-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 54
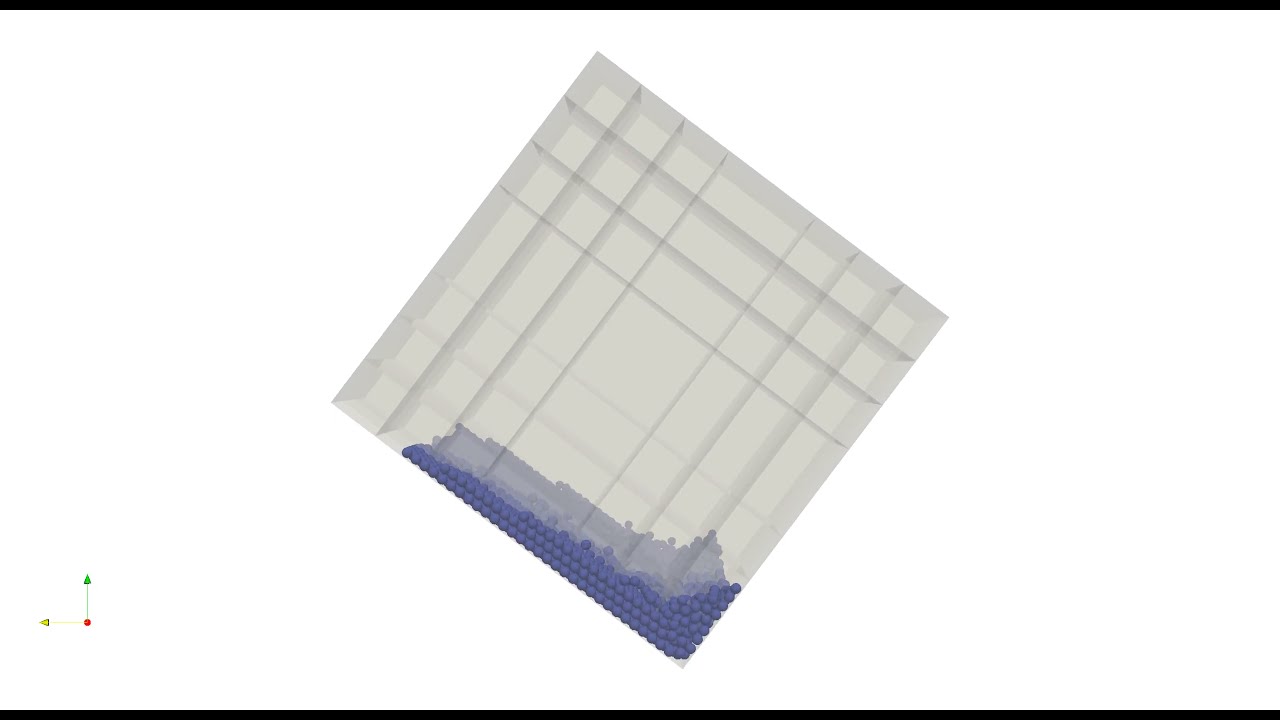
Example 15 : Rotation in Box
This example performs a three-dimensional discrete element method simulation of rotation of a box. We insert 4000 particles (diameter = 1 mm), and rotate the box for 5 s. The box rotates around the x axis and the rotation speed is 1 rad/s.
# --------------------------------------------------
# Simulation and IO Control
#---------------------------------------------------
subsection simulation control
set time step = 1e-5
set time end = 5
set log frequency = 1000
set output frequency = 1000
end
In the model parameters section, particle-particle and particle-wall broad and fine search frequencies are defined. We also define the particle contact search size (neighborhood threshold), contact forces and integration methods. The contact detection method is dynamic, and it needs dynamic contact search size coefficient (a safety factor for dynamic contact search). The rolling resistance torque model is constant_resistance, and velocity_verlet is chosen as the integration method.
# --------------------------------------------------
# Model parameters
#---------------------------------------------------
subsection model parameters
set contact detection method = dynamic
set dynamic contact search size coefficient = 0.9
set neighborhood threshold = 1.3
set particle particle contact force method = pp_nonlinear
set particle wall contact force method = pw_nonlinear
set rolling resistance torque method = constant_resistance
set integration method = velocity_verlet
end
In the physical properties section, the physical properties of particles and walls, including diameter and density of particles, Young's modulus, Poisson's ratios, restitution coefficients, friction and rolling frictions of particle and wall are specified. The gravitational acceleration is also set in this section. Diameter of particles in this example is 1 mm. Total number of particles in this example is 4000.
#---------------------------------------------------
# Physical Properties
#---------------------------------------------------
subsection physical properties
set gx = 0.0
set gy = 0.0
set gz = -9.81
set number of particle types = 1
subsection particle type 0
set size distribution type = uniform
set diameter = 0.001
set number = 4000
set density particles = 1000
set young modulus particles = 1000000
set poisson ratio particles = 0.3
set restitution coefficient particles = 0.3
set friction coefficient particles = 0.1
set rolling friction particles = 0.05
end
set young modulus wall = 1000000
set poisson ratio wall = 0.3
set restitution coefficient wall = 0.3
set friction coefficient wall = 0.1
set rolling friction wall = 0.05
end
Next, we define the insertion properties, which are insertion method, inserted number of particles at each insertion step, insertion frequency, insertion domain and other information regarding the initial positions of particles inside the insertion domain.
#---------------------------------------------------
# Insertion Info
#---------------------------------------------------
subsection insertion info
set insertion method = non_uniform
set inserted number of particles at each time step = 4000
set insertion frequency = 2000000
set insertion box minimum x = -0.019
set insertion box minimum y = -0.019
set insertion box minimum z = -0.01
set insertion box maximum x = 0.019
set insertion box maximum y = 0.019
set insertion box maximum z = 0.019
set insertion distance threshold = 1.5
set insertion random number range = 0.2
set insertion random number seed = 19
end
We use a dealii hyper_cube for creating a box. The edge length of the cube is 0.02 m.
#---------------------------------------------------
# Mesh
#---------------------------------------------------
subsection mesh
set type = dealii
set grid type = hyper_cube
set grid arguments = -0.02 : 0.02 : false
set initial refinement = 3
end
We define a rotational motion of the grid around the x axis. Note that values 0, 1 and 2 for the grid rotational axis mean rotational motion around x, y and z axis, respectively. The rotational speed is 1 rad/s.
#---------------------------------------------------
# Grid Motion
#---------------------------------------------------
subsection grid motion
set motion type = rotational
set grid rotational speed = 1
set grid rotational axis = 0
end
dem_3d solver simulates this example.