McFlight stands for Mechanics of Flight and so far is only a translation of the F-16 model found at Stevens and Lewis book, where the code is in Fortran. I reproduced it using two approaches: (1) in Scilab scripts and (2) by model-based design using xcos. Each folder tree structure is explained below.
(Learn more at http://e-feather.blogspot.com/)
- atmosphere: implementation of International Standard Atmosphere (ISA) model;
- eqm: not only the equations of motion but also the engine and aerodynamic data for the F16;
- sim: scripts of simulation and linearization examples;
- tests: scripts for testing some scripts of the other folders. In case of the atmospheric model, for example, this is only a check of expected values from the literature; for the aerodynamic/engine models, the interpolation is checked as well;
- trim: scripts for finding trim conditions, i.e., steady flight conditions.
Notice that the scripts shall be executed from the root folder mcflight/scripts.
This is a very first version of the toolset for control design and there are many points of potential improvement. Although for a quick check to see if all things are running I'd recommend:
- Run the tests. Setting the current directory to root folder of mcflight/scripts, execute:
--> exec('tests\aerodata_interpolation_f16.tst');
--> exec('tests\atmosphere.tst');
--> exec('tests\engine_f16.tst');
--> exec('tests\eqm_f16.tst');
--> exec('tests\trim_f16.tst');
- Run a script example which plots a comparison between linear and non-linear simulations of F-16 model:
--> exec('sim/plots_lin_nlin_f16.sce');
This is the F16 model implemented using the model-based design approach.
In order to run the simulation with the full model of coordinated turn:
- Set the workspace directory to the xcos root folder (mcflight/xcos)
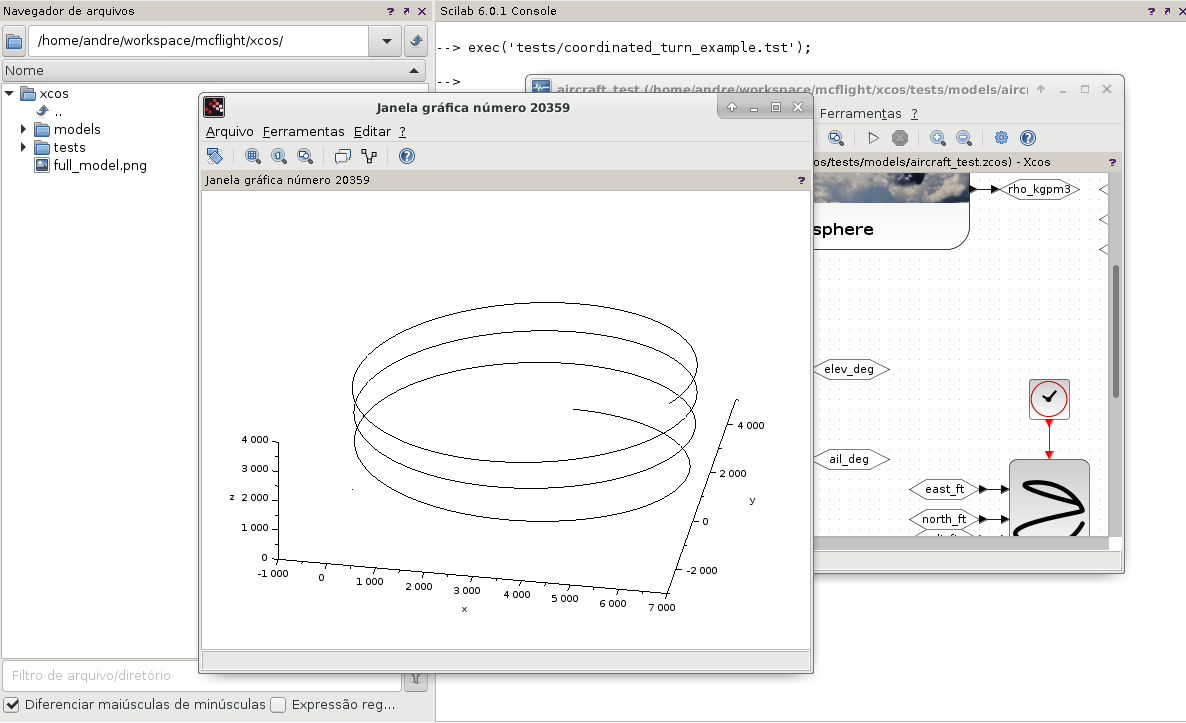
- Run the script 'tests/coordinated_turn_example.tst' (this may open the xcos window with the main model).
--> exec('tests/coordinated_turn_example.tst');
- Hit the simulation play (this may take some seconds) and check the 3d plot with the aircraft trajectory.
It is also possible to simulate a straight level flight ('tests/aircraft_model.tst').
You can run tests for each superblock seperatedly:
- Setting the current directory to root folder mcflight/xcos, execute:
--> exec('tests\aerodynamics_model.tst');
--> exec('tests\atmosphere_model.tst');
--> exec('tests\engine_model.tst');
- Use model references model in Xcos (there are many redundant superblock implementations).
- Try different aircraft models on the same structure.