-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
- Loading branch information
Showing
1 changed file
with
73 additions
and
0 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,73 @@ | ||
| # EquilibratedFlux.jl | ||
|
|
||
| [](https://aerappa.github.io/EquilibratedFlux.jl/stable/) | ||
| [](https://aerappa.github.io/EquilibratedFlux.jl/dev/) | ||
| [](https://github.com/aerappa/EquilibratedFlux.jl/actions/workflows/CI.yml?query=branch%3Amain) | ||
| <!-- [](https://codecov.io/gh/triscale-innov/DataViewer.jl) --> | ||
|
|
||
| This package is based on | ||
| [Gridap.jl](https://github.com/gridap/Gridap.jl/tree/master) to provide | ||
| post-processing tools to calculate reconstructed fluxes associated to the given | ||
| approximate solution of a PDE. | ||
|
|
||
| For simplicity, we consider here the Poisson equation | ||
|
|
||
| ```math | ||
| \begin{align} | ||
| - \Delta u &= f &&\text{in }\Omega\\ | ||
| u &= g &&\text{on }\partial\Omega. | ||
| \end{align} | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| We suppose we have already computed a conforming approximation $u_h \in | ||
| V_h\subset H^1_0(\Omega)$ to the solution $u$ in Gridap.jl by solving | ||
|
|
||
| ```math | ||
| (\nabla u_h, \nabla v_h) = (f, v_h)\quad\forall v_h\in V_h, | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| The `EquilibratedFlux.jl` library then provides the tools to compute a reconstructed flux | ||
| associated to $u_h$. This flux, obtained by postprocessing, is an approximation to the numerical flux, i.e. | ||
|
|
||
| ```math | ||
| \sigma_h \approx -\nabla u_h. | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| This flux has the important property of being "conservative over faces" in the | ||
| sense that | ||
|
|
||
| ```math | ||
| \sigma_h \in \mathbf{H}(\mathrm{div},\Omega). | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| We provide two functions to obtain such an object: | ||
| [`build_equilibrated_flux`](@ref) and [`build_averaged_flux`](@ref) both provide | ||
| reconstructed fluxes, which we denote by $\sigma_{\mathrm{eq},h}$ and | ||
| $\sigma_{\mathrm{ave},h}$ respectively. | ||
|
|
||
| In addition to the properties listed above, the equilibrated flux | ||
| $\sigma_{\mathrm{eq},h}$ satisfies the so-called equilibrium condition, i.e., | ||
| for piecewise polynomial $f$, we have | ||
|
|
||
| ```math | ||
| \nabla\cdot\sigma_{\mathrm{eq},h} = f. | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| More details can be found in the [documentation](https://aerappa.github.io/EquilibratedFlux.jl/dev/). | ||
|
|
||
| ## Examples / Tutorials | ||
|
|
||
| ### Error estimation | ||
|
|
||
| The reconstructed flux is the main ingredient in computing [*a posteriori* error | ||
| estimators](https://aerappa.github.io/EquilibratedFlux.jl/dev/examples/readme/readme/). | ||
|
|
||
| [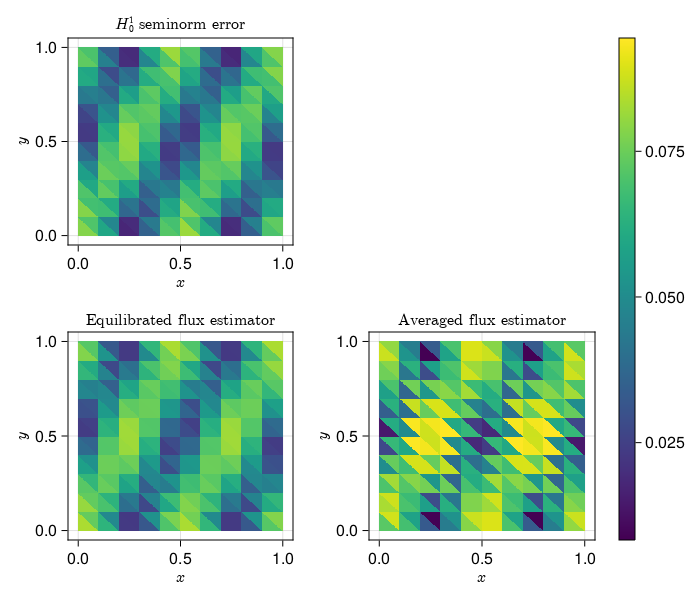](https://aerappa.github.io/EquilibratedFlux.jl/dev/examples/readme/readme/) | ||
|
|
||
| ### Mesh refinement | ||
|
|
||
| Estimators obtained using the equilibrated flux can be used to drive an Adaptive | ||
| Mesh Refinement (AMR) precedure, demonstrated here for the Laplace problem in an | ||
| [L-shaped domain](https://aerappa.github.io/EquilibratedFlux.jl/dev/examples/Lshaped/Lshaped/) | ||
|
|
||
| [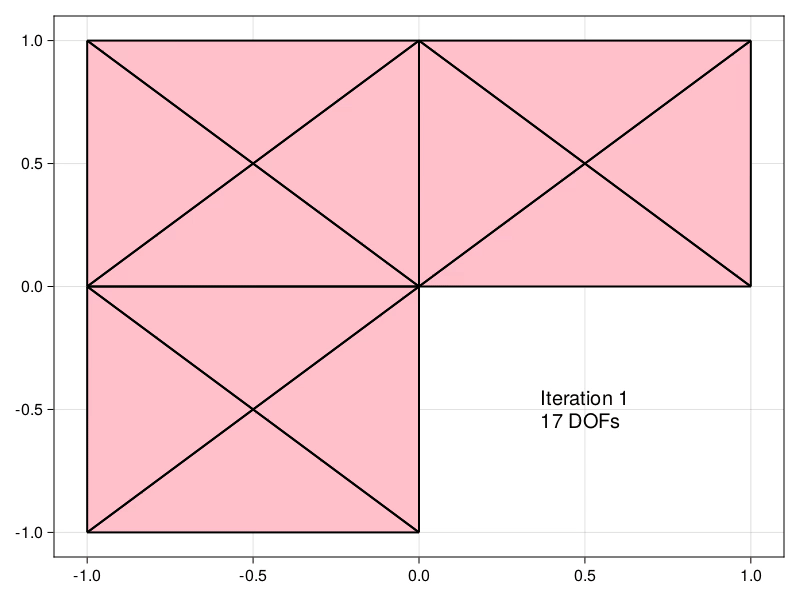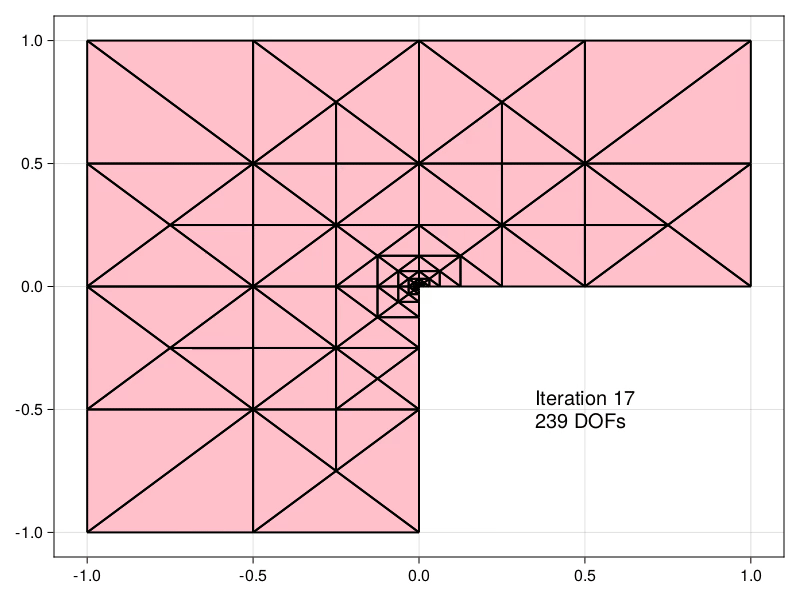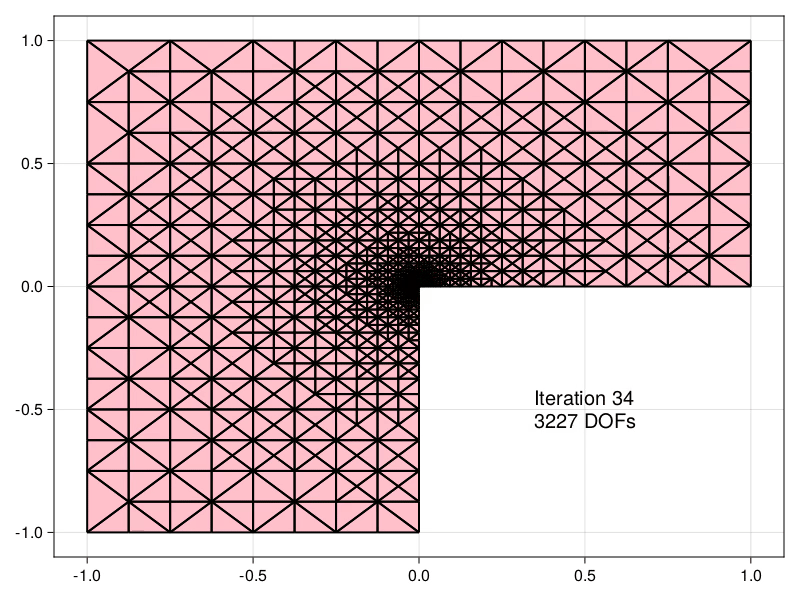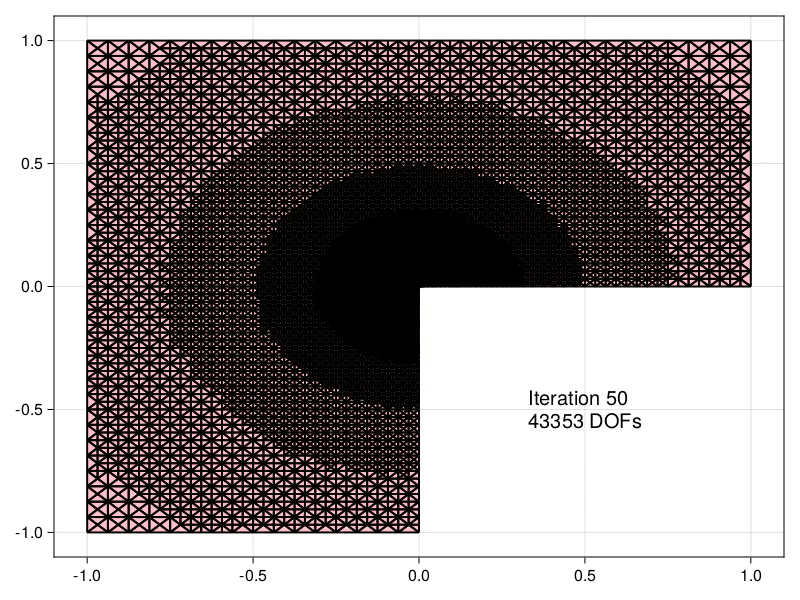](https://aerappa.github.io/EquilibratedFlux.jl/dev/examples/Lshaped/Lshaped/) |