-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 125
Spark Streaming
Awantik Das edited this page Mar 31, 2017
·
3 revisions
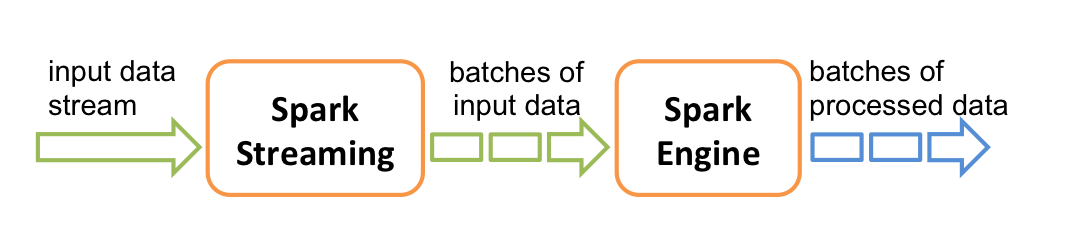
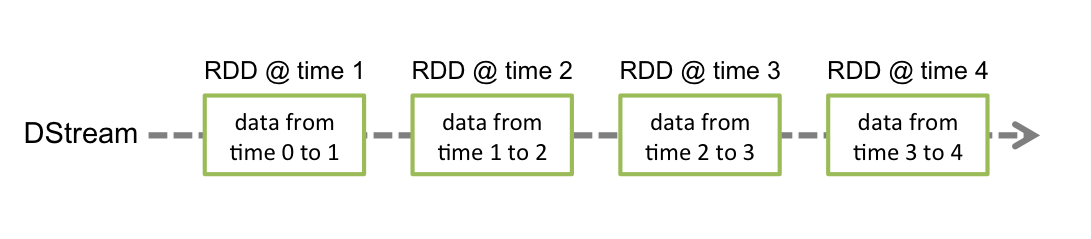
Discretized Stream or DStream is the basic abstraction provided by Spark Streaming. It represents a continuous stream of data, either the input data stream received from source, or the processed data stream generated by transforming the input stream. Internally, a DStream is represented by a continuous series of RDDs, which is Spark’s abstraction of an immutable, distributed dataset
- map(func) Return a new DStream by passing each element of the source DStream through a function func.
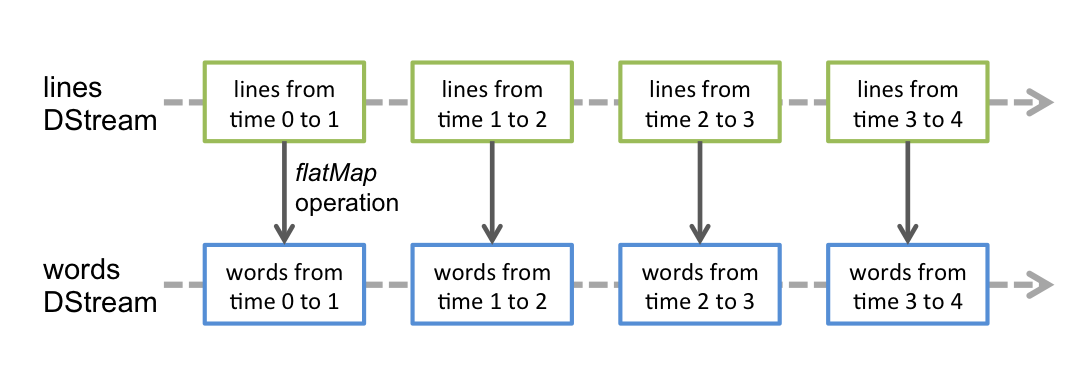
- flatMap(func) Similar to map, but each input item can be mapped to 0 or more output items.
- filter(func) Return a new DStream by selecting only the records of the source DStream on which func returns true.
- repartition(numPartitions) Changes the level of parallelism in this DStream by creating more or fewer partitions.
- union(otherStream) Return a new DStream that contains the union of the elements in the source DStream and otherDStream.
- count() Return a new DStream of single-element RDDs by counting the number of elements in each RDD of the source DStream.
- reduce(func) Return a new DStream of single-element RDDs by aggregating the elements in each RDD of the source DStream using a function func (which takes two arguments and returns one). The function should be associative and commutative so that it can be computed in parallel.
- countByValue() When called on a DStream of elements of type K, return a new DStream of (K, Long) pairs where the value of each key is its frequency in each RDD of the source DStream.
- reduceByKey(func, [numTasks]) When called on a DStream of (K, V) pairs, return a new DStream of (K, V) pairs where the values for each key are aggregated using the given reduce function. Note: By default, this uses Spark's default number of parallel tasks (2 for local mode, and in cluster mode the number is determined by the config property spark.default.parallelism) to do the grouping. You can pass an optional numTasks argument to set a different number of tasks.
- join(otherStream, [numTasks]) When called on two DStreams of (K, V) and (K, W) pairs, return a new DStream of (K, (V, W)) pairs with all pairs of elements for each key.
- cogroup(otherStream, [numTasks]) When called on a DStream of (K, V) and (K, W) pairs, return a new DStream of (K, Seq[V], Seq[W]) tuples.
- transform(func) Return a new DStream by applying a RDD-to-RDD function to every RDD of the source DStream. This can be used to do arbitrary RDD operations on the DStream. updateStateByKey(func) Return a new "state" DStream where the state for each key is updated by applying the given function on the previous state of the key and the new values for the key. This can be used to maintain arbitrary state data for each key.
- print()
- saveAsTextFiles(prefix, [suffix])
- saveAsObjectFiles(prefix, [suffix])
- saveAsHadoopFiles(prefix, [suffix])
- foreachRDD(func)
- Understanding Spark
- Spark Jobs & API
- Architecture
- RDD Internals
- Creating RDD
- Understanding Deployment & Program Behaviour
- RDD Transformation & Action
- Assignments 1
- Best Practices -1
- Introduction to DataFrame
- PySpark SQL
- Pandas to DataFrames
- Machine Learning with PySpark
- Transformers
- Estimators
- Spark Streaming
- Structured Streaming
- GraphX & GraphFrames
- Data Processing Architectures
- Problems