Creating a basic blockchain wallet in Go involves generating pair of cryptographic keys (Public and Private Keys), stroing keys, and providing functionality to sign transactions. Below is a simplified example.
First, install some dependencies for cryptographic functions. We can use the go-ethereum package for this.
go get github.com/ethereum/go-ethereumHere's is a basic structure for a blockchain wallet:
main.go
package main
import (
"crypto/ecdsa"
"crypto/rand"
"crypto/sha256"
"encoding/hex"
"fmt"
"log"
"os"
"github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/crypto"
)
func main() {
privateKey, err := crypto.GenerateKey()
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
publicKey := privateKey.Public().(*ecdsa.PublicKey)
address := crypto.PubkeyToAddress(*publicKey).Hex()
fmt.Printf("Address: %s\n", address)
saveKey(privateKey)
}
func saveKey(privateKey *ecdsa.PrivateKey) {
privateKeyBytes := crypto.FromECDSA(privateKey)
privateKeyHex := hex.EncodeToString(privateKeyBytes)
file, err := os.Create("private_key.txt")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer file.Close()
_, err = file.WriteString(privateKeyHex)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}
func loadKey() (*ecdsa.PrivateKey, error) {
privateKeyHex, err := os.ReadFile("private_key.txt")
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
privateKeyBytes, err := hex.DecodeString(string(privateKeyHex))
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
privateKey, err := crypto.ToECDSA(privateKeyBytes)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return privateKey, nil
}
func signMessage(message string, privateKey *ecdsa.PrivateKey) (string, error) {
hash := sha256.Sum256([]byte(message))
signature, err := crypto.Sign(hash[:], privateKey)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
return hex.EncodeToString(signature), nil
}
func verifyMessage(message, signatureHex string, publicKey *ecdsa.PublicKey) bool {
hash := sha256.Sum256([]byte(message))
signature, err := hex.DecodeString(signatureHex)
if err != nil {
return false
}
return crypto.VerifySignature(crypto.FromECDSAPub(publicKey), hash[:], signature[:len(signature)-1])
}- Generate Key Pair: Generates a new ECDSA key pair using crypto.GenerateKey.
- Address Generation: Uses the public key to generate an Ethereum-style address with crypto.PubkeyToAddress.
- Key Storage: Saves the private key to a file (private_key.txt).
- Load Key: Reads the private key from the file and converts it back to an ECDSA key.
- Sign Message: Signs a message using the private key and SHA-256 hashing.
- Verify Message: Verifies the message signature using the public key.
- Generating Keys
go run main.goThis will generate a key pair and save the private key to private_key.txt.
- Load and Use the Key
Modify
main.goto load the key and sign a message
func main() {
privateKey, err := loadKey()
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
message := "Hello, Blockchain!"
signature, err := signMessage(message, privateKey)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
fmt.Printf("Message: %s\n", message)
fmt.Printf("Signature: %s\n", signature)
publicKey := privateKey.Public().(*ecdsa.PublicKey)
isValid := verifyMessage(message, signature, publicKey)
fmt.Printf("Signature valid: %t\n", isValid)
}The project is enhanced to make it a complete application capable of integrating with other platforms
- Add RESTful APIs: Allow external platforms to interact with the wallet
- Create and manage transactions: Include functionality to create, sign, and broadcast transactions
We'll use gin-gonic framework for the RESTful API and go-ethereum for blockchain interactions.
go get github.com/gin-gonic/gin
go get github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum
blockchain-wallet/
│
├── main.go
├── handlers/
│ └── handlers.go
├── models/
│ └── wallet.go
├── services/
│ └── wallet.go
├── utils/
│ └── crypto.go
├── go.mod
└── go.sumpackage main
import (
"log"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"github.com/jabbala-dev/go-wallet/handlers"
)
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
// Define routes
r.GET("/generate", handlers.GenerateKeyPair)
r.GET("/address", handlers.GetAddress)
r.POST("/sign", handlers.SignMessage)
r.POST("/verify", handlers.VerifyMessage)
// Start the server
if err := r.Run(":8080"); err != nil {
log.Fatal("Failed to run server: ", err)
}
}package handlers
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"github.com/jabbala-dev/go-wallet/services"
)
func GenerateKeyPair(c *gin.Context) {
privateKey, address, err := services.GenerateKeyPair()
if err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"private_key": privateKey, "address": address})
}
func GetAddress(c *gin.Context) {
address, err := services.GetAddress()
if err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"address": address})
}
func SignMessage(c *gin.Context) {
var request struct {
Message string `json:"message"`
}
if err := c.BindJSON(&request); err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": "Invalid request"})
return
}
signature, err := services.SignMessage(request.Message)
if err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"signature": signature})
}
func VerifyMessage(c *gin.Context) {
var request struct {
Message string `json:"message"`
Signature string `json:"signature"`
}
if err := c.BindJSON(&request); err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": "Invalid request"})
return
}
isValid, err := services.VerifyMessage(request.Message, request.Signature)
if err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"valid": isValid})
}package services
import (
"crypto/ecdsa"
"crypto/sha256"
"encoding/hex"
"errors"
"io/ioutil"
"os"
"github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/crypto"
"github.com/jabbala-dev/go-wallet/utils"
)
var privateKeyFile = "private_key.txt"
func GenerateKeyPair() (string, string, error) {
privateKey, err := crypto.GenerateKey()
if err != nil {
return "", "", err
}
publicKey := privateKey.Public().(*ecdsa.PublicKey)
address := crypto.PubkeyToAddress(*publicKey).Hex()
privateKeyHex := hex.EncodeToString(crypto.FromECDSA(privateKey))
err = ioutil.WriteFile(privateKeyFile, []byte(privateKeyHex), 0600)
if err != nil {
return "", "", err
}
return privateKeyHex, address, nil
}
func GetAddress() (string, error) {
privateKey, err := loadKey()
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
publicKey := privateKey.Public().(*ecdsa.PublicKey)
address := crypto.PubkeyToAddress(*publicKey).Hex()
return address, nil
}
func SignMessage(message string) (string, error) {
privateKey, err := loadKey()
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
hash := sha256.Sum256([]byte(message))
signature, err := crypto.Sign(hash[:], privateKey)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
return hex.EncodeToString(signature), nil
}
func VerifyMessage(message, signatureHex string) (bool, error) {
privateKey, err := loadKey()
if err != nil {
return false, err
}
publicKey := privateKey.Public().(*ecdsa.PublicKey)
hash := sha256.Sum256([]byte(message))
signature, err := hex.DecodeString(signatureHex)
if err != nil {
return false, err
}
return crypto.VerifySignature(crypto.FromECDSAPub(publicKey), hash[:], signature[:len(signature)-1]), nil
}
func loadKey() (*ecdsa.PrivateKey, error) {
if _, err := os.Stat(privateKeyFile); os.IsNotExist(err) {
return nil, errors.New("private key file does not exist")
}
privateKeyHex, err := ioutil.ReadFile(privateKeyFile)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
privateKeyBytes, err := hex.DecodeString(string(privateKeyHex))
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
privateKey, err := crypto.ToECDSA(privateKeyBytes)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return privateKey, nil
}package utils
import (
"crypto/ecdsa"
"crypto/sha256"
"encoding/hex"
"github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/crypto"
)
func GenerateKeyPair() (*ecdsa.PrivateKey, error) {
return crypto.GenerateKey()
}
func PublicKeyToAddress(publicKey *ecdsa.PublicKey) string {
return crypto.PubkeyToAddress(*publicKey).Hex()
}
func PrivateKeyToHex(privateKey *ecdsa.PrivateKey) string {
return hex.EncodeToString(crypto.FromECDSA(privateKey))
}
func HexToPrivateKey(hexKey string) (*ecdsa.PrivateKey, error) {
privateKeyBytes, err := hex.DecodeString(hexKey)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return crypto.ToECDSA(privateKeyBytes)
}
func SignMessage(privateKey *ecdsa.PrivateKey, message string) (string, error) {
hash := sha256.Sum256([]byte(message))
signature, err := crypto.Sign(hash[:], privateKey)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
return hex.EncodeToString(signature), nil
}
func VerifyMessage(publicKey *ecdsa.PublicKey, message, signatureHex string) (bool, error) {
hash := sha256.Sum256([]byte(message))
signature, err := hex.DecodeString(signatureHex)
if err != nil {
return false, err
}
return crypto.VerifySignature(crypto.FromECDSAPub(publicKey), hash[:], signature[:len(signature)-1]), nil
}go mod init github.com/yourusername/blockchain-wallet
go mod tidygo run main.go curl http://localhost:8080/generatehttp://localhost:8080/addresscurl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"message":"Hello, Go Wallet"}' http://localhost:8080/signcurl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"message":"Hello, Go Wallet", "signature":"c71274f99339471fdfa73a4ea82d842982bfedf07f5c5b1df6108e9878494c021d1de0955fcc8869e770d83da2d6cc4ae6c5dddd30fa6fb4d313bd28a088650d00"}' http://localhost:8080/verifycurl -X POST http://localhost:8080/transaction -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"to_address": "0xRecipientAddress", "value": 1000000000000000000}'We can create a simple client-side application using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to interact with the blockchain wallet's API endpoints. We use fetch API to make HTTP requests to our Go Backend.
blockchain-wallet/
│
├── main.go
├── handlers/
│ └── handlers.go
├── models/
│ └── wallet.go
├── services/
│ └── wallet.go
│ └── transaction.go
├── utils/
│ └── crypto.go
├── public/
│ └── index.html
│ └── style.css
│ └── app.js
├── go.mod
└── go.sumUpdate the main Go file to serve the static files:
package main
import (
"log"
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"github.com/yourusername/blockchain-wallet/handlers"
)
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
// Serve static files
r.Static("/static", "./static")
// Define routes
r.GET("/generate", handlers.GenerateKeyPair)
r.GET("/address", handlers.GetAddress)
r.POST("/sign", handlers.SignMessage)
r.POST("/verify", handlers.VerifyMessage)
r.POST("/transaction", handlers.CreateAndSendTransaction)
// Serve the main page
r.LoadHTMLFiles("static/index.html")
r.GET("/", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "index.html", nil)
})
// Start the server
if err := r.Run(":8080"); err != nil {
log.Fatal("Failed to run server: ", err)
}
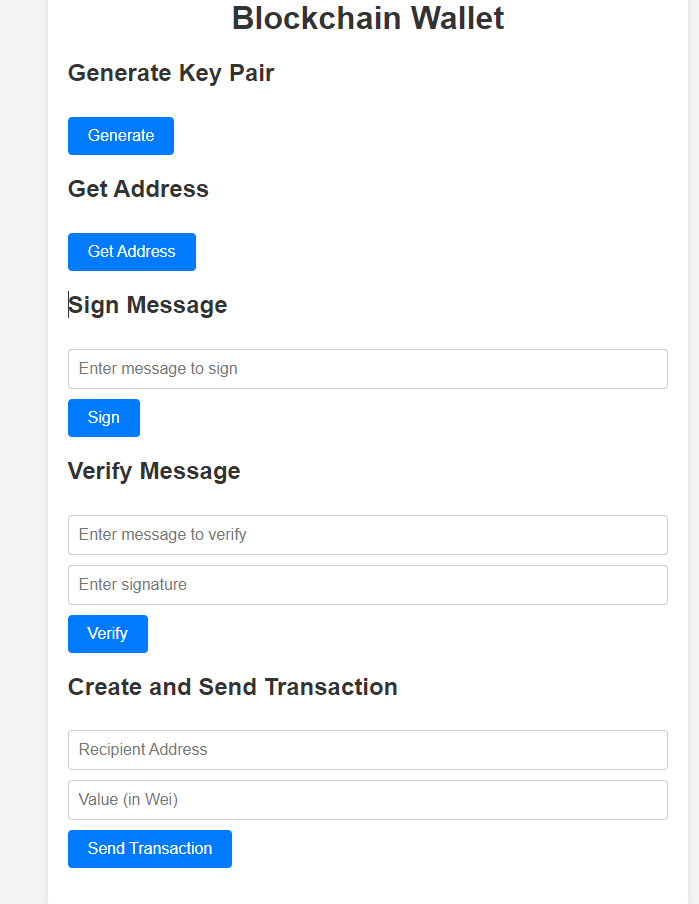
}<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Blockchain Wallet</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/style.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h1>Blockchain Wallet</h1>
<div class="section">
<h2>Generate Key Pair</h2>
<button id="generate-btn">Generate</button>
<p id="generate-result"></p>
</div>
<div class="section">
<h2>Get Address</h2>
<button id="address-btn">Get Address</button>
<p id="address-result"></p>
</div>
<div class="section">
<h2>Sign Message</h2>
<input type="text" id="sign-message" placeholder="Enter message to sign">
<button id="sign-btn">Sign</button>
<p id="sign-result"></p>
</div>
<div class="section">
<h2>Verify Message</h2>
<input type="text" id="verify-message" placeholder="Enter message to verify">
<input type="text" id="verify-signature" placeholder="Enter signature">
<button id="verify-btn">Verify</button>
<p id="verify-result"></p>
</div>
<div class="section">
<h2>Create and Send Transaction</h2>
<input type="text" id="tx-to-address" placeholder="Recipient Address">
<input type="text" id="tx-value" placeholder="Value (in Wei)">
<button id="transaction-btn">Send Transaction</button>
<p id="transaction-result"></p>
</div>
</div>
<script src="/static/app.js"></script>
</body>
</html>Create a CSS file for basic styling:
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
background-color: #f5f5f5;
color: #333;
padding: 20px;
}
.container {
max-width: 600px;
margin: 0 auto;
background-color: #fff;
padding: 20px;
border-radius: 8px;
box-shadow: 0 0 10px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
}
h1 {
text-align: center;
}
.section {
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
button {
display: inline-block;
padding: 10px 20px;
font-size: 16px;
cursor: pointer;
background-color: #007bff;
color: #fff;
border: none;
border-radius: 4px;
margin-top: 10px;
}
button:hover {
background-color: #0056b3;
}
input[type="text"] {
width: calc(100% - 22px);
padding: 10px;
font-size: 16px;
margin-top: 10px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 4px;
}
p {
margin-top: 10px;
font-size: 16px;
word-break: break-all;
}Create a JavaScript file to handle the frontend logic and interact with the backend API:
document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', () => {
const generateBtn = document.getElementById('generate-btn');
const generateResult = document.getElementById('generate-result');
const addressBtn = document.getElementById('address-btn');
const addressResult = document.getElementById('address-result');
const signBtn = document.getElementById('sign-btn');
const signMessage = document.getElementById('sign-message');
const signResult = document.getElementById('sign-result');
const verifyBtn = document.getElementById('verify-btn');
const verifyMessage = document.getElementById('verify-message');
const verifySignature = document.getElementById('verify-signature');
const verifyResult = document.getElementById('verify-result');
const transactionBtn = document.getElementById('transaction-btn');
const txToAddress = document.getElementById('tx-to-address');
const txValue = document.getElementById('tx-value');
const transactionResult = document.getElementById('transaction-result');
generateBtn.addEventListener('click', async () => {
const response = await fetch('/generate');
const data = await response.json();
generateResult.textContent = `Private Key: ${data.private_key}, Address: ${data.address}`;
});
addressBtn.addEventListener('click', async () => {
const response = await fetch('/address');
const data = await response.json();
addressResult.textContent = `Address: ${data.address}`;
});
signBtn.addEventListener('click', async () => {
const message = signMessage.value;
const response = await fetch('/sign', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({ message })
});
const data = await response.json();
signResult.textContent = `Signature: ${data.signature}`;
});
verifyBtn.addEventListener('click', async () => {
const message = verifyMessage.value;
const signature = verifySignature.value;
const response = await fetch('/verify', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({ message, signature })
});
const data = await response.json();
verifyResult.textContent = `Valid: ${data.valid}`;
});
transactionBtn.addEventListener('click', async () => {
const toAddress = txToAddress.value;
const value = txValue.value;
const response = await fetch('/transaction', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({ to_address: toAddress, value: parseInt(value) })
});
const data = await response.json();
transactionResult.textContent = `Transaction Hash: ${data.transaction_hash}`;
});
});Open your web browser and navigate to http://localhost:8080. You should see the client-side interface with buttons and input fields to interact with the blockchain wallet API.
This project demonstrates the creation of a basic blockchain wallet application in Go, providing key functionalities such as generating key pairs, retrieving wallet addresses, signing messages, and verifying signatures. By structuring the project into well-defined modules and utilizing the gin-gonic framework for RESTful APIs, we have laid a strong foundation for further development and integration with other platforms.
- Enhancement: Implement functionality for creating, signing, and broadcasting transactions to the blockchain network.
- Benefit: Enables the wallet to perform actual transfers of cryptocurrency, making it fully functional.
- Enhancement: Integrate with blockchain nodes (e.g., Ethereum, Bitcoin) to fetch and display wallet balances and transaction history.
- Benefit: Provides real-time information and enhances user interaction with the blockchain.
- Enhancement: Implement secure storage solutions for private keys (e.g., hardware wallets, encrypted storage).
- Benefit: Increases the security of private keys, protecting users from potential threats and attacks.
- Enhancement: Add user authentication and authorization mechanisms to secure API endpoints.
- Benefit: Ensures that only authorized users can access and manage their wallets, enhancing security.
- Enhancement: Implement comprehensive error handling and logging throughout the application.
- Benefit: Helps in debugging, monitoring, and maintaining the application more effectively.
- Enhancement: Develop unit and integration tests to ensure the reliability and correctness of the application.
- Benefit: Improves code quality and reduces the likelihood of bugs and regressions.
- Enhancement: Develop user-friendly web and mobile interfaces for interacting with the wallet.
- Benefit: Enhances accessibility and user experience, making the wallet more appealing to a broader audience.
- Enhancement: Extend the wallet to support multiple cryptocurrencies.
- Benefit: Increases the utility of the wallet by allowing users to manage various assets within a single application.
By addressing these areas for improvement, we can transform this basic blockchain wallet into a robust, secure, and user-friendly application capable of competing with existing solutions in the market.