A fully managed message queue service offered by AWS. It provides a reliable, scalable, and cost-effective way to decouple and coordinate distributed software systems and microservices.
- GO: sqs, to wrap and simplify aws-sdk-go/service/sqs. Example is at go-amazon-sqs-sample
- The libraries to implement this flow are:
- mq for GOLANG. Example is at go-amazon-sqs-sample
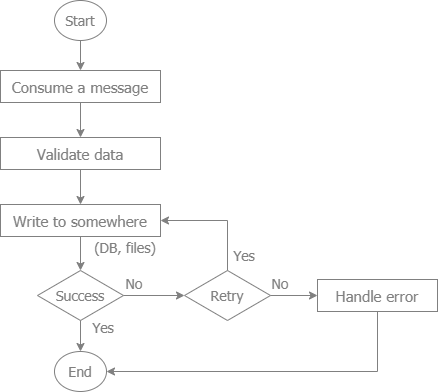
- Scenario: Separating different parts of an application to ensure that a failure in one part does not affect others.
- Benefit: Enhances fault tolerance and scalability by allowing asynchronous communication between services.
- Scenario: Handling tasks that do not need immediate processing, such as batch processing or background tasks.
- Benefit: Improves system efficiency and response times for end-users.
- Scenario: Managing and distributing jobs to worker processes.
- Benefit: Balances load and ensures all tasks are completed without overloading any single worker.
- Scenario: Processing customer orders, where each order can be handled as a separate task.
- Benefit: Ensures reliable and scalable processing of orders, even during high demand.
- Scenario: Smoothing out bursty traffic in applications to prevent overload.
- Benefit: Protects the system from spikes in traffic by buffering messages.
- Scenario: Orchestrating steps in a complex workflow, such as image processing pipelines.
- Benefit: Coordinates different stages of processing in a reliable and scalable manner.
- Type: Managed message queuing service.
- Use Case: Decoupling and scaling microservices, asynchronous tasks.
- Scalability: Automatically scales.
- Delivery Guarantees: At-least-once, FIFO (exactly-once).
- Integration: Deep integration with AWS services.
- Delivery Models: Primarily pull, with long polling.
- Type: Managed real-time messaging service.
- Use Case: Event-driven architectures, real-time analytics.
- Scalability: Automatically scales.
- Delivery Guarantees: At-least-once delivery.
- Integration: Tight with Google Cloud services.
- Delivery Models: Push and pull.
- Type: Open-source event streaming platform.
- Use Case: High-throughput messaging, event sourcing, log aggregation.
- Scalability: High with partitioned topics.
- Delivery Guarantees: Configurable (at-least-once, exactly-once).
- Integration: Broad ecosystem with various connectors.
- Delivery Models: Pull-based consumer groups.
- Management: Pub/Sub and SQS are managed services, while Kafka is typically self-managed or via managed services like Confluent.
- Use Case Focus: Pub/Sub and Kafka are ideal for real-time processing, whereas SQS is great for decoupling microservices and handling asynchronous tasks.
- Delivery Models: Pub/Sub supports push and pull, SQS supports pull with long polling, and Kafka primarily uses pull with consumer groups.
- Scalability: All three are highly scalable, but Kafka offers the most control over performance tuning.
- Integration: Pub/Sub integrates well with Google Cloud, SQS with AWS, and Kafka has a broad integration ecosystem.
Please make sure to initialize a Go module before installing core-go/sqs:
go get -u github.com/core-go/sqsImport:
import "github.com/core-go/sqs"