py -pn {your_project_name}
Without the --force argument, the real robot will not move, i.e., it will dryrun. The --terminate argument can be used to automatically terminate the program if the value of TerminateFlag exceeds the threshold value. The threshold value can be set with -tt argument.
rosrun mohou_ros execute_pr2.py -pn {your_project_name} --force