This is the Dark mAtteR iNvestigator (DARN) software package.
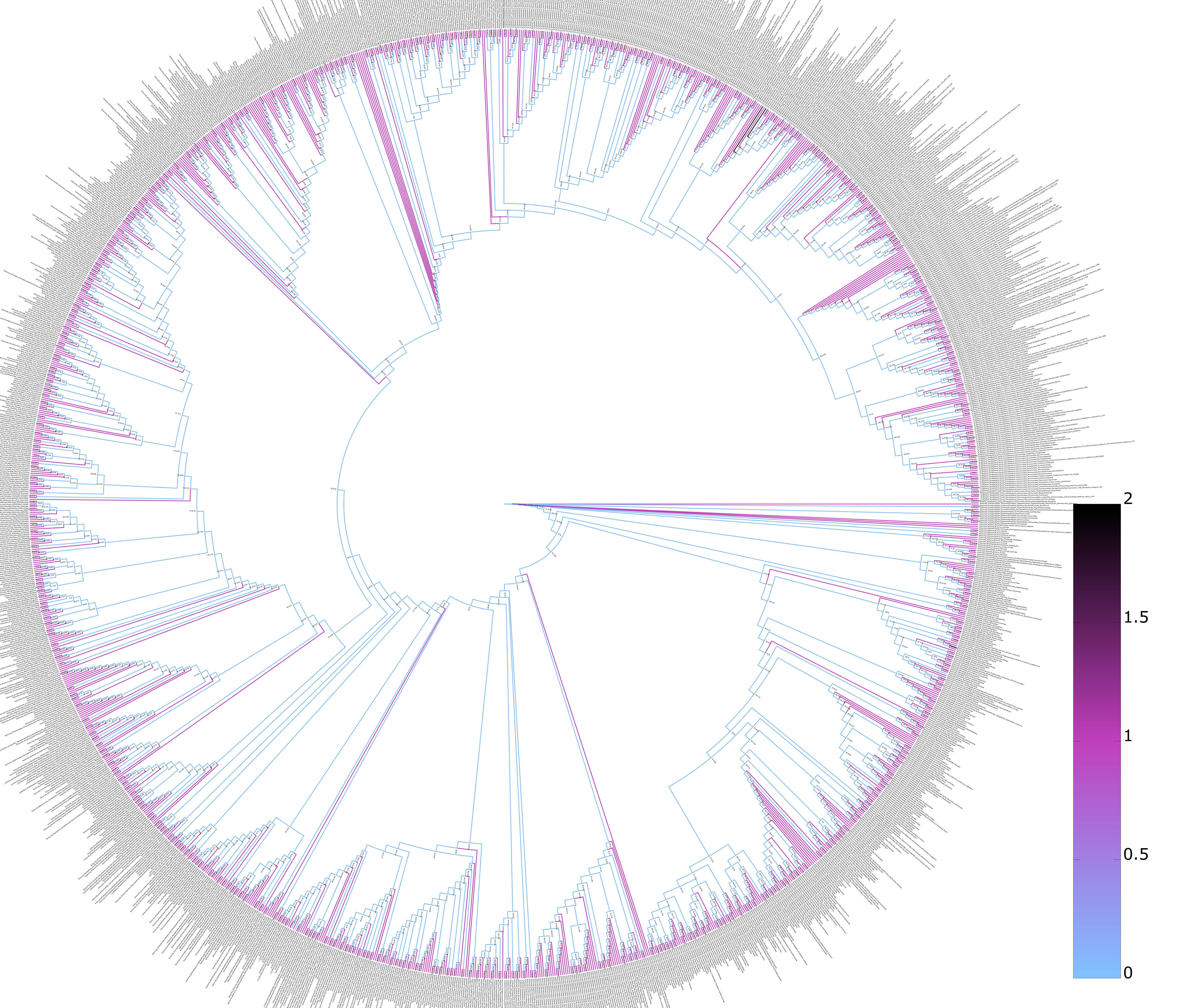
DARN uses a COI reference tree covering all domains of life (eukaryotes, bacteria, archaea) to assign your sequences to the 3 domains of life.
Its purpose is not to provide you with certain taxonomic assignment but to give an overview of the species present.
darn is a available as a container, meaning you need a containerized technology to use it.
And that its only dependency! 🥳
If you are about to use darn locally, on your personal computer, then probably you will find Docker as the easiest way to go for it.
However, if you are working on a server or in a High Performance Computing (HPC) environment, then Singulariy is the best if not (in cases where your admin does not allow Docker) the oncly choice.
To install Docker you may follow there instructions here depending on the operation system you are working at.
Once Docker is set, you may get darn as a Docker image by running:
docker pull hariszaf/darn
To install Singularity you may follow the instructions described here or you can probably ask your sys-admin to do that for you, in case you are working in a server, HPC, cloud etc.
Once Singularity is set, you will need to build your .sif file based on the Docker image.
To do so, you may run:
singularity pull darn.sif docker://hariszaf/darn
All darn needs as input is a fasta input.fasta file with the sequnces you wish to run.
Overall, running darn is a 2-steps process:
- first, you need to mount the directory at your actual computer where your
input.fastais located (dir, e.g./home/haris/Desktop/my_darn_analysis) in a certain directory of the container. This works as a bridge between your computer and the container, allowing the container to have access on the files of the directory you mount and vice-versa. - then, you run
darnfrom inside the container
In all cases, darn will always return its output in the dir directory you mount.
To mount the directory <dir> where your input.fasta is located to darn
you may run
docker run --rm -it -v <dir>/:/mnt darn
The
-vparameter denotes your bridge; the<dir>directory of your computer, will be mounted in the/mntpath of thedarncontainer. Parameter--rmis simply there to make sure that your Docker container will be completely removed when you will exit from it, while the-itenables running shell for the container you are about to initiate.
Once the shell is on you just need to run:
./darn.sh -s /mnt/input.fasta -t <number_of_threads>
The output of darn will be returned in the same directory that you mount, i.e you may find your results under dir.
Here is a shell recording for how to get and run darn assuming you have already set Docker on your computing system.
The marine_part.fasta file that is used as an input.fasta here, along with the darn outcome, can be found under the analysis folder of this repo.
Likewise, you need to first mount the <dir> path where you input.fasta is located in the container.
Now, you may run darn with a sole command
singularity run --bind <dir>/:/mnt darn_latest.sif -s /mnt/query_freshwater_short_all_seqs.fasta -t 20
Or, by using the same way as in the Docker case, meaning you first open a shell
singularity shell --bind <dir>/:/mnt darn_latest.sif
and once shell appears:
cd /home
./darn.sh -s /mnt/your_sample.fasta -t <number_of_threads_available>
In case you are are working on a HPC system, depending on the queing system used, you need to build a job script first and include the previous commands into it.
Once darn is completed, 2 new directories will be available in the dir folder:
- one called
intermediate, includinggappabest and exhaustive hits as well as the.jplacetree file with the assignments of the query sequences in the phylogenetic tree - and a second one, called
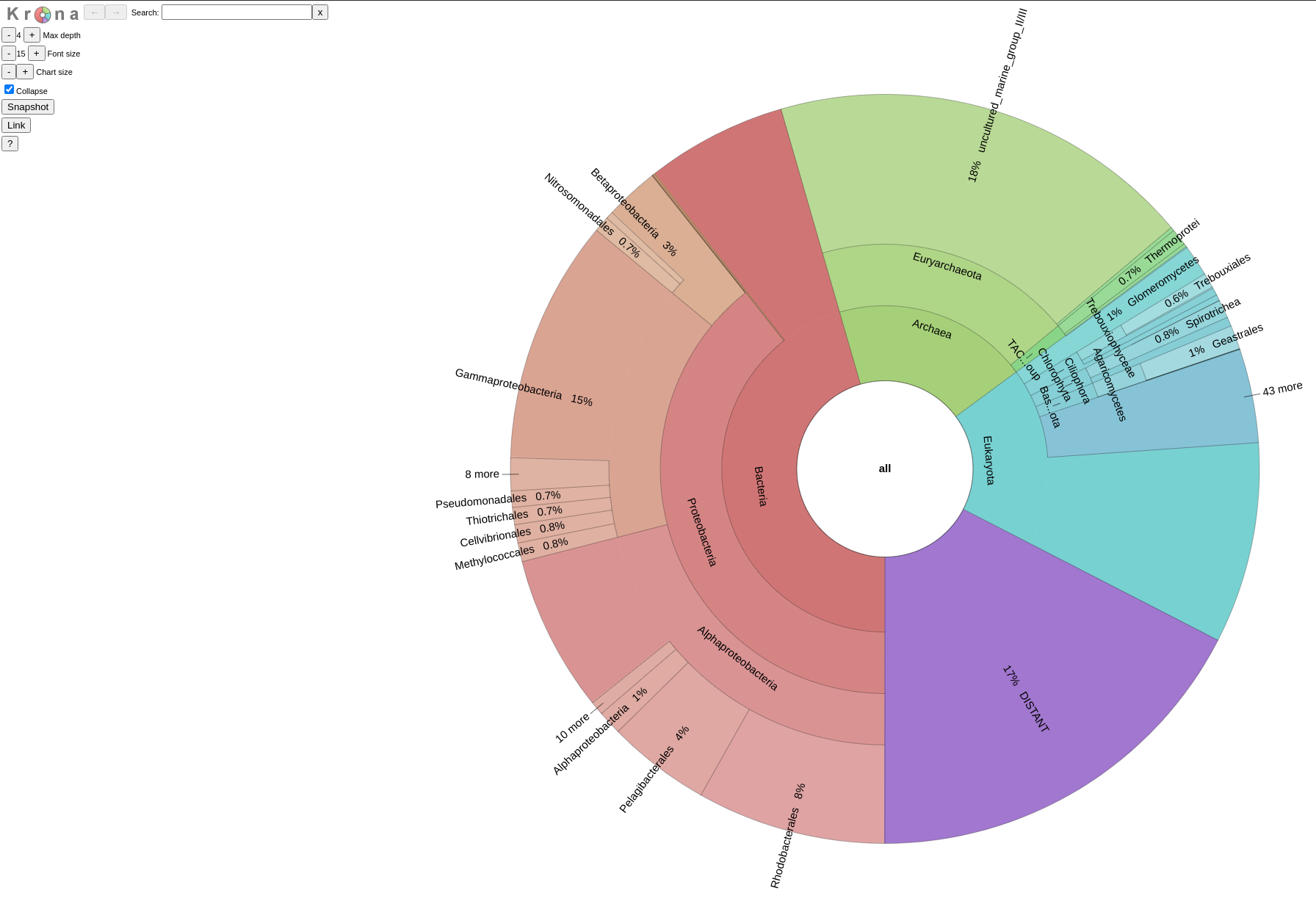
final_outcomewhere a.jsonfile with the entries assigned in each domain of life and a.fastafile with the sequences assigned in each of these domain can be found, as well as a Krona plot, as.htmlfile, representing the composition of the sequence sample based on the number of species found per taxonomic group.
An example of such a Krona plot can be found
The first Krona plot, is based on the likelihood values of the best hit assignments of your query sequences. This way, you may have an overview of what is most likely to actually have on your sample. For a more thorough look on such a Krona, just cilck here.
The second Krona plot, is based on a binary interpretation of the best hits assignments of your sequences, meaning that no matter the likelihood value of the best hit of each query, we treat all the assignments as equal to get a quantitative overview of the assignments. For more click here.
The Krona plots are accompanied by the profiles they came from and by a .json file with all the qurey assignments per domain (Bacteria, Archaea, Eukaryota) and a series of .fasta files; one for each domain found, with the sequences that have been assigned to it.
You may have a look on the DARN output over here.
darn is under the GNU GPLv3 license (for 3rd party components separate licenses apply).
darn makes use of the following software:
Zafeiropoulos H, Gargan L, Hintikka S, Pavloudi C, Carlsson J. The Dark mAtteR iNvestigator (DARN) tool: getting to know the known unknowns in COI amplicon data. Metabarcoding and Metagenomics. 2021 Mar 11;5:e69657. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3897/mbmg.5.69657