-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 10.4k
Azure Dev Spaces
Please go to the official Dev Spaces documentation for details.
You should be familiar with the topics that follow.
CONTENT
- Enabling Dev Spaces
- Prepare environment for Dev Spaces
- Deploy to a dev space
- Deploy to a child dev space
You need an AKS created in an admitted Dev Spaces region. Then just type:
az aks use-dev-spaces -g your-aks-devspaces-resgrp -n YourAksDevSpacesClusterNote: This command will install the Azure Dev Spaces CLI if not installed in your computer.
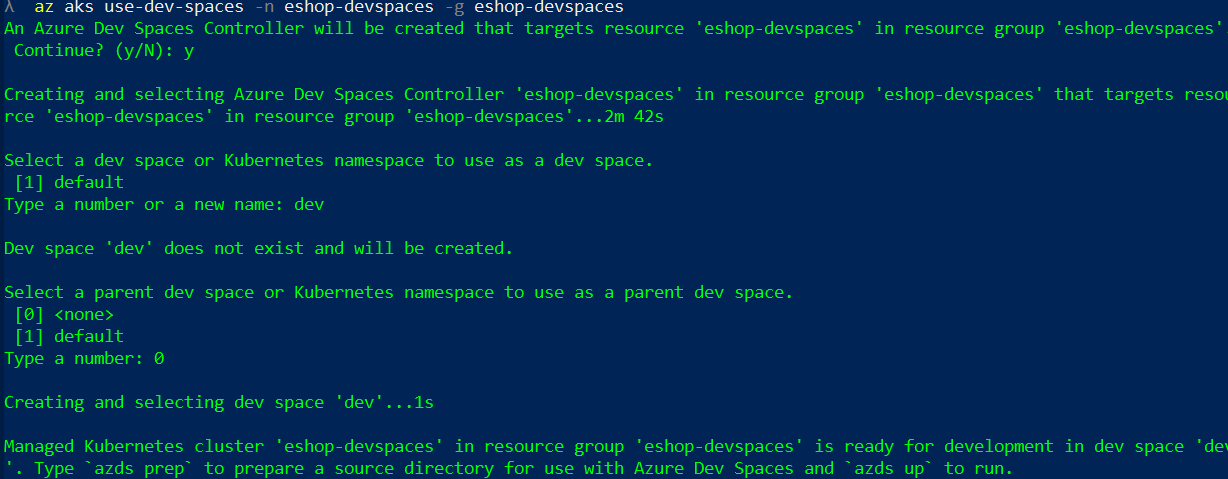
The tool will ask us to create a dev space. Enter the name of the dev space (i. e. dev) and make it a root dev space by selecting none when prompted for their parent dev space:
Once Dev Spaces tooling is added, type azds --version to get the version of Dev Spaces tooling.
Tested DevSpaces tooling version was:
Azure Dev Spaces CLI (Preview)
0.1.20190320.5
API v2.17Future versions should work, unless they introduce breaking changes.
From a Power Shell console, go to /src folder and run prepare-devspaces.ps1 (no parameters needed). This script will copy the inf.yaml and app.yaml files from /k8s/helm to all project folders. This is needed due to a limitation of Dev Spaces tooling used. Note that the files copied are added in .gitignore.
Remember that the inf.yaml and app.yaml contains the parameters needed for the helm charts to run.
Dev Spaces deployment is done using the same helm charts used to deploy on a "production" cluster.
If you want to deploy a project to a specific dev space, just go to its source folder (where the .csproj is) and type azds up. This will deploy the project to the current dev space. You can use the -v modifier to have more verbosity and the -d modifier to detach the terminal from the application. If -d is not used, the azds up command is attached to the service running and you are able to see its logs.
The command azds up will:
- Sync files with the dev space builder container
- Deploy the helm chart
- Build the service container
- Attach current console to the container output (if not
-dis passed)
Note You should deploy all enabled Dev Spaces projects (one by one) in the parent dev space
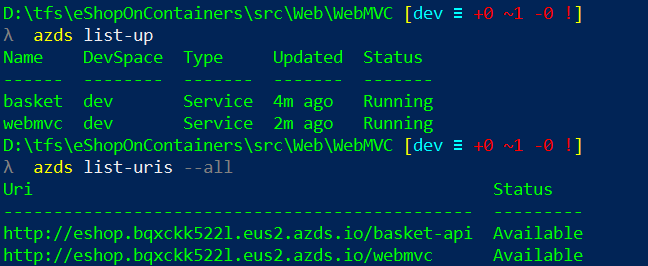
The command azds list-up will show which APIs are deployed in the dev space. The command azds list-uris will show the ingress URLs:
Once everything is deployed to the root dev space, use azds space select to create a child dev space.
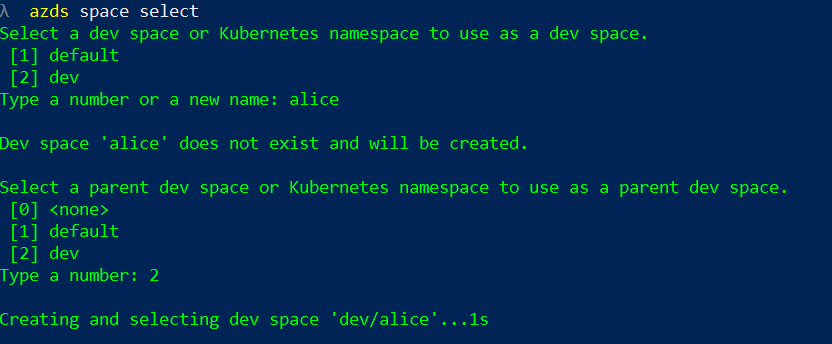
Then deploy the desired service to this child dev space (using azds up again). Use azds list-up to verify that the service is deployed in the child dev space. The image shows the WebMVC deployed in the child dev space alice:
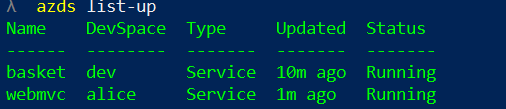
The azds list-uris will show you the new ingress URL for the child dev space:
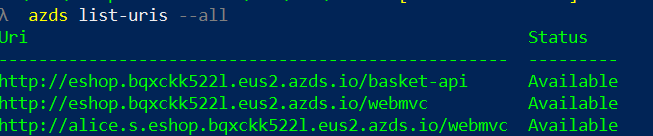
If you use the child URL (starting with alice.s.), the Web MVC that will run will be the one that is deployed in the child dev space. This web will use all services deployed in the child dev space and if not found, will use the ones deployed in the parent dev space.
If using the parent dev space URL, Web MVC that will run will be the one deployed in parent dev space, using only the services deployed in parent dev space.
Usually you deploy everything in the parent dev space, and then create one child dev space per developer. The developer deploys only the service he is updating in his/her namespace.
Please refer to Dev Spaces documentation for more info.
Note: Web SPA is not enabled to use Dev Spaces (so, you can't deploy the SPA in a dev space). Use the Web MVC for testing.
- System requirements
- Development setup
- Databases & containers
- Architecture
- Application
- Code
- Logging and Monitoring
- Tests