-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 2
Daysim
DaySim is an activity-based (AB) travel demand model. DaySim simulates 24-hour itineraries for individuals with parcel-level spatial resolution and minute-level temporal resolution. DaySim can generate outputs at the level of resolution required as input to dynamic traffic simulation. DaySim’s forecasts in all dimensions (activity and travel generation, tours and trip-chaining, destinations, modes, and timing) are sensitive to travel times and costs that vary by mode, origin–destination path, and time of day. As a result, DaySim uses the improved network travel costs and times output from a dynamic traffic simulator as inputs. DaySim captures the effects of travel time and cost upon activity and travel choices. These effects are balanced across modes and times of day and are consistent with the econometric theory of nested choice models. DaySim can be used in a distributed manner by running different partitions of the study area population on separate processors and then merging the results.
DaySim comprises several subcomponents and is structured as a series of hierarchical or nested choice models. DaySim's hierarchy places the long-term models at the top of the choice hierarchy and places the short-term models at successively lower levels in the hierarchy. The detailed hierarchy and flow through the model is illustrated in the figure below.
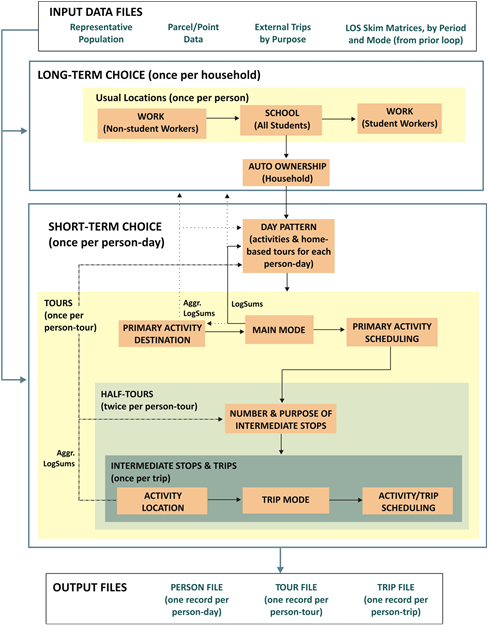
The flow generally proceeds in a linear fashion from the long-term models to the short-term models. The choices made in the long-term models influence or constrain the choices made in the lower-level models. For example, household auto ownership affects both day pattern and tour (and trip) mode choice by including auto ownership variables in those component models. In addition to these direct influences, utilities from lower-level models flow upward to higher-level models. “Logsums” (expected utilities) from tour destination and tour mode choice models affect other short-term models and also affect the upper-level, longer-term models. Some of the logsums from lower-level models are aggregated for use in the long-term models in order to reduce the computational time required to use fully detailed disaggregate logsums in a complex nesting structure.
More information is available in the following locations:
-
Details of DaySim's inputs are provided here
-
Details of DaySim's outputs are provided here
-
Configuration settings available for a DaySim run are here
-
Daysim model variable descriptions here
-
Daysim user guide here
-
Additional information about DaySim is available here
Daysim is an activity simulator developed by RSG, Inc. BKRCast and Soundcast use Daysim to generate resident travel throughout the region.
Daysim can be customized. For the details of Daysim customization, please read document here.
In application, the work location and school location choice models do not constrain the choice set to alternatives that have not yet been chosen. In other words, more workers can select a parcel than there are jobs in that parcel. To resolve this inconsistency between workers and jobs, Daysim has a shadow pricing procedure that works on each iteration of a model run in each zone. If a zone is over-selected a negative term will be added to the utility, so that in the next iteration it is less attractive. We have found that workers and jobs are usually fairly well balanced after two to three iterations of running this procedure.
https://www.psrc.org/sites/default/files/2022-03/2015psrc-locationchoicemodels.pdf
https://www.psrc.org/sites/default/files/2022-03/2015psrc-daypatternmodels.pdf
https://www.psrc.org/sites/default/files/2022-03/2015psrc-modechoiceautomodels.pdf
https://www.psrc.org/sites/default/files/2022-03/2015psrc-timeofdaymodels.pdf
-
Model System
-
Model Setup
-
Model Network
-
Land Use
-
Model Components
-
Model Directory
-
Calibration