Kerberos allows MySQL and applications to take advantage of existing authentication infrastructure and processes. MySQL Enterprise provides support for Kerberos authentication of MySQL clients
Kerberos is a network authentication protocol developed by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). The Kerberos protocol uses secret-key cryptography to provide secure communications over a non-secure network. Primary benefits are strong encryption and single sign-on (SSO).
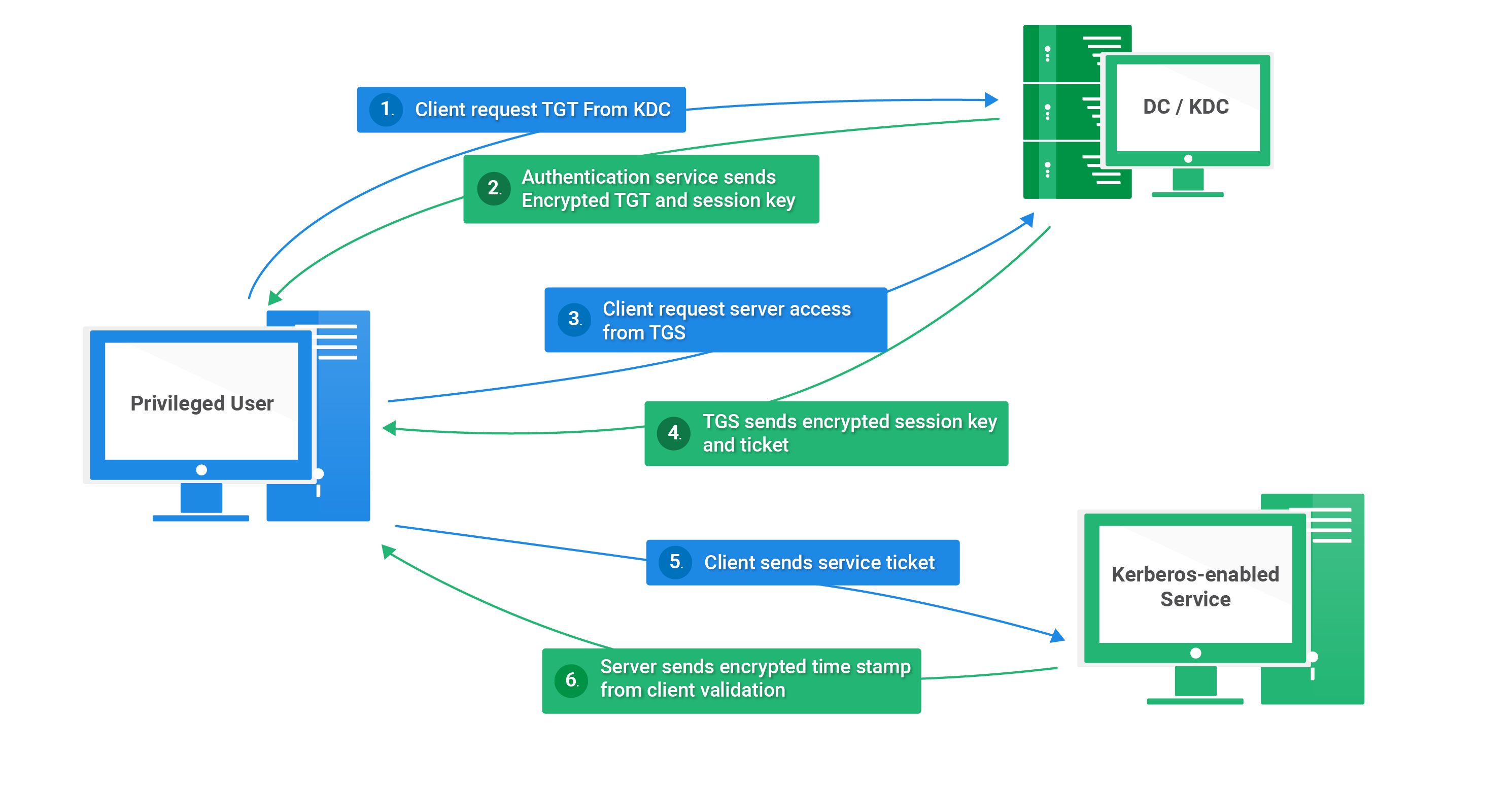
Kerberos runs as a third-party trusted server known as the Key Distribution Center (KDC). Each user and service on the network is a principal. The KDC has three main components:
- An authentication server that performs the initial authentication and issues ticket-granting tickets for users.
- A ticket granting server that issues service tickets that are based on the initial ticket-granting tickets.
- A principals database of secret keys for all the users and services that it maintains.
In order to achieve MySQL authentification using Kerberos we will need three virtual Ubuntu machines inside VirtualBox each with a distinct ip address with roles as follow:
- Client
- KDC
- Service server
Notes:
Kerberos uses timestamp to ensure key integrity.
to check that all our machines are synchronized we can use the command:
timedatectlTo set hostnames for each machine, you can use the commands :
- for kdc :
hostnamectl --static set-hostname kdc.insat.tn- for client :
hostnamectl --static set-hostname client.insat.tnWe need to add DNS rules for our machines. You can edit host names and addresses for the local host and other hosts in the Internet network by consulting the file /etc/hosts.Therefore we mapped each machine ip address with it's respective hostname.
Once we define our DNS we can check available hosts using
getent hosts- kdc getent
- client getent
ps: We can check the IP addresses of all three machines by running hostname -I. We can check that our machines are reachable using ping.
First of all we need to install the following packages on the kdc machine:
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install krb5-kdc krb5-admin-server krb5-config
We will be asked to provide the following configuration:
- the realm : 'INSAT.TN' (must be all uppercase)
- the Kerberos server : 'kdc.insat.tn'
- the administrative server : 'kdc.insat.tn'
PS: A Realm is a logical network, similar to a domain, that defines a group of systems under the same master KDC
Once the installation is complete,we need to set the master key for this KDC database:
$ sudo krb5_newrealm
In the context of Kerberos each client or service of the realm is named a Principal that should be managed an admin user to do so follow the command bellow :
$ sudo kadmin.local
kadmin.local: add_principal root/admin
Then, we need to grant all access rights to the Kerberos database to admin principal root/admin using the configuration file /etc/krb5kdc/kadm5.acl by adding the following line : */admin@INSAT.TN *
ps: In order for changes to take effect we need to restart the server by sudo service krb5-admin-server restart
Once our server is configured we need to create principals for our client as well as for our service server.
- For the client:
$ sudo kadmin.local
kadmin.local: add_principal meriem
- For the service server
$ sudo kadmin.local
kadmin.local: add_principal meriem/mysql.insat.tn
- we can check that our principal have been added with list_principals`
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install krb5-user libpam-krb5 libpam-ccredsAs edited for the kdc server before :
- the realm : 'INSAT.TN' (must be all uppercase)
- the Kerberos server : 'kdc.insat.tn'
- the administrative server : 'kdc.insat.tn'
We need to extract the service principal from KDC principal database to a keytab file.
$ ktutil
ktutil: add_entry -password -p mysql/pg.insat.tn@INSAT.TN -k 1 -e aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96
Then we need to send the keytab file to the service machine at the directory /home/mysql/data :

ps: We need to have openssh-server package installed on the service server : sudo apt-get install openssh-server.
We can check that our keytab has been sent succesfully
We can also verify that the service principal was succesfully extracted from the KDC database by reading the krb5 keytab into the current keylist by ktutil: read_kt home/meriem/mysql/data/mysql.keytab then listing the current keylist by ktutil: list
Before starting configuring MySQL we need to update packages
sudo apt-get update
Then we need to install necessary packages for MySQL
sudo apt-get install mysql-server
During the installation process, you will be prompted to set a password for the MySQL root user.
To enable kerberos authentication we need to edit /etc/mysql/my.cnf file where we add the following .
Note that we make use of the plugin auth_gssapi_server_iso offered by MySQL in GSSAPI mode. Using GSSAPI, the MySQL server creates a Kerberos server-side authentication session. The server validates the user identity and the validity of the user request.
Note also that you need to include the location of the file that contains the security credentials that MySQL needs to authenticate itself to the Kerberos server. By configuring MySQL to use Kerberos authentication in this way, users can connect to the MySQL server without transmitting their passwords, making the connection more secure.
In order for changes to take place we need to run sudo systemctl restart mysql
We can check the status of our service by the following :sudo systemctl status mysql