The CIB (Corporate Invention Board) dataset is a database characterising the patent portfolios of the largest industrial firms worldwide. The CIB combines information extracted from the Industrial R&D Investment Scoreboard (EU Commission), the ORBIS financial database and the RISIS Patent database ( enriched version of the Patstat EPO database).
The aim of CIB is to facilitate a dataset for the analysis on the transformation of global patent portfolios in the last two decades for industrial groups with the highest R&D investments and for their conrrespondent consolidate subsidiaries as well.
- About the RPD and ORBIS databases - A brief description about the two data sources used for generating CIB
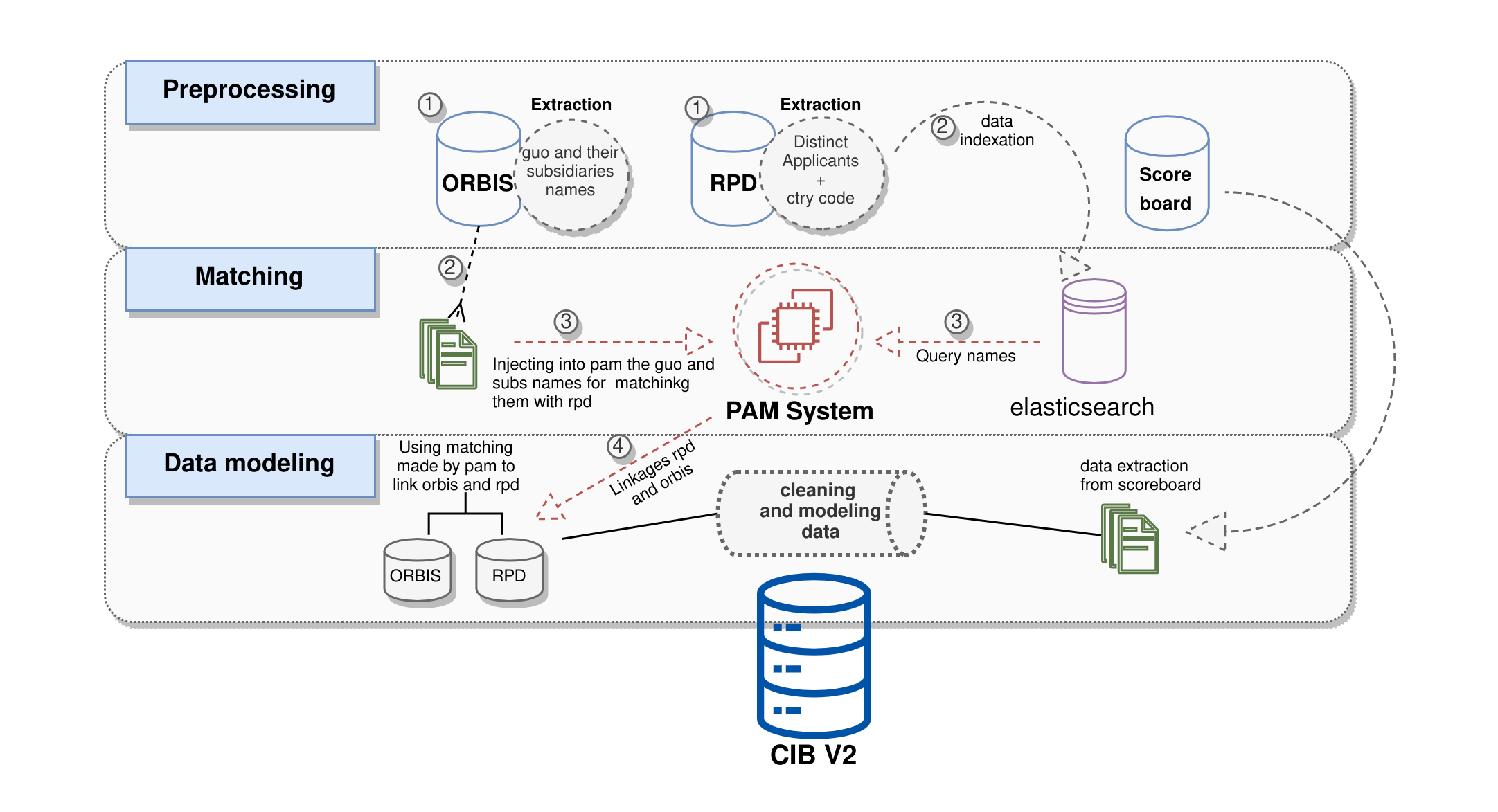
- Overview diagram - Simple diagram describing the steps taken for building CIB
- Data acquisition - Criterias and methods for extracting orbis guo and subsidiaries
- Matching entities using PAM System - Description of the followed process in order to link entities
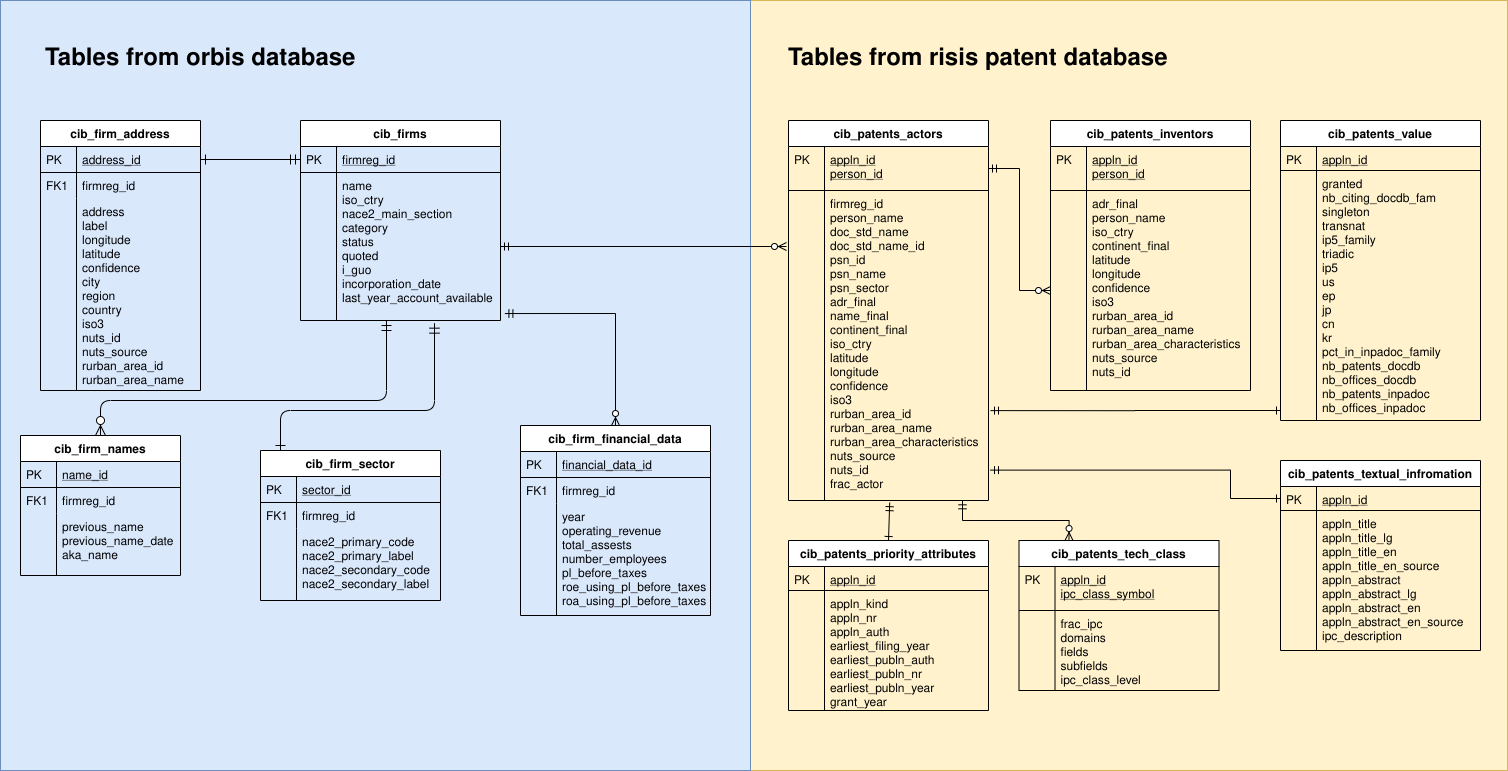
- Database Modeling - The relational database design used for CIB database
- Funding - Banner with the funding organizations
ORBIS has information on over 280 million companies across the globe. It’s the biggest resource for company data making simple to compare companies internationally. Orbis is mostly used to find, analyse and compare companies for better decision making and increased efficiency.
RPD is a patent database that has been set up using the European Patent Office (EPO) Worldwide Patent Statistical Database, henceforth PATSTAT developed by the EuropeanPatent Office. The conceptual model of the database offers the ability to manipulate relations between more than 30 tables. Each table contains a set of variables that enable studying several analytical dimensions: contents (title, abstract...), knowledge dynamics (bibliographical links for science and technology, fine grained description of the technological fields...), organizations (intellectual property through applicant names), geography (localization of the inventions and collaborations).
But RPD is as well an augmented version of the generic PATSTAT database in the sense that it includes a series of enrichment thanks to the filling of information missing in the initial PATSTAT database (e.g: addresses), the harmonisation of raw information from the initial PATSTAT database (e.g: country information) and the addition of new information (e.g: technological classification).
There are two repositories that includes the process for building RPD:
The CIBv2 database uses several sources of information to identify the worldwide top corporate R&D performers and define their consolidated perimeters (3992 parent companies and their subsidiaries owned by the parent company with shares higher than 50.01%). The sources of company names are: the European R&D Industrial Scoreboard (editions from 2008 to 2014), the lists of the PCT top applicants published by the World Intellectual Property Organisation1 (editions from 2008 to 2014) and the ORBIS database (Bureau van Dijk). The CIB2 patent source is the Risis Patent Database (RPD), an enriched and simplified Patstat DB (Patstat April 2017). CIB2 benefits from all the enrichments and adjustments made in RPD (see the RPD documentation for details).
For defining the list of the worldwide top corporate R&D performers we have follow the next steps
• The lists of the companies of the European Industrial R&D Investment Scoreboard for seven editions from 2008 to 2014. Each Scoreboard edition ranks a number of companies (European firms and non European firms) which have invested the largest sums in R&D during the previous year. We have ended with approximatively with 17 000 company names with redundancy over the editions and with the World and European lists.
• The lists of the top PCT patent applicants provided yearly by WIPO (i.e. applicants applying for a minimum of 10 PCT patents in a given year). About 13 500 company names were retrieved when adding names given from 2008 to 2014. We ended with approximatively 30 000 company names with a lot of duplicates (several companies were present in both sources for several years with the same name or different names).
We have first cleaned and harmonised the company names. Then, using the Orbis database we have identified for all the names, the parent company, most often the Global Ultimate Owner (GUO) when the GUO was an industrial company or the higher intermediate industrial company owned by the GUO when the GUO was not an industrial company but a country, a family or a holding company. In that latter case, the parent company was tagged as a IGUO (industrial GUO). The final list contains 3992 parent companies.
The consolidated perimeters of the 3992 parent companies (GUO or IGUO) were obtained using the Orbis database. It includes all subsidiaries with a majority share capital owned by the parent companies (share >50.01%). The consolidated perimeter of the parent companies was determined based on information available in Orbis in autumn 2017 (the perimeter for a few firms were built a bit later). The names of the parent companies as well as their subsidiaries were downloaded from Orbis. Moreover a set of available variables was also retrieved (company name, location, sectors, employees, financial data…). We have ended with approximately 320 000 different company names (GUOs, IGUOs and subsidiaries).
In order to retrieve from the Risis Patent Database, the priority patents applied by the 3992 parent companies, the 320 000 list of Orbis company names had to be matched with the names of legal applicants (doc_std_name) in more than 13 millions of priority patents from the Risis Patent Database.
We used the Pam system (Patent approximation matches system) that is a textual analysis tool that has been designed at LISIS (UGE) for matching legal type entities with patent applications, for pairing entities. The Pam system relies on the company name and combines full text search techniques using Elasticsearch with some of the most famous approximate string matching algorithms such as Jaro-Winkler, Levensthein and Ratcliff1. Moreover, it uses each of these scores for calculating its own pam score in order to select the best candidates and dismiss the wrong ones.
The complete manual of how configure and use PAM System can be found by following this link:
 |
The RISIS project aims at creating a distributed research infrastructure to support and advance science and innovation studies. The project is funded by the European Union under Horizon2020 Research and Innovation Programme Grant Agreement n°82409. |
|---|