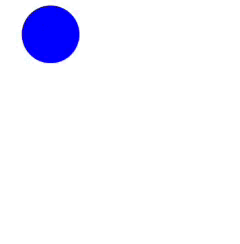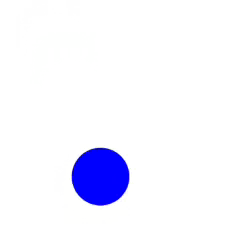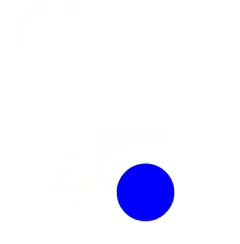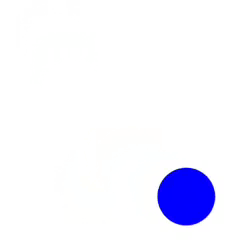
Clase para crear y manipular animaciones de manera sencilla y directa con Javascript en el navegador empleando internamente setTimeout y requestAnimationFrame.
Primeramente añada el archivo animate.min.js a su proyecto.
<script src="animate.min.js"></script>Animación sencilla de desplazamiento de un elemento
let elem = document.getElementById("myDiv");
let animation = new Animate({
duration: 5000,
draw: function (progress) {
elem.style.left = (150 * progress) + "px";
}
});
animation.play(); // iniciar animaciónEl ejemplo anterior pero extendido a todos los parámetros:
let elem = document.getElementById("myDiv");
let animation = new Animate({
duration: 5000,
fps: 30,
erase: "in",
timing: Animate.LINEAR,
statics: {},
draw: function (progress, anima) {
elem.style.left = (150 * progress) + "px";
}
});
animation.play(); // iniciar animaciónAcepta como único parámetro un objeto de opciones que contiene:
number
(requerido) Duración de la animación en milisegundos.
(requerido)
Es la función que toma el estado de finalización de la animación y la dibuja. El valor progress=0 denota el estado inicial de la animación y progress=1 el estado final.
Esta es la función que dibuja la animación, o hacer lo que sea con ella:
function draw (progress) {
elem.style.left = progress + "px";
}El segundo argumento es la animación donde se está usando la función de dibujado.
number | "auto"
(por defecto "auto")
Los cuadros por segundo, a mayor fps, más fluida es la animación, si su valor es "auto", los fps serán asignados según indique el navegador.
Animate.TIMING
(por defecto Animate.LINEAR)
Función de sincronización. Obtiene la fracción de tiempo que pasó (0 al inicio, 1 al final) y devuelve la finalización de la animación.
Hay varias que pueden ser usadas:
Animate.LINEAR
Animate.REVERSE
Animate.QUAD
Animate.QUBIC
Animate.CIRC
Animate.ARROW
Animate.BOUNCE
Animate.ELASTICA diferencia de la animación CSS, aquí podemos hacer cualquier función de sincronización y cualquier función de dibujo. La función de sincronización no está limitada por las curvas de Bézier. Y draw puede ir más allá de las propiedades, crear nuevos elementos para alguna animación de fuegos artificiales o algo así.
"in" | "out" | "in-out"
(por defecto "in")
Dirección de sincronización, la orientación normal es easeIn.
Si se desea invertir el sentido, se deberá usar easeOut.
Aquí hay un uso práctico, si se quiere que la animación finalice de manera suave, se deberá utilizar easeOut en la sincronización QUBIC:
let a = new Animate({
duration: 3200,
timing: Animate.QUBIC,
ease: "out",
draw: function(progress) {
elem.style.width = progress * 200 + "px";
elem.style.height = progress * 120 + "px";
}
});Animación de rebote:
let a = new Animate({
duration: 5000,
timing: Animate.BOUNCE,
ease: "out",
draw: function(progress) {
elem.style.top = progress * 250 + "px";
}
});(por defecto undefined)
Variable personalizable donde podremos almacenar cualquier informacion en nuestra animación
let a = new Animate({
duration: 15000,
timing: Animate.ELASTIC,
ease: "in-out",
statics: {
x: 5,
y: 60.7
},
draw: function(progress, animation) {
let statics = animation.statics;
console.log(statics.x) // 5
console.log(statics.y) // 60.7
}
});El mismo valor de duración introducido como parámetro. Puede ser modificado dinámicamente para alterar las velocidades durante la animación:
new Animate({
duration: 10000,
timing: Animate.CIRC,
ease: "out",
draw: function(progress, animation) {
elem.style.width = progress * 100 + "px";
animation.duration --; //reducir duración a medida que avanza
}
});La función de dibujado introducida como parámetro.
La función de sincronización que está siendo usada en la animación, ya transformada por los métodos ease.
string
Indica el estado actual de la animación: pausada, detenida o ejecutandose.
"paused"
"stoped"
"playing"El valor de la cantidad de cuadros por segundos a ejecutar.
Retorna una nueva instancia Animate con las mismas características que el original.
Destruye por completo la animación, despues de ser usado este método la animación quedará como un objeto vacío.
Comenzar la animación, si estaba pausada, continuará por donde se dejó:
Pausar animación, se guardará el avance actual, si se llama al método play() continuará la reproducción.
Detener completamente la animación, si se llama el método play(), comenzará desde el inicio.
Avanzar o retroceder la animación hasta el cuadro indicado.
frame debe ser un valor entre 0 y 1, el 0 indica el inicio, y el 1 el final. Así por ejemplo, el frame=0.5 representaría la mitad de la animación
let animation = new Animate({
duration: 6000,
timing: Animate.REVERSE,
ease: "in",
draw: function(progress) {
let angle = progress * 90;
elem.style.transform = "rotation(" + angle + "deg)";
}
})
animation.toFrame(0.5);
animation.play();Declarar eventos para la animación. Los eventos disponibles son:
"onplay"
"onstop"
"onend"
"onpause"El evento onend será llamado cuando la animación llegue al frame 1 (cuando la animación finalice), los demás eventos solo ocurrirán si se llaman estrictamente a sus métodos (play(), stop() ó pause())
let animation = new Animate({
duration: 6000,
timing: Animate.REVERSE,
ease: "in",
draw: function(progress) {
let angle = progress * 90;
elem.style.transform = "rotation(" + angle + "deg)";
}
});
animation.on("play", ()=>{
console.log("the animation has started");
});
animation.on("end", ()=>{
console.log("the animation has finished");
});
animation.play();